Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dredging environmental impact
Navigating the complexities of dredging environmental impact presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany. As organizations seek to enhance their operational efficiency while ensuring environmental stewardship, understanding the multifaceted implications of dredging is crucial. This guide delves into the various types of dredging operations, their applications in infrastructure development and environmental remediation, and the critical environmental impacts associated with sediment disturbance, habitat alteration, and water quality degradation.
In the sections that follow, readers will find a comprehensive analysis of supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for mitigating negative environmental effects. By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that balance operational needs with environmental responsibility. Understanding the environmental impact of dredging not only aids in compliance with local regulations but also enhances corporate sustainability initiatives, fostering goodwill among stakeholders and the communities in which they operate.
Join us as we explore the intricate landscape of dredging, ensuring that your next project is both economically viable and environmentally sound.
Indice dei contenuti
- Top 1 Dredging Environmental Impact Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dredging environmental impact
- Understanding dredging environmental impact Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of dredging environmental impact
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dredging environmental impact’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for dredging environmental impact
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dredging environmental impact
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dredging environmental impact’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dredging environmental impact Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dredging environmental impact With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dredging environmental impact
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dredging environmental impact Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dredging environmental impact
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dredging environmental impact
- Disclaimer importante e condizioni d'uso
Understanding dredging environmental impact Types and Variations
| Nome del tipo | Caratteristiche distintive principali | Applicazioni primarie B2B | Brevi pro e contro per gli acquirenti |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment Disruption | Disturbance of sediment layers leading to contaminant release | Environmental remediation, construction projects | Pro: Can improve navigability; Contro: May harm water quality and aquatic life. |
| Increased Turbidity | Elevated levels of suspended particles affecting light penetration | Harbor maintenance, dredging for shipping lanes | Pro: Essential for maintaining waterway depth; Contro: Affects photosynthesis and aquatic ecosystems. |
| Habitat Disturbance | Alteration or destruction of marine habitats | Coastal development, infrastructure projects | Pro: Necessary for construction; Contro: Loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services. |
| Nutrient Release | Resuspension of nutrients leading to potential algal blooms | Aquaculture, dredging for nutrient management | Pro: Can enhance marine productivity; Contro: Risk of oxygen depletion and water quality decline. |
| Water Flow Alteration | Changes in natural water flow and circulation patterns | Flood prevention, floodplain management | Pro: Can mitigate flooding; Contro: Disruption of ecological balance and sediment transport. |
What Are the Characteristics of Sediment Disruption in Dredging?
Sediment disruption occurs when dredging activities disturb the seabed, releasing harmful contaminants into the water column. This phenomenon can significantly affect water quality, leading to immediate and long-term ecological consequences. For B2B buyers, understanding the implications of sediment disruption is crucial, especially when considering projects that involve environmental remediation or construction in sensitive areas. Proper planning and execution are essential to mitigate adverse effects while achieving project goals.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
How Does Increased Turbidity Impact Dredging Projects?
Increased turbidity arises from suspended sediments during dredging, which can limit light penetration in water bodies. This reduction affects photosynthesis in aquatic plants, consequently impacting the food chain. B2B buyers need to weigh the benefits of maintaining navigable waterways against the ecological risks posed by increased turbidity. Effective water quality monitoring and sediment management strategies can help minimize negative outcomes, making it a critical consideration for buyers engaged in harbor maintenance or shipping lane dredging.
Why Is Habitat Disturbance a Major Concern in Dredging?
Habitat disturbance from dredging activities can lead to the destruction of vital marine habitats, such as seagrass beds and coral reefs. This loss can reduce biodiversity and disrupt the ecological balance. For businesses involved in coastal development or infrastructure projects, understanding the trade-offs is essential. Engaging in thorough environmental impact assessments and implementing strategies to minimize habitat loss can not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also enhance corporate sustainability efforts.
What Are the Implications of Nutrient Release in Dredging?
Nutrient release occurs when dredging resuspends sediments, potentially increasing nutrient levels in the water. While this can boost marine productivity, it also carries the risk of algal blooms and subsequent oxygen depletion. For B2B buyers in aquaculture or nutrient management, recognizing the dual nature of nutrient release is vital. Buyers should consider technologies and methodologies that allow for nutrient management while mitigating the risks of water quality degradation.
How Does Water Flow Alteration Affect Dredging Outcomes?
Water flow alteration is a significant consequence of dredging that can disrupt natural circulation patterns in aquatic ecosystems. This disruption can affect nutrient distribution, oxygen levels, and overall ecosystem health. For businesses involved in flood prevention or floodplain management, understanding the implications of water flow alteration is critical for project success. Collaborative planning with environmental experts can help ensure that necessary alterations do not compromise ecological integrity.
