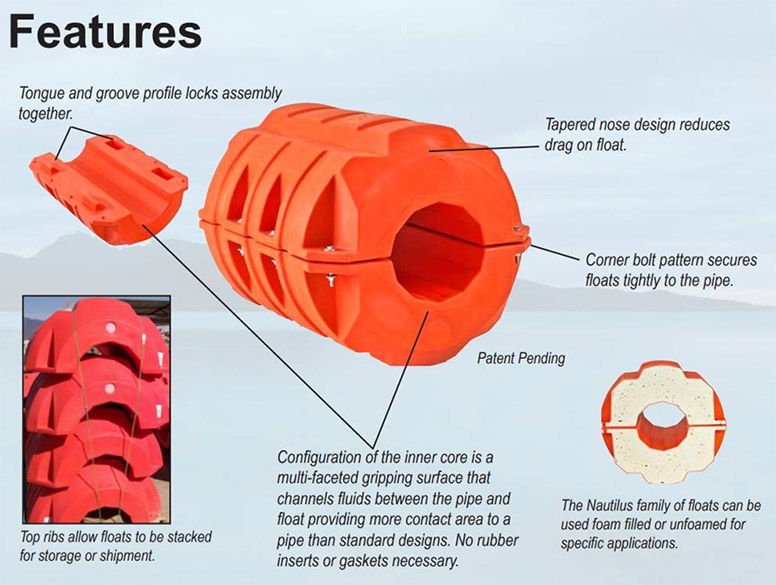
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is rubber vulcanization
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, understanding rubber vulcanization is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to enhance product quality and performance. Vulcanization, a process that involves treating rubber with heat and sulfur, transforms standard rubber into a superior material that boasts increased strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. For companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Germany and Saudi Arabia—navigating the complexities of sourcing vulcanized rubber can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify rubber vulcanization by exploring its various types, applications, and the intricate process behind it.
By examining the benefits of vulcanized rubber, this comprehensive resource will empower international buyers to make informed decisions, whether they’re selecting materials for automotive components, industrial machinery, or consumer goods. Furthermore, the guide will delve into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for integrating vulcanized rubber into production lines. With actionable insights and expert analysis, this guide equips B2B buyers to optimize their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the best rubber solutions that meet their specific needs while staying competitive in the global market.
Table des matières
- Top 4 What Is Rubber Vulcanization Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is rubber vulcanization
- Understanding what is rubber vulcanization Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is rubber vulcanization
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is rubber vulcanization’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is rubber vulcanization
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is rubber vulcanization
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is rubber vulcanization’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is rubber vulcanization Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is rubber vulcanization With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is rubber vulcanization
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is rubber vulcanization Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is rubber vulcanization
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is rubber vulcanization
- Avis de non-responsabilité et conditions d'utilisation
Understanding what is rubber vulcanization Types and Variations
| Nom du type | Principales caractéristiques | Applications primaires B2B | Avantages et inconvénients pour les acheteurs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfur Vulcanization | Utilizes sulfur as the primary cross-linking agent. | Tires, gaskets, seals | Pour : High strength and elasticity; Cons : Long curing time. |
| Peroxide Vulcanization | Employs peroxides for cross-linking; less odor. | Automotive parts, footwear | Pour : Excellent thermal stability; Cons : Higher cost of materials. |
| Accelerated Vulcanization | Involves accelerators to speed up the curing process. | Industrial rubber products, belts | Pour : Faster production times; Cons : May require precise control of conditions. |
| Steam Vulcanization | Uses steam heat for vulcanization, reducing energy use. | Large-scale rubber components, hoses | Pour : Efficient energy usage; Cons : Equipment investment can be high. |
| Cold Vulcanization | Uses chemical agents at room temperature; no heat required. | Repair applications, smaller parts | Pour : Simple application; Cons : Lower strength compared to heat methods. |
What Are the Characteristics of Sulfur Vulcanization?
Sulfur vulcanization is the most traditional method, where sulfur is mixed with rubber to create cross-links that enhance strength and elasticity. This method is widely used in manufacturing tires and gaskets due to its ability to withstand high pressures and stresses. B2B buyers should consider the curing time, as it can take longer than other methods, impacting production schedules. However, its proven reliability makes it a go-to choice for many applications.
How Does Peroxide Vulcanization Differ?
Peroxide vulcanization employs organic peroxides as the cross-linking agent, which results in a vulcanized rubber that is particularly resistant to heat and aging. This method is favored in applications requiring high-performance materials, such as automotive parts and specialized footwear. B2B buyers should weigh the higher material costs against the benefits of enhanced durability and lower odor, which can be significant in consumer-facing products.
What Are the Advantages of Accelerated Vulcanization?
Accelerated vulcanization incorporates accelerators to hasten the curing process, allowing for quicker production cycles. This method is particularly advantageous for industrial rubber products and belts, where rapid turnaround is essential. Buyers should consider the need for precise control over the vulcanization conditions, as improper management can lead to defects. The speed of production is a strong selling point for businesses looking to meet high demand.
Why Choose Steam Vulcanization?
Steam vulcanization uses steam heat to cure rubber, which can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional methods. This process is well-suited for large-scale applications, such as hoses and other rubber components. While the initial equipment investment may be higher, the long-term energy savings can justify the cost. B2B buyers should evaluate their production capacity and energy costs when considering this method.
What Is Cold Vulcanization and Its Uses?