Key Industrial Applications of dredging environmental impact
| Industria/Settore | Specific Application of dredging environmental impact | Valore/Beneficio per l'azienda | Considerazioni chiave sull'approvvigionamento per questa applicazione |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maritime and Shipping | Maintenance of shipping channels and harbors | Ensures safe navigation and reduces shipping delays | Compliance with environmental regulations and sediment management plans |
| Construction and Infrastructure | Site preparation for coastal and marine construction projects | Facilitates construction timelines and project efficiency | Assessing environmental impact assessments and monitoring systems |
| Environmental Remediation | Removal of contaminated sediments in polluted areas | Restores ecosystems and enhances community health | Selection of eco-friendly dredging technologies and practices |
| Pesca e acquacoltura | Habitat restoration for fish populations | Supports sustainable fishing practices and biodiversity | Understanding local regulations and ecological assessments |
| Petrolio e gas | Pipeline installation and maintenance in marine environments | Minimizes environmental disruption and operational downtime | Evaluation of dredging techniques to mitigate ecological risks |
How Does Dredging Environmental Impact Benefit the Maritime and Shipping Industry?
In the maritime and shipping sector, dredging is crucial for maintaining navigable waterways and harbors. By removing sediment buildup, dredging enhances safety and efficiency in shipping routes, ultimately reducing delays and operational costs. International buyers in this sector must consider compliance with local environmental regulations, as improper dredging can lead to significant ecological damage. It is essential to source dredging services that adhere to best practices in sediment management to minimize environmental impact.
What Role Does Dredging Play in Construction and Infrastructure Projects?
Dredging is often a prerequisite for coastal and marine construction projects, such as building ports, bridges, and offshore platforms. It enables the preparation of sites by creating stable foundations and ensuring access for construction vessels. For B2B buyers, understanding the environmental implications of dredging is critical, as they need to secure services that provide comprehensive environmental impact assessments and monitoring systems to comply with local laws and regulations, especially in sensitive ecological areas.
How is Dredging Used in Environmental Remediation Efforts?
In environmental remediation, dredging is employed to remove contaminated sediments from water bodies, thus restoring aquatic ecosystems and improving water quality. This application is vital for industries focused on sustainability and corporate responsibility. Buyers should prioritize sourcing eco-friendly dredging technologies and practices that minimize further environmental damage while effectively addressing contamination issues. Engaging with experts who have experience in local ecosystems will also enhance project outcomes.
Why is Dredging Important for Fisheries and Aquaculture?
Dredging can facilitate habitat restoration for fish and other aquatic organisms, thus supporting sustainable fisheries and aquaculture operations. By enhancing habitats, dredging helps maintain biodiversity and ensures the long-term viability of fish stocks. B2B buyers in this sector must be aware of local regulations regarding habitat protection and restoration, ensuring that dredging activities are conducted in a manner that promotes ecological health and sustainability.
What are the Considerations for Dredging in Oil and Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, dredging is necessary for the installation and maintenance of underwater pipelines. This process must be managed carefully to minimize environmental disruption and maintain operational efficiency. Buyers need to evaluate dredging techniques that effectively mitigate ecological risks while ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards. Understanding the local marine environment is crucial for selecting the right dredging methods that align with operational goals while safeguarding ecological integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dredging environmental impact’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Regulatory Compliance in Dredging Projects
Il problema:
B2B buyers in the dredging sector often face significant challenges in adhering to environmental regulations. With increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies and the public regarding the environmental impacts of dredging, buyers must ensure that their operations comply with local, national, and international laws. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, project delays, and damage to reputation, making it crucial for companies to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
La soluzione:
To manage regulatory compliance effectively, buyers should invest in robust environmental impact assessments (EIAs) before commencing dredging operations. Collaborating with environmental consultants who specialize in dredging can help identify potential impacts on local ecosystems and water quality. Additionally, implementing real-time water quality monitoring solutions can ensure that sediment disruption and contaminant release are kept within acceptable limits. Establishing a clear communication channel with regulatory authorities can also provide guidance on evolving regulations and help buyers adapt their practices accordingly.
Scenario 2: Addressing Public Concerns About Environmental Impact
Il problema:
In many regions, particularly in Africa and South America, dredging projects can provoke public outcry due to fears about environmental degradation. Local communities often express concerns about the potential loss of biodiversity, water pollution, and habitat destruction, which can lead to protests and delays in project execution. This backlash can significantly hinder project timelines and escalate costs.
La soluzione:
To address public concerns, it is essential for buyers to engage in proactive community outreach. This involves organizing informational sessions to educate local stakeholders about the dredging process and its environmental safeguards. Demonstrating commitment to sustainable practices—such as using eco-friendly dredging technologies and employing best management practices—can foster trust. Moreover, incorporating community feedback into project planning can help mitigate resistance and build a collaborative approach to environmental stewardship.
Scenario 3: Mitigating Environmental Damage During Dredging Operations
Il problema:
B2B buyers often grapple with the immediate environmental impacts of dredging, such as sediment resuspension, habitat destruction, and increased turbidity. These issues can lead to detrimental effects on aquatic life and water quality, creating long-term ecological consequences that can also affect the buyer’s operations and sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
La soluzione:
To mitigate environmental damage during dredging operations, buyers should adopt a phased and monitored approach. Utilizing advanced dredging equipment that minimizes sediment disturbance and employing techniques such as silt curtains can significantly reduce turbidity and protect surrounding habitats. Additionally, implementing a comprehensive environmental monitoring program throughout the dredging process allows for the immediate identification of adverse effects, enabling quick corrective actions. Investing in training for crews on environmentally responsible dredging practices can further enhance operational efficiency while safeguarding marine ecosystems.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can not only enhance their operational effectiveness but also contribute positively to environmental conservation efforts in their respective regions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dredging environmental impact
Which Materials Are Most Effective for Dredging Environmental Impact?