Cold vulcanization employs chemical agents to cure rubber at room temperature, making it ideal for repair applications and smaller parts. This method is simple and does not require specialized equipment, which can be a major advantage for businesses needing flexible solutions. However, buyers should note that cold vulcanization typically results in lower strength compared to heat-based methods, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
Key Industrial Applications of what is rubber vulcanization
| Industrie/secteur | Specific Application of what is rubber vulcanization | Valeur/bénéfice pour l'entreprise | Principales considérations en matière d'approvisionnement pour cette application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Tires and Seals | Enhanced durability and performance under stress | Quality certifications, compliance with international standards, and sourcing from reliable suppliers. |
| La construction | Gaskets and Sealing Solutions | Improved resistance to weathering and mechanical stress | Material certifications, compatibility with construction materials, and local sourcing options. |
| Consumer Goods | Footwear and Sporting Equipment | Increased comfort, durability, and aesthetic appeal | Customization options, availability of eco-friendly materials, and scalability of production. |
| Electronics | Keypads and Insulation Materials | Enhanced product lifespan and user experience | Technical specifications, compatibility with electronic components, and rapid prototyping capabilities. |
| Industrial Machinery | Vibration Dampers and Hoses | Reduced equipment wear and improved operational efficiency | Performance testing results, resistance to chemicals, and availability of various sizes and shapes. |
How is Rubber Vulcanization Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber vulcanization is crucial for manufacturing tires and seals. Vulcanized rubber enhances durability, providing resistance against wear and tear, which is essential for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. B2B buyers in this industry must consider suppliers who offer high-quality materials that meet international safety standards, ensuring compliance and reliability in harsh driving conditions. Additionally, sourcing from regions with established rubber production can help mitigate costs and lead times.

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
What Role Does Rubber Vulcanization Play in Construction?
In construction, vulcanized rubber is widely used for gaskets and sealing solutions. These components are vital for ensuring airtight and watertight seals in various structures, protecting against environmental factors. The enhanced weather resistance and mechanical strength of vulcanized rubber help prevent leaks and structural damage, ultimately leading to cost savings on repairs. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certified materials that align with local building regulations and offer customization to fit specific project requirements.
How is Rubber Vulcanization Beneficial in Consumer Goods?
The consumer goods industry leverages rubber vulcanization for products like footwear and sporting equipment. This process improves the comfort and durability of these items, allowing them to withstand rigorous use while maintaining aesthetic appeal. B2B buyers should seek manufacturers who can provide sustainable options and customization to cater to diverse market demands. Additionally, assessing the supplier’s ability to scale production can be crucial for meeting market trends and consumer preferences.
What Advantages Does Rubber Vulcanization Offer in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, vulcanized rubber is used in keypads and insulation materials, contributing to product longevity and user satisfaction. The enhanced elasticity and durability of vulcanized rubber help protect sensitive electronic components from damage. Buyers need to ensure that suppliers can meet technical specifications and provide materials compatible with existing electronic designs. Rapid prototyping capabilities are also beneficial for developing innovative products that can quickly adapt to market changes.

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
Why is Rubber Vulcanization Important for Industrial Machinery?
Rubber vulcanization finds significant application in industrial machinery through components like vibration dampers and hoses. These products help reduce wear on machinery, improving operational efficiency and extending equipment lifespan. B2B buyers must consider performance testing results to ensure that the materials can withstand specific industrial conditions, including exposure to chemicals and high temperatures. Sourcing from established manufacturers with a track record in industrial applications can provide peace of mind regarding product reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is rubber vulcanization’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Costs Associated with Rubber Vulcanization
Le problème : B2B buyers often face uncertainty regarding the costs involved in the vulcanization process. Many manufacturers are unsure about the pricing of raw materials, labor, and energy consumption required for vulcanization. This lack of clarity can lead to budget overruns or insufficient funding for projects, ultimately affecting production timelines and quality. For instance, a company looking to produce high-quality tires may underestimate the costs, resulting in delays and potential loss of market competitiveness.
La solution : To effectively manage costs, buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand the price fluctuations of key materials such as sulfur and accelerators. Engaging in long-term contracts with suppliers can also help stabilize costs over time. Additionally, it is essential to work with experienced engineers who can provide insights into the most efficient vulcanization methods, reducing energy consumption and waste. Implementing a cost-analysis tool or software can further help track and optimize expenses throughout the production process, ensuring that projects stay within budget.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality Control in Vulcanized Rubber Products
Le problème : A significant concern for B2B buyers is maintaining the quality of vulcanized rubber products. Poor quality can lead to product failures, safety hazards, and a tarnished reputation. For example, a manufacturer producing automotive parts may discover that their vulcanized rubber components are not meeting industry standards, leading to costly recalls and loss of customer trust.