When selecting materials for dredging projects, especially with a focus on minimizing environmental impact, it’s crucial to consider properties such as durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with specific media. Below, we analyze four common materials used in dredging operations, highlighting their key properties, pros and cons, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Dredging Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in dredging equipment due to its strength and versatility. It offers high tensile strength and can withstand significant pressure and temperature variations. However, steel is prone to corrosion, especially in saline environments, which can affect its longevity and performance.
Pro: Steel’s durability makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, making it a popular choice for dredging companies.
Contro: The susceptibility to corrosion requires additional protective coatings or treatments, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs. Moreover, in regions with high salinity, such as coastal areas in the Middle East, the lifespan of steel components may be significantly reduced.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Dredging Operations?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of fiberglass and resin, are gaining traction in dredging applications. They offer excellent corrosion resistance and are lightweight, which can improve fuel efficiency during operations.
Pro: The corrosion resistance of composites extends the lifespan of dredging equipment, reducing maintenance costs. Their lightweight nature also allows for easier handling and transportation.
Contro: Composites can be more expensive than traditional materials like steel, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, they can be less robust under extreme mechanical stress, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Provide for Dredging Equipment?
Aluminum is another material used in dredging, particularly for smaller vessels or components. It is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for marine environments.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
Pro: The low weight of aluminum enhances fuel efficiency and maneuverability, which is beneficial for operations in shallow waters. Its natural resistance to corrosion reduces the need for protective coatings.
Contro: While aluminum is strong, it may not withstand the same level of stress as steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty dredging applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more costly than steel, impacting budget considerations for projects.
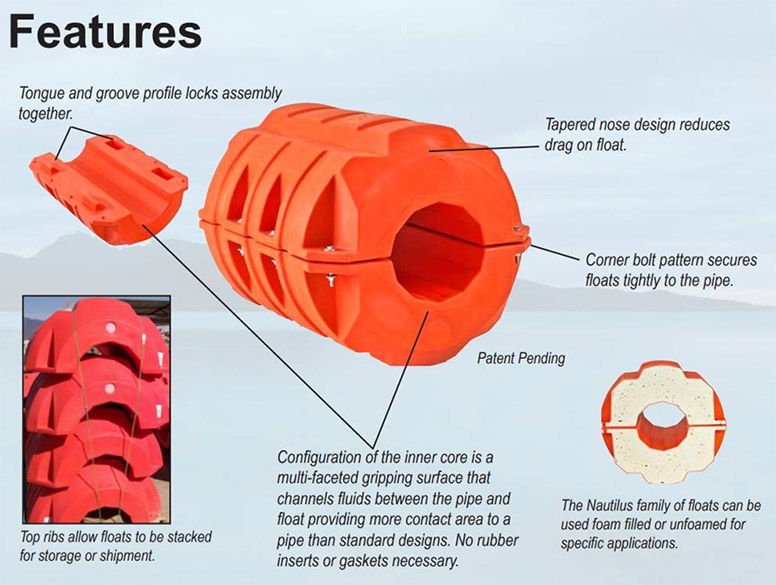
Why Is Rubber Important in Dredging Applications?
Rubber is primarily used in dredging for hoses and seals, where flexibility and resistance to wear are essential. It can handle a variety of media, including sediments and debris, without degrading.
Pro: Rubber’s flexibility allows it to adapt to various conditions, making it ideal for complex dredging environments. It also provides excellent wear resistance, which is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
Contro: The lifespan of rubber can be affected by exposure to UV light and extreme temperatures, necessitating regular replacements. Furthermore, rubber components may not be suitable for high-pressure applications, limiting their use in some dredging scenarios.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Dredging Environmental Impact
| Materiale | Typical Use Case for dredging environmental impact | Vantaggio chiave | Svantaggi/limitazioni principali | Costo relativo (basso/medio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio | Structural components of dredging equipment | High tensile strength | Suscettibile alla corrosione | Medio |
| Composito | Lightweight dredging vessels | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost than steel | Alto |
| Aluminum | Smaller dredging vessels and components | Leggero e resistente alla corrosione | Less robust under heavy stress | Medio |
| Gomma | Hoses and seals in dredging operations | Flexibility and wear resistance | Limited lifespan in harsh conditions | Basso |
Selecting the right materials for dredging operations is critical for minimizing environmental impact while ensuring operational efficiency. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and environmental standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dredging environmental impact
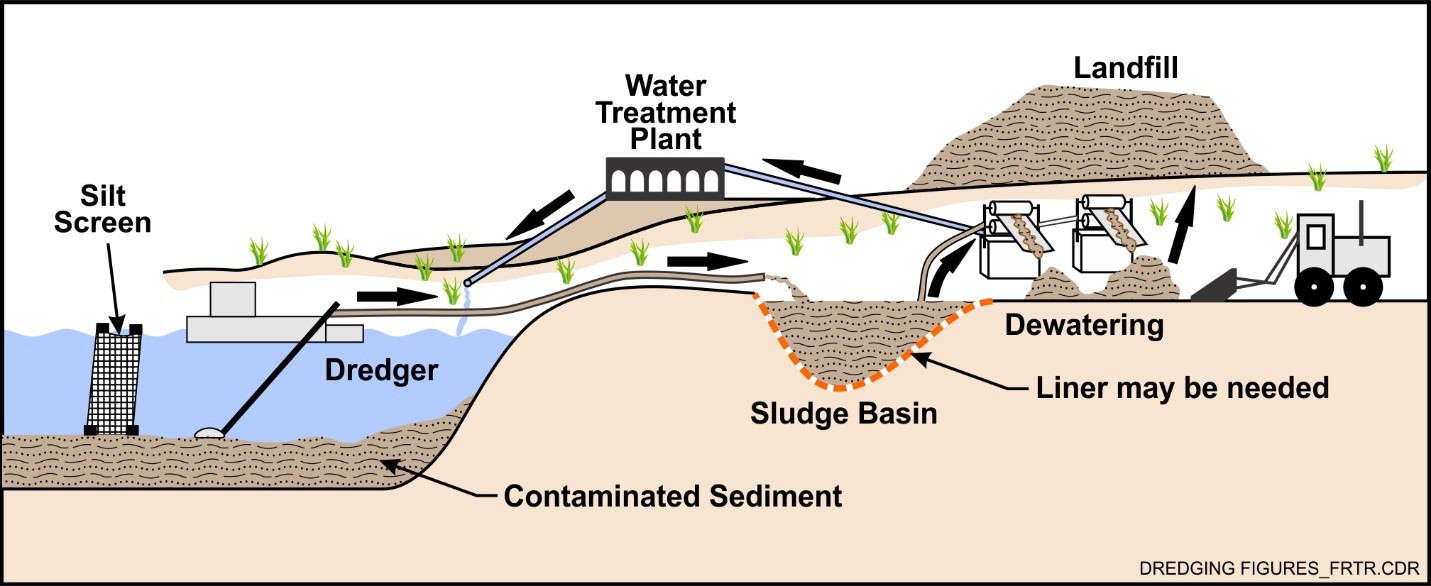
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Dredging Equipment?
The manufacturing of dredging equipment involves a series of intricate processes that ensure the final products meet stringent environmental and operational standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in dredging solutions that minimize environmental impact.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Dredging Equipment?