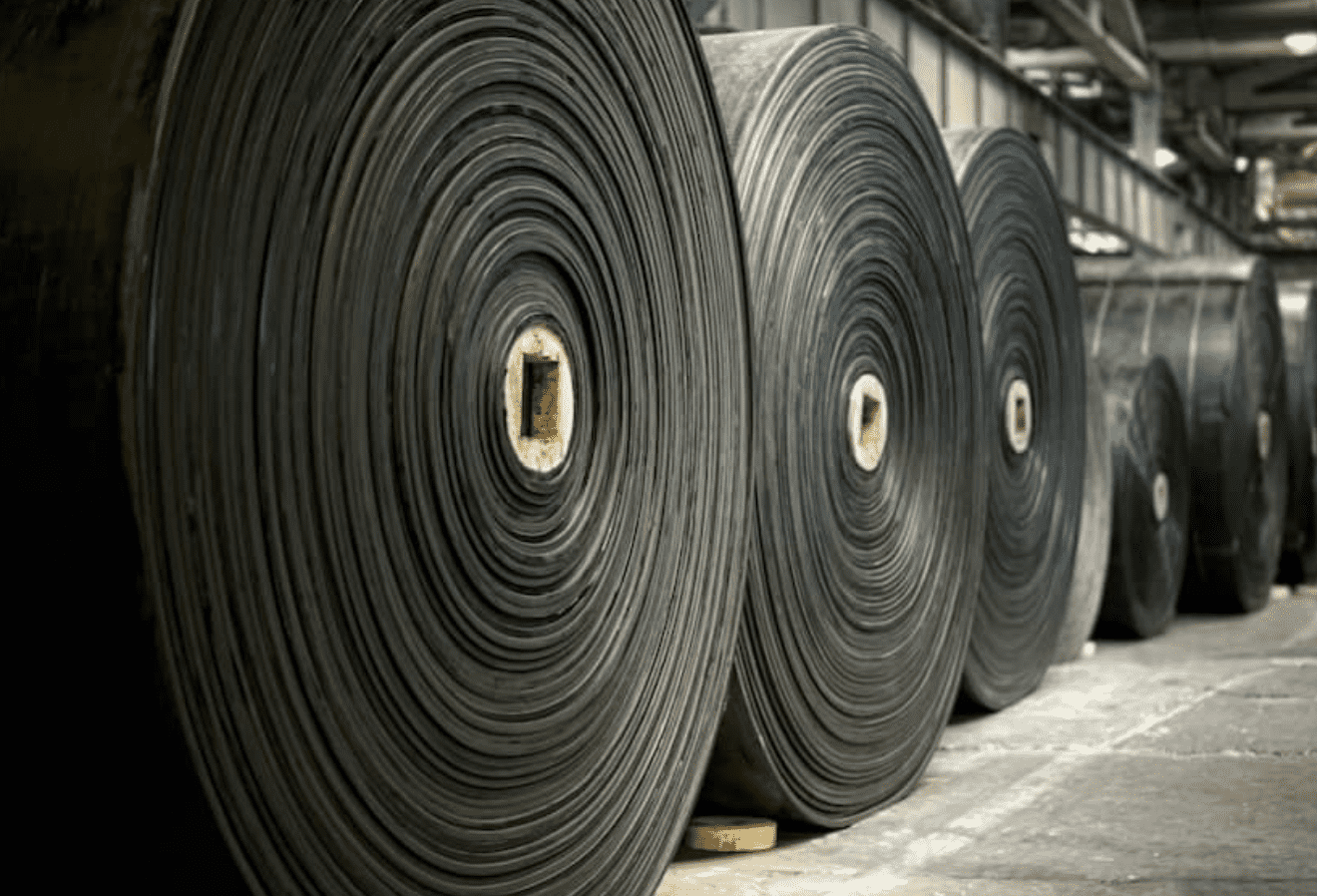

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
La solution : To ensure quality, buyers must establish stringent quality control protocols throughout the vulcanization process. This includes implementing regular testing of raw materials and finished products, such as tensile strength and elasticity tests. Collaborating with certified laboratories for independent quality assessments can also provide an additional layer of assurance. Furthermore, suppliers should be vetted for their quality management systems and certifications, ensuring they adhere to international standards. Continuous training for production staff on best practices in the vulcanization process is also crucial for minimizing errors and enhancing product reliability.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Technical Complexity of Vulcanization Processes
Le problème : The technical intricacies of the vulcanization process can overwhelm B2B buyers, particularly those new to rubber manufacturing. Misunderstandings regarding the correct ratios of sulfur and other additives or the appropriate heating times can lead to improperly vulcanized products, affecting performance and durability. For instance, a company may find that their rubber components are either too brittle or too soft, resulting in product failures and costly redesigns.
La solution : To navigate this complexity, buyers should invest in training programs for their technical teams, focusing on the fundamentals of rubber chemistry and the vulcanization process. Partnering with suppliers who offer technical support and expertise can also provide valuable guidance. Additionally, implementing a systematic approach to document and analyze previous vulcanization batches can help identify optimal formulations and processing conditions. Utilizing advanced software for simulation and modeling of the vulcanization process can also aid in predicting outcomes, allowing for better planning and execution of manufacturing processes. By leveraging these resources, businesses can achieve more consistent and reliable results in their rubber products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is rubber vulcanization
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rubber Vulcanization?
When considering rubber vulcanization, several materials play a crucial role in enhancing the properties of rubber products. This section analyzes four common materials—natural rubber, synthetic rubber, sulfur, and accelerators—focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
How Does Natural Rubber Perform in Vulcanization?
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of rubber trees, is known for its excellent elasticity and tensile strength. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including automotive and industrial uses. However, it is less resistant to aging and environmental factors compared to synthetic alternatives.
Pour : Natural rubber is biodegradable and has superior elasticity, making it ideal for products requiring flexibility, such as tires and seals.
Cons : Its susceptibility to ozone and UV degradation can limit its lifespan, and it is generally more expensive than synthetic options.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with environmental regulations may necessitate sourcing sustainably harvested natural rubber. Understanding local standards, such as ASTM D2000, is also crucial for ensuring product quality.
What Role Does Synthetic Rubber Play in Vulcanization?
Synthetic rubber, produced from petroleum by-products, offers enhanced resistance to heat, aging, and chemicals. Common types include styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM). Synthetic rubber can handle higher temperatures (up to 120°C) and is often preferred for automotive and industrial applications.
Pour : Its durability and resistance to various chemicals make synthetic rubber suitable for demanding environments.
Cons : The production process can be more complex and environmentally taxing, leading to higher costs in some cases.
International buyers should be aware of the varying regulations regarding synthetic rubber in different regions. For example, European markets may have stricter compliance requirements related to chemical safety and environmental impact.
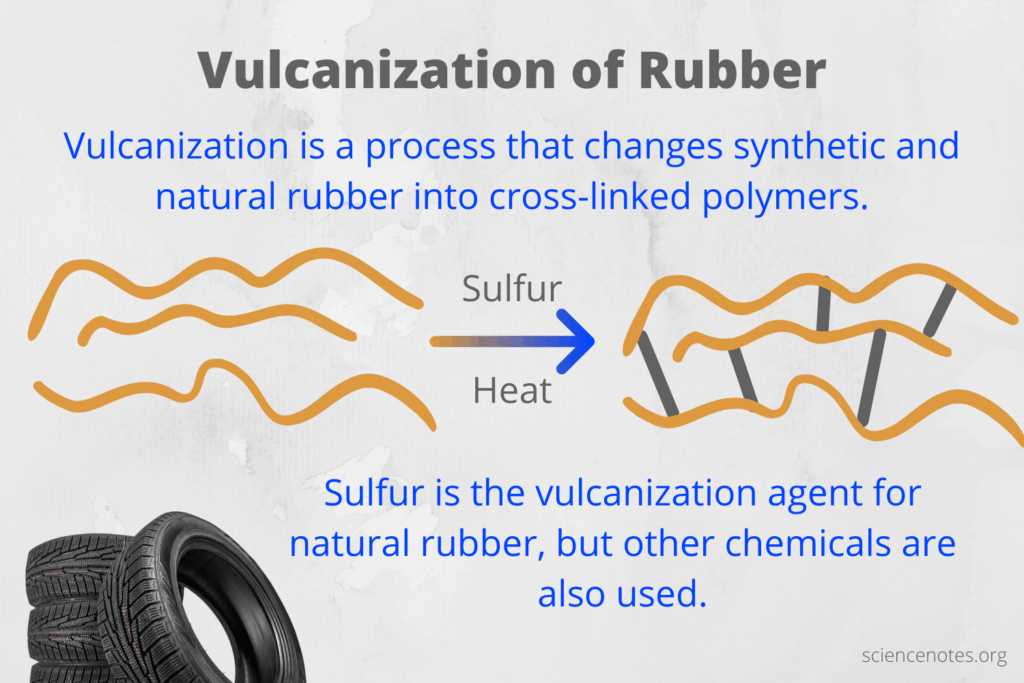
Why Is Sulfur Essential in the Vulcanization Process?
Sulfur is the primary agent used in the vulcanization process, facilitating the cross-linking of rubber molecules. By introducing sulfur into the rubber matrix, the material gains significant strength and elasticity. The typical vulcanization temperature ranges from 140°C to 180°C.
Pour : Sulfur is relatively inexpensive and enhances the mechanical properties of rubber, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Cons : The vulcanization process can be slow without accelerators, which may increase production time.
For B2B buyers, understanding the sulfur content and its implications on product performance is essential. Compliance with standards such as DIN 53529 is critical for ensuring product quality, especially in European markets.
How Do Accelerators Impact Rubber Vulcanization?
Accelerators are additives that speed up the vulcanization process, allowing for lower temperatures and improved efficiency. Common accelerators include thiazoles and sulfenamides. They help achieve optimal cross-linking in a shorter time frame.
Pour : Accelerators enhance production efficiency and reduce energy costs during manufacturing.
Cons : The use of certain accelerators may lead to environmental concerns, necessitating careful selection based on compliance with local regulations.
For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, it is vital to ensure that the chosen accelerators meet local safety and environmental standards, such as REACH in the EU.
Summary Table of Key Materials for Rubber Vulcanization
| Matériau | Typical Use Case for what is rubber vulcanization | Avantage clé | Principaux inconvénients/limites | Coût relatif (faible/moyen/élevé) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Tires, seals, gaskets | Superior elasticity and biodegradability | Susceptible to aging and environmental factors | Haut |
| Synthetic Rubber | Automotive parts, industrial applications | Enhanced durability and chemical resistance | Higher production complexity and environmental impact | Moyen |
| Sulfur | General vulcanization agent | Cost-effective and improves mechanical properties | Slow vulcanization process without accelerators | Faible |
| Accelerators | Speeding up vulcanization | Increases production efficiency | Potential environmental concerns | Moyen |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions regarding rubber vulcanization materials tailored to their specific market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is rubber vulcanization
The manufacturing process of rubber vulcanization is a multi-step operation that transforms raw rubber into a durable, elastic material suitable for a wide range of applications, from tires to industrial components. Understanding this process, along with the quality assurance measures in place, is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality vulcanized rubber products.
What Are the Main Stages of the Rubber Vulcanization Manufacturing Process?
How is Material Prepared for Vulcanization?
The first step in the vulcanization process is the preparation of the raw materials. This includes both natural and synthetic rubbers, which are often mixed with additives such as sulfur, accelerators, and fillers. The precise formulation is critical; for instance, the ratio of sulfur typically ranges from 5% to 30%, depending on the desired properties of the final product. Additionally, zinc oxide and other activators are incorporated to enhance the cross-linking reaction.
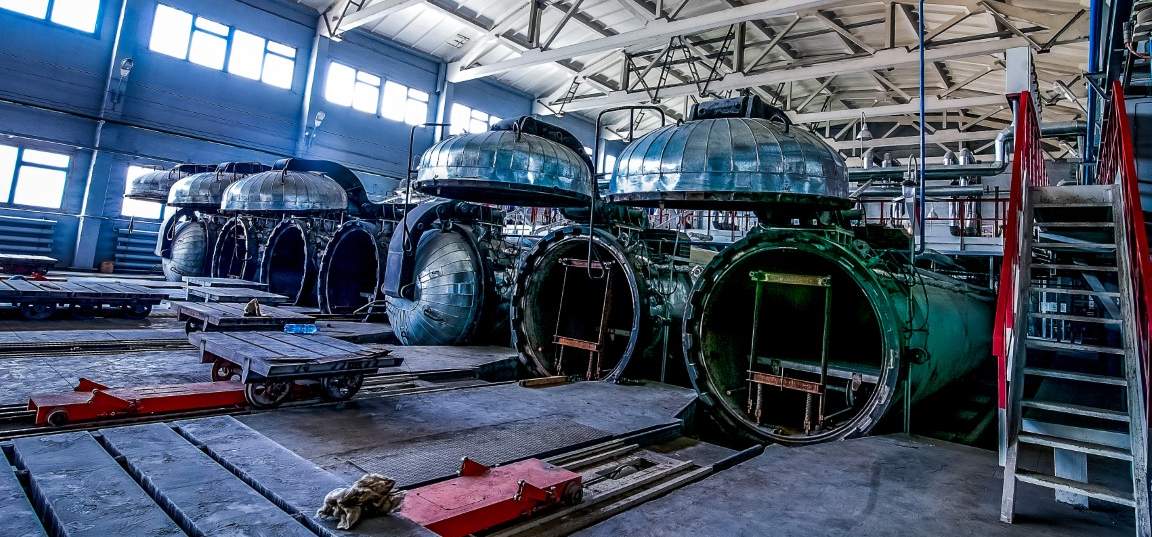

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
Before mixing, the rubber is usually processed to remove impurities, which can significantly affect the final product’s quality. This might involve washing, drying, and grinding the rubber to achieve a uniform consistency, ensuring that the vulcanization process can proceed smoothly.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Vulcanized Rubber Products?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. The rubber mixture is typically shaped using molding techniques, which can involve compression, transfer, or injection molding. Each method has its advantages; for instance, injection molding allows for complex shapes and is ideal for mass production.