The first stage of manufacturing involves selecting appropriate materials that can withstand harsh marine environments. Common materials include high-strength steel for the hull and structural components, corrosion-resistant alloys for components exposed to seawater, and specialized polymers for seals and gaskets. This stage also includes sourcing sustainable materials where possible, which aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly practices in the dredging industry.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
Once materials are prepared, the forming process begins. Techniques such as cutting, bending, and welding are employed to create the basic shapes of dredging equipment. Advanced methods like CNC machining and laser cutting offer precision in forming components, which is essential for ensuring the equipment’s efficiency and longevity. Moreover, the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software allows for the creation of complex geometries that enhance the operational capabilities of dredgers.
Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
After forming, the next step is assembly, where various components are integrated to create the final product. This phase may involve both manual labor and automated processes to ensure precision and reduce human error. Key components such as pumps, dredging heads, and hydraulic systems are assembled with care to ensure they function seamlessly together. Effective communication between engineering teams and assembly workers is vital during this stage to address any design challenges that may arise.
How Is Finishing Achieved in Dredging Equipment Manufacturing?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments, painting, and coating to enhance durability and resistance to corrosion. Techniques such as sandblasting and powder coating are commonly used to prepare surfaces for painting, ensuring that protective coatings adhere properly. This stage not only improves the aesthetic appeal of the equipment but also extends its operational life, which is particularly important for equipment exposed to marine environments.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Dredging Equipment?
Ensuring that dredging equipment meets quality standards is critical, especially when considering the potential environmental impact. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the quality assurance processes.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems and is applicable across various manufacturing sectors, including dredging equipment. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers follow best practices in quality management, leading to consistent product quality.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as the CE marking in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for equipment used in oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications indicate that the equipment meets specific safety and performance criteria, which is crucial for B2B buyers concerned about regulatory compliance.
Quali sono i principali punti di controllo della qualità?
Quality Control (QC) throughout the manufacturing process typically includes several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to ensure that components meet design specifications. This may include dimensional checks and functional tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it meets all operational and safety standards. This may involve performance tests and environmental impact assessments.
Come possono gli acquirenti B2B verificare il controllo qualità dei fornitori?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is essential to mitigate risks associated with equipment failures and environmental impacts.
What Auditing Practices Should Be Followed?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality assurance practices. Buyers should request audits from third-party organizations that specialize in quality management systems. These audits provide insights into the manufacturer’s adherence to relevant standards and their commitment to continuous improvement.
How Can Buyers Access Quality Assurance Reports?
Requesting quality assurance reports and certifications is another crucial step for buyers. These documents should outline the quality control processes implemented by the manufacturer, as well as any relevant test results. Transparent communication regarding quality assurance is a positive indicator of a supplier’s reliability.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific certification requirements that may differ by region. For instance, the CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, while buyers in the Middle East may prioritize compliance with local regulations and standards. Engaging with local industry experts or legal counsel can help navigate these complexities.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Critical for Dredging Equipment?