After shaping, the rubber is subjected to heat in a controlled environment. This step is crucial as it activates the sulfur and accelerators, initiating the cross-linking process that gives vulcanized rubber its strength and elasticity. Typically, the rubber is heated to temperatures ranging from 300°F to 400°F (about 150°C to 200°C) for a specific duration, depending on the thickness and type of rubber being processed.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Applied?
After vulcanization, the rubber products undergo finishing processes to enhance their performance and appearance. This may include trimming excess material, surface treatments to improve abrasion resistance, and the application of coatings for enhanced durability. Quality control checks are often integrated into this stage to ensure that the final products meet specified standards before they are packaged and shipped.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented During Rubber Vulcanization?
Quelles sont les normes internationales que les acheteurs B2B devraient connaître ?
Quality assurance in rubber vulcanization is critical, and several international standards apply. ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management standard, ensuring that companies meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. For specific applications, buyers should also consider certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for industrial rubber products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Contrôle de la qualité à l'arrivée (IQC) : This is the first checkpoint where raw materials are inspected before they enter the production line. Ensuring that the rubber and additives meet specified quality criteria is essential for the overall quality of the final product.
-
Contrôle de la qualité en cours de fabrication (IPQC) : Continuous monitoring occurs during the manufacturing process. This includes checking temperatures, pressure settings, and the consistency of the rubber mixture. Any deviations can lead to defects that compromise the product’s integrity.
-
Contrôle de qualité final (CQF) : After the vulcanization and finishing processes, the final products are subjected to rigorous testing. This might include tensile strength tests, elongation tests, and abrasion resistance assessments. The results help verify that the products meet the required specifications and standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Vulcanized Rubber?
To ensure the quality of vulcanized rubber, several testing methods are commonly employed:
-
Tensile Testing: This method measures the strength and elasticity of rubber by stretching it until it breaks. The results provide insight into the material’s ability to withstand stress and deformation.
-
Hardness Testing: Shore durometers are often used to measure the hardness of the rubber, which can affect its performance in different applications.
-
Abrasion Testing: This assesses the rubber’s resistance to wear and tear, a critical factor for products exposed to friction.
-
Thermal Aging Tests: These tests evaluate how the rubber performs under elevated temperatures, simulating long-term usage conditions.
Comment les acheteurs B2B peuvent-ils vérifier le contrôle de la qualité des fournisseurs ?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with quality standards. This includes reviewing their quality management systems, production processes, and adherence to international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their testing methodologies, results, and any corrective actions taken in case of deviations.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an independent verification of a supplier’s quality control processes and product quality. This is particularly beneficial for buyers operating in regions with varying compliance standards.
Quelles sont les particularités du contrôle de la qualité pour les acheteurs internationaux B2B ?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances. Understanding local regulations and compliance standards is crucial. For example, while CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, other regions may have different requirements.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can affect communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear, documented quality agreements with suppliers can mitigate these issues and ensure mutual understanding of quality standards.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for rubber vulcanization is vital for B2B buyers. By being informed about the stages of production, quality control checkpoints, and testing methods, buyers can make better decisions and ensure they source high-quality vulcanized rubber products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is rubber vulcanization’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of rubber vulcanization, this practical guide outlines essential steps for effective sourcing. Understanding the vulcanization process is critical for selecting the right materials and suppliers, ensuring high-quality products that meet specific requirements. This checklist will guide you through the key considerations to make informed decisions.
Étape 1 : Définir les spécifications techniques
Clearly articulating your technical requirements is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. Determine the specific properties you need from vulcanized rubber, such as tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. This will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure they can meet your needs.
- Consider applications: Identify the end-use applications of the vulcanized rubber—whether for automotive parts, industrial seals, or consumer products—as this will influence your specifications.
Étape 2 : Recherche de fournisseurs potentiels
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in rubber vulcanization. Look for companies that specialize in the type of rubber you require, be it natural or synthetic.

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
- Check industry experience: Suppliers with extensive experience in your specific industry are more likely to understand your needs and provide tailored solutions.
Étape 3 : Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any agreements, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with industry standards that ensure quality and safety.
- Quality assurance: Certifications indicate a commitment to quality control and adherence to best practices, which is crucial for the production of reliable vulcanized rubber products.
Étape 4 : Demande d'échantillons à tester
Obtaining samples of vulcanized rubber from suppliers allows you to evaluate material properties firsthand. This step is vital for assessing whether the rubber meets your defined specifications.
- Conduct performance tests: Test the samples for key properties such as flexibility, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors relevant to your application.
Étape 5 : Assess Production Capabilities
Understanding the production capabilities of your potential suppliers is essential. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, machinery, and capacity to handle your orders, especially for large-scale projects.
- Flexibility and scalability: Ensure that the supplier can accommodate fluctuations in demand and has the capability to scale production as needed.
Étape 6 : Négocier les conditions et les prix
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, lead times, and payment terms. A clear agreement on these aspects will help avoid misunderstandings later in the process.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Look beyond the initial price—factor in shipping, duties, and any potential tariffs, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
Étape 7 : Établir un plan de communication
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership with your supplier. Establish a regular communication schedule to discuss updates, address any issues, and provide feedback on product performance.