In the context of dredging, quality assurance is not just about meeting regulatory requirements; it is also about ensuring the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems. By understanding the manufacturing processes and the importance of quality control, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with both operational needs and environmental responsibilities. Investing in high-quality dredging equipment ultimately leads to better performance, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced long-term viability for projects across diverse regions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dredging environmental impact’
Introduzione
Navigating the complexities of dredging and its environmental impact requires a strategic approach, especially for international buyers. This guide offers a step-by-step checklist to help you assess and procure dredging services while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and standards. By following these steps, you can minimize adverse effects on aquatic ecosystems and enhance the sustainability of your dredging projects.
Fase 1: Assess Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Understanding local and international environmental regulations is crucial before initiating any dredging project. Each region, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, has specific guidelines governing dredging activities.
– Look for compliance with laws such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations in the U.S. or the European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive.
– Engage with local authorities to ensure that all necessary permits are obtained before commencing dredging operations.
Fase 2: Define Your Project Objectives
Clearly outlining the objectives of your dredging project will guide the selection of appropriate techniques and equipment. This includes identifying whether the focus is on maintenance, restoration, or new construction.
– Specify the desired outcomes, such as improving navigability, restoring habitats, or removing contaminants.
– Understand the environmental trade-offs associated with each objective to make informed decisions.
Fase 3: Valutare i potenziali fornitori
Before committing to a supplier, thorough vetting is essential. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar projects.
– Assess their experience with environmentally sensitive dredging and their track record in minimizing ecological impact.
– Consider suppliers’ technology and methods to ensure they employ best practices in dredging operations.
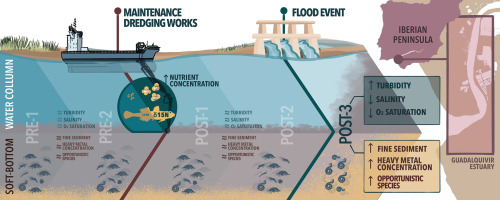
Passo 4: Verify Environmental Management Plans
A robust Environmental Management Plan (EMP) is vital for mitigating potential impacts on water quality and marine ecosystems. Ensure that your chosen supplier has a comprehensive EMP in place.
– Review the plan for effectiveness in addressing issues such as sediment disruption, habitat disturbance, and nutrient release.
– Check for monitoring protocols that track water quality and ecological health pre-, during, and post-dredging.
Passo 5: Conduct Risk Assessments
Engage in detailed risk assessments to identify potential environmental impacts associated with the dredging process. This proactive approach helps in minimizing unforeseen consequences.
– Focus on sediment contamination risks, changes in water flow, and habitat loss.
– Utilize third-party environmental consultants for an unbiased assessment of potential risks.
Passo 6: Implement Monitoring and Reporting Protocols
Establishing a monitoring framework is essential for ongoing assessment of the dredging project’s environmental impact.
– Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help measure the success of the dredging operation in terms of environmental sustainability.
– Ensure regular reporting mechanisms are in place to communicate findings to stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
Passo 7: Review Post-Dredging Rehabilitation Plans
Finally, ensure that your supplier has a clear plan for rehabilitation following dredging activities. This step is critical for restoring the ecological balance of the affected area.
– Evaluate the strategies proposed for habitat restoration and sediment stabilization.
– Consider long-term ecological monitoring to ensure the recovery of the ecosystem and adherence to environmental standards.
Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions that not only meet your project goals but also safeguard the environment against the adverse effects of dredging.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dredging environmental impact Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Dredging Environmental Impact Projects?
When considering the cost structure for dredging environmental impact projects, several key components must be analyzed. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
I materiali: The cost of materials used in dredging, such as sediment removal equipment, containment systems, and environmental monitoring tools, can vary significantly based on project specifications and environmental regulations. Suppliers may offer different grades of materials, influencing the overall cost.
-
Lavoro: Labor costs are often one of the largest expenses in dredging projects. Skilled personnel are required for operations, environmental assessments, and compliance checks. Labor rates can differ based on the region, with higher wages typically seen in Europe compared to Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: This includes costs related to the maintenance and operation of dredging equipment. Overhead costs can be influenced by the age and efficiency of the machinery, while tooling costs will vary depending on the customization required for specific projects.
-
Quality Control: Implementing effective QC measures is essential to ensure compliance with environmental standards. This may incur additional costs but is necessary to avoid fines and ensure long-term project viability.
-
Logistica: Transporting equipment and materials to and from the dredging site can significantly affect costs. Factors such as distance, local infrastructure, and the complexity of the logistics chain play a crucial role in determining these expenses.
-
Margine: Profit margins for dredging projects can vary based on competition, project scope, and perceived risks. Companies often adjust their margins based on client relationships and the strategic importance of the project.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Dredging Environmental Impact Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in the dredging sector, affecting both the overall project cost and the buyer’s ability to negotiate effectively.
-
Volume e quantità minima d'ordine (MOQ): Larger projects typically benefit from economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs. Buyers should consider negotiating for bulk pricing, especially if they anticipate ongoing dredging needs.
-
Specifiche e personalizzazione: Custom requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define project specifications to avoid unexpected expenses related to adjustments or additional features.
-
Materiali e certificazioni di qualità: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality, certified materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to lower long-term maintenance expenses and better environmental outcomes.
-
Fattori di fornitura: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better guarantees regarding quality and compliance, which can mitigate risks for buyers.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. These terms govern the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, directly impacting the total cost of ownership.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Dredging Projects?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to cost savings and more favorable contract terms for B2B buyers involved in dredging projects.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
-
Comprendere il costo totale di proprietà (TCO): Consider not only the initial project costs but also ongoing expenses such as maintenance, environmental compliance, and potential fines. This holistic view can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Leverage Long-term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms. Suppliers may offer discounts or priority service to established clients.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If terms do not meet your budgetary constraints, be prepared to explore other suppliers. This can often prompt suppliers to offer better terms to retain your business.
-
Explore Alternative Financing Options: For large projects, consider financing options that can spread costs over time, making it easier to manage cash flow while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
-
Research Market Rates: Stay informed about market trends and pricing for dredging services. Understanding the competitive landscape can empower buyers to negotiate more effectively.
Final Thoughts
When sourcing for dredging environmental impact projects, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies is crucial. By focusing on these areas, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions that lead to successful project outcomes while ensuring compliance with environmental standards. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so it is advisable to seek multiple quotes and conduct due diligence to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dredging environmental impact With Other Solutions
When evaluating the environmental impact of dredging, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider viable alternatives that can achieve similar objectives with potentially reduced ecological footprints. The following analysis compares dredging with other methods, helping decision-makers choose the most suitable solution for their projects.
| Aspetto di confronto | Dredging Environmental Impact | Alternative 1: Sediment Filtration | Alternative 2: Mechanical Removal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prestazioni | Effective for deep sediment removal but can disrupt ecosystems significantly. | Can improve water quality by filtering out sediments and contaminants, but may not remove large deposits. | Highly effective for localized sediment removal, minimizing disruption to surrounding areas. |
| Costo | High operational and environmental monitoring costs. | Moderate initial investment but lower long-term costs due to reduced ecological impact. | High initial setup costs but can be cost-effective in the long run through reduced ecological remediation. |
| Facilità di implementazione | Requires specialized equipment and permits; complex regulatory compliance. | Easier to implement in urban settings; minimal regulatory barriers. | Requires heavy machinery, but can be straightforward with proper planning. |
| Manutenzione | Ongoing monitoring and maintenance required to mitigate environmental impacts. | Low maintenance once established; requires periodic checks for effectiveness. | Moderate maintenance needed to ensure machinery remains operational and effective. |
| Il miglior caso d'uso | Suitable for large-scale projects in navigable waterways; necessary for certain infrastructure developments. | Ideal for urban water bodies needing pollution control; effective in areas with high sedimentation rates. | Best for localized sediment issues in smaller water bodies or construction sites. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Sediment Filtration as an Alternative to Dredging?
Sediment filtration systems are designed to enhance water quality by filtering out harmful sediments and contaminants from the water column. The primary advantage of this method is its ability to improve water quality with minimal disruption to the surrounding ecosystem. Additionally, the operational costs can be lower over time due to reduced environmental impact. However, sediment filtration may not be effective for large-scale sediment deposits, limiting its application in some scenarios.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
How Does Mechanical Removal Compare to Dredging in Terms of Environmental Impact?
Mechanical removal involves the physical extraction of sediments using specialized machinery, which can be tailored to minimize environmental disruption. This method is particularly effective for localized sediment issues, allowing for targeted interventions. While the initial costs can be high, mechanical removal can be more sustainable in the long run by reducing the need for extensive environmental remediation. On the downside, it may still involve significant machinery and labor costs, and careful planning is required to ensure minimal impact on the ecosystem.
How Should B2B Buyers Decide Between Dredging and Alternative Methods?
In selecting the right solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific project needs, budget constraints, and environmental considerations. Dredging may be necessary for significant infrastructure projects, but alternatives like sediment filtration and mechanical removal can offer more sustainable options in many cases. Decision-makers should conduct thorough environmental assessments and consider the long-term implications of each method on water quality and aquatic ecosystems. By weighing the pros and cons of these alternatives, buyers can make informed choices that align with both their operational goals and environmental responsibilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dredging environmental impact
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Assessing Dredging Environmental Impact?
Understanding the technical properties associated with dredging is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are several key specifications that are vital for evaluating the environmental impact of dredging projects:
-
Sediment Quality Index (SQI)
– Definition: The SQI evaluates the chemical, physical, and biological properties of sediment. It helps identify contamination levels and overall sediment health.
– B2B Importance: A high SQI indicates clean sediment, which is less likely to release harmful pollutants during dredging. Buyers should prioritize projects with favorable SQI results to mitigate environmental risks and comply with regulatory standards. -
Hydraulic Conductivity
– Definition: This property measures how easily water can flow through sediment or soil. It is crucial for understanding how dredging will affect water movement and contaminant dispersion.
– B2B Importance: High hydraulic conductivity can lead to the rapid spread of contaminants if disturbed during dredging. Understanding this property helps in risk assessment and project planning, ensuring that proper containment measures are in place. -
Turbidity Levels
– Definition: Turbidity refers to the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles. It is a critical parameter for assessing water quality before, during, and after dredging activities.