- Build relationships: A strong relationship with your supplier can lead to better service, support, and potentially more favorable terms in the long run.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for rubber vulcanization, ensuring they select suppliers who can deliver quality products tailored to their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is rubber vulcanization Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Vulcanization?
Understanding the cost structure of rubber vulcanization is crucial for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Matériaux: The primary materials in vulcanization are natural or synthetic rubber and sulfur. The choice of rubber type significantly affects costs, with synthetic rubber often being more expensive due to its petroleum base. Additional materials like accelerators, fillers, and color pigments also contribute to overall material costs.
-
Travail: Labor costs encompass skilled technicians required for the mixing, molding, and curing processes. Given that vulcanization is a technical procedure, it necessitates trained personnel, which can vary significantly by region. In countries with higher labor costs, like Germany, this may impact the overall pricing structure.
-
Frais généraux de fabrication: This includes utilities, rent, and maintenance of equipment used in the vulcanization process. Facilities that require advanced technology or comply with stringent quality standards may incur higher overhead costs.
-
Outillage: Custom molds and tooling for specific products can drive up costs. The complexity of the design and the materials used for tooling directly influence the initial investment required for production.
-
Contrôle de la qualité (CQ): Maintaining quality is essential in the vulcanization process. Investments in QC processes, including testing and certifications, add to the overall costs but are vital for ensuring product reliability.
-
Logistique: Transportation and warehousing of raw materials and finished products can vary in cost depending on location and delivery methods. International buyers should consider these logistics costs, especially when sourcing from different continents.
-
Marge: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rubber Vulcanization Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in rubber vulcanization, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing structures often benefit bulk orders. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to achieve lower per-unit costs.
-
Spécifications et personnalisation: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to unique tooling and materials. Buyers should evaluate whether custom solutions are necessary or if standard products will suffice.
-
Qualité des matériaux et certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS) can increase costs but may be essential for compliance in specific markets. Understanding the required certifications for your region can help in budgeting.
-
Facteurs liés au fournisseur: The reputation and reliability of suppliers also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but they often provide better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly influence total costs. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to budget effectively for shipping and insurance.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Rubber Vulcanization Costs?
When sourcing vulcanized rubber, consider these negotiation and cost-efficiency tips:
-
Coût total de possession (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Evaluate factors like durability and performance to understand the long-term value of your investment.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers may offer discounts for loyal customers or for timely payments.
-
Étude de marché: Conduct thorough market research to understand average pricing and trends in the rubber industry. This knowledge will empower you during negotiations.
-
Consider Regional Differences: Costs can vary significantly between regions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should factor in local economic conditions and labor costs when negotiating.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: While established suppliers may offer reliability, exploring emerging suppliers can provide competitive pricing options without compromising quality.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for rubber vulcanization are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and other economic factors. It is advisable for buyers to obtain quotes and conduct due diligence to ensure accurate budgeting and cost planning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is rubber vulcanization With Other Solutions
In the realm of rubber manufacturing, vulcanization stands out as a crucial process for enhancing the properties of rubber. However, there are alternative methods that also serve to improve rubber’s durability, elasticity, and resistance to environmental factors. This section will compare rubber vulcanization with other viable solutions, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
| Aspect comparatif | What Is Rubber Vulcanization | Alternative 1: Peroxide Curing | Alternative 2: Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High elasticity and strength; excellent abrasion resistance | Comparable strength; good thermal stability | Flexible, with moderate strength; lower abrasion resistance |
| Coût | Moderate; additional materials and energy required | Higher due to special additives | Generally lower; less energy-intensive production |
| Facilité de mise en œuvre | Requires controlled heating and chemical mixing | More complex due to precise conditions needed | Easy to implement; can be processed like plastics |
| Maintenance | Low; stable performance under normal conditions | Moderate; sensitive to temperature and moisture | Low; stable and durable over time |
| Meilleur cas d'utilisation | Tires, industrial gaskets, high-performance applications | Automotive seals, high-temperature applications | Consumer products, flexible applications like footwear |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Peroxide Curing as an Alternative to Vulcanization?
Peroxide curing is a chemical process that uses peroxide compounds to cross-link rubber molecules, resulting in improved thermal stability and resistance to aging. This method is particularly effective in applications requiring high-performance materials under extreme conditions, such as automotive seals and gaskets. However, the cost of additives and the complexity of the curing process can make it less appealing for standard applications. Moreover, peroxide-cured rubber may not achieve the same level of elasticity as vulcanized rubber, which could be a limitation in specific use cases.
How Do Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) Compare to Vulcanized Rubber?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) represent a versatile class of materials that combine the properties of rubber and plastic. They can be molded and processed like plastics while providing rubber-like elasticity. This makes TPEs easy to implement in manufacturing, as they can be produced using conventional plastic processes. While TPEs are generally lower in cost and energy consumption, they may not offer the same durability and abrasion resistance as vulcanized rubber, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications such as tires or industrial seals.
Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Rubber Processing Solution?
Selecting the right rubber processing solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your application. If durability, elasticity, and performance under stress are paramount, rubber vulcanization remains the gold standard. However, for applications where cost and ease of processing are critical, exploring alternatives like peroxide curing or thermoplastic elastomers may yield beneficial results. Consider factors such as performance needs, budget constraints, and production capabilities when making your decision, ensuring that the chosen method aligns with both current and future project demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is rubber vulcanization
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Vulcanization?
Rubber vulcanization enhances the properties of both natural and synthetic rubber, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries. Below are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Qualité des matériaux
Material grade refers to the specific classification of rubber based on its formulation and properties. Common grades include natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene-propylene diene monomer (EPDM). Understanding material grades is essential as they dictate the performance characteristics such as durability, heat resistance, and elasticity. For instance, SBR is widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance.