– B2B Importance: Elevated turbidity can hinder photosynthesis in aquatic plants and disrupt the feeding habits of marine organisms. Monitoring turbidity levels can help buyers ensure compliance with environmental regulations and safeguard local ecosystems. -
Nutrient Loading
– Definition: This term refers to the concentration of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, in the water column. Dredging can resuspend sediments, potentially increasing nutrient levels.
– B2B Importance: While some nutrient enrichment can be beneficial, excessive levels can lead to harmful algal blooms and oxygen depletion. Buyers must assess nutrient loading to balance ecological health and project efficacy. -
Biodiversity Index
– Definition: This index measures the variety of species in a given area and is essential for assessing the ecological impact of dredging.
– B2B Importance: A decrease in biodiversity can signify potential long-term ecological harm. Understanding biodiversity impacts helps buyers make informed decisions about project viability and compliance with environmental standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Dredging Environmental Impact?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the dredging sector. Here are several terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers evaluate the quality and reliability of dredging equipment, ensuring they procure the best tools for minimizing environmental impact. -
MOQ (quantità minima d'ordine)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is vital for budget planning and inventory management, especially for large-scale dredging projects where material requirements can be substantial. -
RFQ (Richiesta di offerta)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers compare pricing and terms from different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making that aligns with environmental and budgetary goals. -
Incoterms (Termini commerciali internazionali)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping liabilities and costs, which is crucial for managing timelines and budgets in dredging operations. -
EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment)
– Definition: A process that evaluates the potential environmental effects of a proposed project before it is carried out.
– Importance: Conducting an EIA is often a legal requirement for dredging projects and is essential for ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and securing necessary permits.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their understanding of the complexities associated with dredging and its environmental impacts, leading to more responsible and informed decision-making.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dredging environmental impact Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Dredging Environmental Impact Sector?
The dredging environmental impact sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by global economic trends, regulatory pressures, and technological advancements. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe ramp up infrastructure projects, the demand for dredging services is on the rise. Notably, nations like Saudi Arabia and Germany are investing heavily in port expansions and coastal protection initiatives, which are critical for trade and environmental sustainability.
Emerging technologies, such as automated dredging equipment and advanced sediment management systems, are becoming essential for minimizing environmental impacts. These innovations allow for more precise dredging operations, reducing sediment disruption and habitat destruction. Additionally, the increasing adoption of data analytics in project planning helps companies anticipate and mitigate potential environmental consequences, making operations more efficient and compliant with local regulations.
International buyers should be aware of the growing emphasis on compliance with environmental standards and sustainability practices. Projects are increasingly scrutinized for their ecological footprints, and companies that demonstrate a commitment to minimizing negative impacts are likely to gain a competitive edge. Thus, understanding local regulations and sourcing practices is crucial for successful project execution.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in Dredging?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the dredging sector. The environmental impact of dredging activities, particularly on water quality and aquatic ecosystems, has led to heightened awareness among B2B buyers regarding the importance of ethical sourcing. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who employ sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and technologies that minimize environmental damage.
In addition, certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards are gaining traction. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also reassure stakeholders of their commitment to environmental stewardship. By sourcing from certified suppliers, businesses can ensure that their operations align with global sustainability goals, which is particularly important for buyers from regions facing strict environmental regulations.
Moreover, the integration of ‘green’ materials and sustainable practices in dredging projects can lead to cost savings in the long run. For instance, utilizing biodegradable products or advanced waste management techniques can significantly reduce disposal costs and regulatory fines. As such, B2B buyers must consider the long-term benefits of sustainability when making procurement decisions.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Dredging Practices and Their Environmental Impacts?
Historically, dredging has been a critical component of maritime infrastructure development, dating back to ancient civilizations that recognized the need for navigable waterways. However, the environmental impacts of dredging have only recently gained significant attention. In the past, the primary focus was on enhancing navigation and supporting economic growth, often at the expense of aquatic ecosystems.
Over the last few decades, research has increasingly highlighted the adverse effects of dredging, including sediment disruption, habitat loss, and pollution. This shift has prompted regulatory bodies to implement stricter guidelines and encourage the adoption of best practices in dredging operations. Today, companies are not only tasked with improving navigability but also with ensuring that their activities do not compromise the health of marine environments. This historical evolution underscores the necessity for B2B buyers to engage with suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices and responsible dredging techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dredging environmental impact
1. How do I assess the environmental impact of dredging projects?
To assess the environmental impact of dredging projects, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). This process involves evaluating potential changes to water quality, sediment disturbance, habitat loss, and effects on aquatic life. Engaging with local environmental authorities and stakeholders is essential for gathering data and ensuring compliance with regulations. Additionally, utilizing advanced monitoring technologies can provide real-time insights into water quality and ecosystem health, allowing for informed decision-making throughout the dredging process.
2. What are the best practices for minimizing dredging environmental impacts?
Best practices for minimizing environmental impacts during dredging include employing state-of-the-art dredging technology that reduces sediment disturbance, scheduling dredging during periods of low ecological sensitivity, and utilizing silt curtains to contain turbidity. Additionally, conducting pre- and post-dredging environmental assessments can help identify sensitive areas and monitor recovery. Collaboration with environmental experts and local communities can also facilitate the implementation of sustainable dredging practices that balance project needs with ecological preservation.

Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
3. How do I choose a reliable dredging contractor?
Choosing a reliable dredging contractor involves assessing their track record, certifications, and experience in environmentally sensitive projects. Requesting references and case studies can provide insights into their past performance and adherence to environmental regulations. Evaluate their approach to sustainability and how they manage environmental risks. Additionally, ensure they have the necessary equipment and technology to meet the specific requirements of your project while minimizing ecological impacts.
4. What factors should I consider when sourcing dredging equipment?
When sourcing dredging equipment, consider factors such as the specific type of dredging required (e.g., maintenance, capital), the environmental conditions of the site, and the equipment’s efficiency and environmental compliance. It’s also important to assess the equipment’s operational capabilities, maintenance requirements, and the supplier’s support services. Customization options may be necessary to meet specific project needs, so inquire about suppliers’ flexibility in modifying equipment to suit your requirements.
5. What is the typical lead time for dredging project delivery?
The lead time for dredging project delivery can vary significantly based on project scope, equipment availability, and regulatory approvals. Generally, it can range from a few weeks to several months. Factors such as environmental assessments, permits, and logistical arrangements can extend timelines. It’s advisable to discuss project timelines with contractors upfront to set realistic expectations and ensure that all necessary preparations are made in advance.
Illustrative image related to dredging environmental impact
6. What are the common payment terms in dredging contracts?
Payment terms in dredging contracts typically include an upfront deposit, progress payments based on project milestones, and a final payment upon project completion. Terms can vary by supplier and project size, so it’s essential to negotiate clear and mutually agreeable payment schedules. Additionally, consider including terms related to performance guarantees and penalties for delays to protect your investment and ensure timely project execution.
7. How can I ensure quality assurance in dredging operations?
To ensure quality assurance in dredging operations, establish clear performance metrics and monitoring protocols before project initiation. Regular site inspections and adherence to industry standards and environmental regulations are critical. Collaborating with third-party environmental consultants can provide an unbiased assessment of compliance and performance. Furthermore, implementing a feedback loop with contractors to address any issues promptly can help maintain quality throughout the project lifecycle.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international dredging projects?
For international dredging projects, logistics considerations include transportation of equipment, supply chain management, and local regulatory compliance. Ensure that you understand import/export regulations and potential customs issues related to equipment and materials. It’s also important to coordinate with local authorities for permits and approvals. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in handling large-scale projects can streamline operations and mitigate potential delays, ensuring that equipment and resources are available when needed.
Top 1 Dredging Environmental Impact Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Azocleantech – Innovative Dredging Solutions
Dominio: azocleantech.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduzione: 1. Toolbot Project: A highly accurate remote-operated vehicle (ROV) developed for selective and precise dredging, minimizing turbidity and optimizing sediment transportation.
2. Tiamat: An eco-friendly dredging solution by Haven Dredging, which injects water into sediment to extract diluted silt for responsible relocation. Achievements include a 50% cost reduction and a 65% decrease in greenhouse…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dredging environmental impact
In conclusion, the intricate balance between dredging activities and environmental health necessitates a well-informed approach to strategic sourcing. Key takeaways for international B2B buyers highlight the critical need for comprehensive assessments of water quality impacts, sediment disruption, and habitat disturbance associated with dredging. Understanding these factors enables buyers to make informed decisions when selecting dredging services and technologies that prioritize environmental sustainability.
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates potential risks associated with dredging but also enhances operational efficiency and compliance with environmental regulations. By investing in advanced monitoring technologies and engaging with experienced contractors, businesses can significantly reduce adverse environmental impacts while ensuring the successful execution of dredging projects.
Looking forward, it is essential for stakeholders in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to collaborate on best practices and innovative solutions that protect aquatic ecosystems. By prioritizing sustainable dredging practices, businesses can contribute to preserving biodiversity and enhancing the health of marine environments. Engage with trusted partners and invest in sustainable dredging solutions today to secure a more resilient future for our waterways.
Disclaimer importante e condizioni d'uso
⚠️ Disclaimer importante
Le informazioni fornite in questa guida, compresi i contenuti relativi ai produttori, alle specifiche tecniche e all'analisi di mercato, hanno uno scopo puramente informativo ed educativo. Non costituiscono una consulenza professionale in materia di acquisti, né una consulenza finanziaria o legale.
Pur avendo compiuto ogni sforzo per garantire l'accuratezza e la tempestività delle informazioni, non siamo responsabili di eventuali errori, omissioni o informazioni non aggiornate. Le condizioni di mercato, i dettagli aziendali e gli standard tecnici sono soggetti a modifiche.
Gli acquirenti B2B devono condurre una due diligence indipendente e approfondita. prima di prendere qualsiasi decisione di acquisto. Per questo è necessario contattare direttamente i fornitori, verificare le certificazioni, richiedere campioni e chiedere una consulenza professionale. Il rischio di affidarsi alle informazioni contenute in questa guida è esclusivamente a carico del lettore.