2. Hardness (Shore Durometer)
Hardness is measured using the Shore durometer scale and indicates the rubber’s resistance to indentation. Hardness levels typically range from 30A (very soft) to 90A (very hard). This specification is crucial for B2B buyers as it impacts the rubber’s performance in specific applications, such as seals and gaskets where a softer rubber may provide a better seal, while harder rubber may be used in applications requiring greater strength.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can withstand before failure. This property is critical in applications where the rubber will be subjected to stretching or pulling forces, such as in conveyor belts and automotive parts. A higher tensile strength indicates a more durable product, which is a key factor for manufacturers seeking reliability.
4. Elongation at Break
Elongation at break refers to the percentage increase in length that a rubber sample can undergo before breaking. This property is a measure of elasticity and flexibility, and it is particularly important for applications that require stretching, such as in hoses or elastic components. Understanding this property helps B2B buyers select the right rubber for their specific application needs.
5. Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance indicates the range of temperatures that vulcanized rubber can withstand without degrading. Different formulations offer varying degrees of heat and cold resistance. This specification is vital for industries like automotive and aerospace, where components are exposed to extreme temperatures. Selecting the right temperature-resistant rubber can prevent premature failure and enhance product longevity.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Rubber Vulcanization?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the rubber vulcanization sector. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of rubber vulcanization, OEMs often seek custom rubber parts tailored to specific requirements. Knowing this term helps buyers identify suppliers that can meet their unique specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and procurement strategies. Understanding MOQs can help businesses plan their purchases effectively and avoid overstocking or understocking.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare pricing and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making when sourcing vulcanized rubber products.
4. Incoterms (conditions commerciales internationales)
Incoterms are standardized international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transportation of rubber products.
5. Curing Agent
A curing agent, often sulfur or other additives, is used in the vulcanization process to enhance the properties of rubber. Recognizing this term allows buyers to understand the composition of the rubber they are sourcing and how it may affect performance in their applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in the procurement of vulcanized rubber, ensuring that they select the right materials and suppliers for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is rubber vulcanization Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Rubber Vulcanization Sector?
The rubber vulcanization sector is influenced by several global drivers that shape its market landscape. One significant trend is the increasing demand for high-performance materials across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. As these sectors emphasize durability and reliability, vulcanized rubber’s superior properties, including enhanced elasticity and resistance to wear, become essential. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles is driving new applications for vulcanized rubber in battery components and seals, offering B2B buyers fresh opportunities for sourcing.
Technological advancements are another critical factor. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is streamlining the vulcanization process, enhancing quality control, and improving production efficiency. Suppliers that leverage these technologies can offer competitive pricing and faster turnaround times, which are crucial for international buyers looking to optimize their supply chains. Furthermore, the increasing use of synthetic rubbers, which can be tailored for specific applications, is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling buyers to select materials that meet precise performance criteria.

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
Emerging markets in Africa and South America are also becoming focal points for sourcing rubber products. These regions offer access to abundant natural rubber resources and growing manufacturing capabilities. For B2B buyers, understanding local regulations and establishing reliable partnerships in these markets can lead to sustainable sourcing solutions and potential cost savings.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Rubber Vulcanization Industry?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of the rubber vulcanization industry. The environmental impact of rubber production, particularly from deforestation and chemical pollution, has raised concerns among consumers and regulators alike. As a result, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as sourcing natural rubber from certified plantations that follow responsible forestry practices.
Ethical supply chains are crucial for maintaining brand integrity and meeting consumer expectations. Buyers are encouraged to seek partnerships with suppliers who possess green certifications, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Rainforest Alliance. These certifications not only assure buyers of the sustainability of their materials but also enhance their market positioning in an increasingly eco-conscious landscape.
Moreover, the shift towards circular economy practices is gaining traction. This includes recycling and reusing rubber products, which minimizes waste and reduces the carbon footprint associated with new material production. B2B buyers should explore suppliers that offer recycled vulcanized rubber options, which can provide both environmental benefits and cost efficiencies.
What Is the Historical Context of Rubber Vulcanization and Its Relevance Today?
The process of vulcanization has its roots in the mid-19th century when Charles Goodyear discovered that heating rubber with sulfur significantly enhanced its properties. This breakthrough transformed rubber from a fragile, sticky material into a durable, elastic product suitable for various applications, including tires and industrial components.
Over the years, the vulcanization process has evolved, incorporating advanced additives and techniques to improve efficiency and product performance. Today, the ability to customize vulcanized rubber for specific applications is more accessible than ever, making it a vital component in modern manufacturing.
Understanding the historical context of vulcanization is essential for B2B buyers. It highlights the ongoing innovations in material science that continue to shape the industry. As companies increasingly focus on performance and sustainability, the legacy of vulcanization serves as a foundation for future developments in rubber technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is rubber vulcanization
1. How does rubber vulcanization improve product durability?
Vulcanization enhances rubber’s durability by introducing sulfur cross-links between polymer chains, resulting in a stronger and more elastic material. This process enables vulcanized rubber to withstand greater pressure and stress, making it less prone to wear and tear. Products made from vulcanized rubber, such as tires and gaskets, exhibit superior abrasion resistance and longevity, which is essential for industries that demand high-performance materials. For B2B buyers, sourcing vulcanized rubber ensures that end products meet rigorous quality and durability standards.
2. What types of rubber can be vulcanized for industrial applications?
Both natural and synthetic rubbers can undergo vulcanization. Natural rubber, derived from latex, offers excellent elasticity and strength, while synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), provides better resistance to heat and aging. The choice of rubber depends on the specific application requirements, such as environmental conditions and mechanical stress. For manufacturers, understanding the properties of different rubber types allows for better product design and selection, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.

Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
3. What are the key considerations when sourcing vulcanized rubber?
When sourcing vulcanized rubber, key considerations include material specifications, manufacturing processes, and supplier certifications. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s ability to meet industry standards and ensure quality control measures are in place. Additionally, assessing the supplier’s experience in the specific application of vulcanized rubber can provide insights into their capability to meet unique requirements. Engaging in thorough supplier vetting helps mitigate risks and ensures reliable partnerships.
4. How can I customize vulcanized rubber products for my specific needs?
Customization of vulcanized rubber products is typically achieved through collaboration with manufacturers during the design phase. Buyers can specify the desired properties, such as hardness, elasticity, and color, as well as any additives needed for particular applications. It’s essential to communicate detailed requirements and work closely with suppliers to develop prototypes. This collaborative approach ensures that the final product meets specific performance standards and enhances overall product effectiveness.
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for vulcanized rubber products?
Minimum order quantities for vulcanized rubber products can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the product. Generally, suppliers may set MOQs to ensure cost-efficiency in production. For B2B buyers, it’s advisable to discuss potential MOQs with suppliers upfront and explore options for smaller orders or trial runs if needed. Understanding MOQ policies can help buyers effectively manage inventory and budget for new product launches.
6. What payment terms are commonly accepted in international rubber trade?
Payment terms in international rubber trade typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. It’s crucial for buyers to negotiate favorable payment terms that align with their cash flow needs while ensuring security in transactions. Clear communication regarding payment methods will facilitate smoother business transactions and strengthen supplier relationships.
7. How do I ensure quality assurance for vulcanized rubber products?
To ensure quality assurance, buyers should establish clear quality standards and inspection protocols with suppliers before production begins. This may include defining acceptable tolerances, testing methods, and certification requirements. Conducting regular audits and requesting samples for evaluation can also help maintain quality throughout the manufacturing process. Furthermore, partnering with suppliers who adhere to internationally recognized quality management systems, such as ISO certifications, enhances confidence in product quality.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vulcanized rubber?
When importing vulcanized rubber, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. It’s essential to work with reliable freight forwarders who understand the complexities of international shipping and can navigate customs requirements effectively. Additionally, buyers should factor in the potential for delays and plan for adequate inventory levels to avoid disruptions in production. Understanding the logistics landscape will help ensure timely delivery and smooth supply chain operations.
Top 4 What Is Rubber Vulcanization Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Walker Rubber – Custom Rubber Extrusions
Domaine : walker-rubber.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction : Rubber Extrusions, Custom Rubber Extrusions, Angle Extrusion, Rubber Boat Window Seals, Brick Grabs, Cab Tyres, Rubber Cable Protection, Coloured Extrusions, Container Door Seal Extrusion, Conveyor Side Skirting, Rubber Door Seals, EPDM Extrusions, Rubber Expansion Seals, Rubber Façade Seal Extrusions, Flame Retardant Extrusions, Food Grade Extrusions, Rubber Gate Seals, Rubber Glazing Seals, H Pr…
2. Britannica – Vulcanization Process
Domaine : britannica.com
Enregistré : 1995 (30 ans)
Introduction : Vulcanization is a chemical process that improves the physical properties of natural or synthetic rubber, resulting in higher tensile strength, resistance to swelling and abrasion, and increased elasticity over a wider temperature range. The process involves heating rubber with sulfur, discovered by inventor Charles Goodyear in 1839. Accelerators can be added to speed up vulcanization or lower the…
3. ScienceDirect – Vulcanization Process
Domaine : sciencedirect.com
Enregistré : 1997 (28 ans)
Introduction : Vulcanization is a chemical process that enhances the elasticity and retractile force of rubbery or elastomeric materials by forming a crosslinked molecular network. This process reduces permanent deformation after the removal of applied forces and typically involves the insertion of crosslinks between polymer chains using sulfur or other vulcanizing agents. Key benefits of vulcanization include i…
4. Merriam-Webster – Vulcanization Explained
Domaine : merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction : Vulcanization is the process of chemically treating natural or synthetic polymers, especially rubber, to enhance their properties such as elasticity, strength, and stability. During this process, sulfur is added to rubber and heated under pressure to form sulfur cross-links between the polymer chains, which increases the material’s durability. The term was named by Charles Goodyear in 1846, after …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is rubber vulcanization
How Can B2B Buyers Leverage Rubber Vulcanization for Competitive Advantage?
In conclusion, understanding rubber vulcanization is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. The vulcanization process significantly increases the strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance of rubber, making it an invaluable material across various industries, from automotive to consumer goods. By strategically sourcing vulcanized rubber, companies can not only improve their product performance but also reduce long-term costs associated with material failure and replacement.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis on quality and durability in products is paramount. As global markets continue to evolve, aligning procurement strategies with suppliers who specialize in advanced vulcanization techniques will be essential. Investing in high-quality vulcanized rubber can set your offerings apart in competitive landscapes.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable and high-performance materials will only grow. International B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with leading rubber manufacturers who prioritize innovation and sustainability. By doing so, you position your business for success in an increasingly competitive market. Engage with suppliers today to secure the best materials for your future projects.
Illustrative image related to what is rubber vulcanization
Avis de non-responsabilité et conditions d'utilisation
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
Les informations fournies dans ce guide, y compris le contenu concernant les fabricants, les spécifications techniques et l'analyse du marché, sont uniquement destinées à des fins d'information et d'éducation. Elles ne constituent pas un conseil professionnel en matière d'achat, un conseil financier ou un conseil juridique.
Bien que nous ayons fait tout notre possible pour garantir l'exactitude et l'actualité des informations, nous ne sommes pas responsables des erreurs, des omissions ou des informations obsolètes. Les conditions du marché, les détails de l'entreprise et les normes techniques sont susceptibles d'être modifiés.
Les acheteurs B2B doivent faire preuve d'une diligence raisonnable indépendante et approfondie. avant de prendre toute décision d'achat. Il convient notamment de contacter directement les fournisseurs, de vérifier les certifications, de demander des échantillons et de solliciter une consultation professionnelle. Le risque lié à l'utilisation des informations contenues dans ce guide est supporté uniquement par le lecteur.