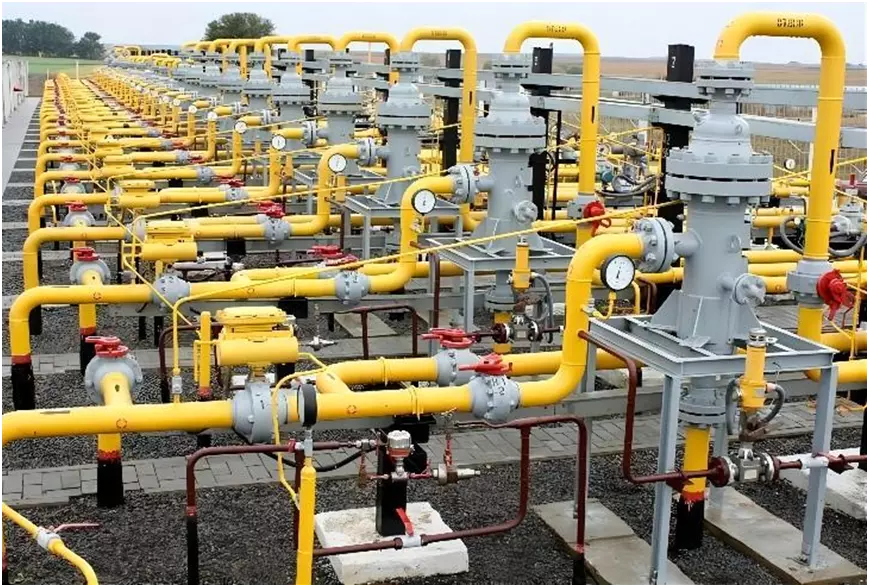
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pipeline systems
In today’s global economy, sourcing reliable pipeline systems is critical for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. As industries expand across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of pipeline procurement can pose significant challenges. This guide is designed to equip international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, addressing everything from the types of pipelines—such as oil, gas, and water systems—to their various applications in industrial settings.
Understanding the nuances of pipeline systems is essential for selecting the right solutions that align with specific operational needs. This comprehensive resource delves into the different types of pipelines, their construction and operation, and best practices for supplier vetting. Additionally, we explore cost considerations and emerging technologies that can further optimize pipeline performance.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will gain actionable insights that empower them to identify trusted suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and ultimately enhance their supply chain resilience. Whether you’re a procurement manager in Nigeria or an operations director in Saudi Arabia, this guide is tailored to facilitate strategic purchasing decisions in the complex landscape of global pipeline systems.
Indice dei contenuti
- A Look at Pipeline Systems Manufacturers & Suppliers
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pipeline systems
- Understanding pipeline systems Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of pipeline systems
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pipeline systems’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for pipeline systems
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pipeline systems
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pipeline systems’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pipeline systems Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pipeline systems With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pipeline systems
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pipeline systems Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pipeline systems
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pipeline systems
- Disclaimer importante e condizioni d'uso
Understanding pipeline systems Types and Variations
| Nome del tipo | Caratteristiche distintive principali | Applicazioni primarie B2B | Brevi pro e contro per gli acquirenti |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water and Sewer Pipelines | Underground networks; various materials like PVC, steel | Municipal water supply, sewage treatment | Pros: Essential for public health; Cons: High initial installation cost. |
| Oil Pipelines | High-pressure systems; typically steel construction | Transportation of crude oil and refined products | Pros: Cost-effective for long distances; Cons: Environmental risks if leaks occur. |
| Gas Pipelines | Transport natural gas; often insulated for safety | Energy distribution, heating applications | Pros: Reliable supply; Cons: Vulnerable to pressure fluctuations. |
| Slurry Pipelines | Transport solid-liquid mixtures; specialized pumps | Mining, waste management | Pros: Efficient for long distances; Cons: Higher maintenance due to wear. |
| Pneumatic Pipelines | Uses air pressure to transport materials | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Clean and efficient; Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Water and Sewer Pipelines?
Water and sewer pipelines form the backbone of municipal infrastructure, delivering potable water and removing wastewater. Typically buried underground, these pipelines utilize materials such as PVC, ductile iron, and concrete. B2B buyers should consider the lifecycle cost, including installation and maintenance, as well as regulatory compliance regarding water quality. Choosing the right material is crucial for durability and resistance to corrosion, which can significantly impact long-term operational costs.
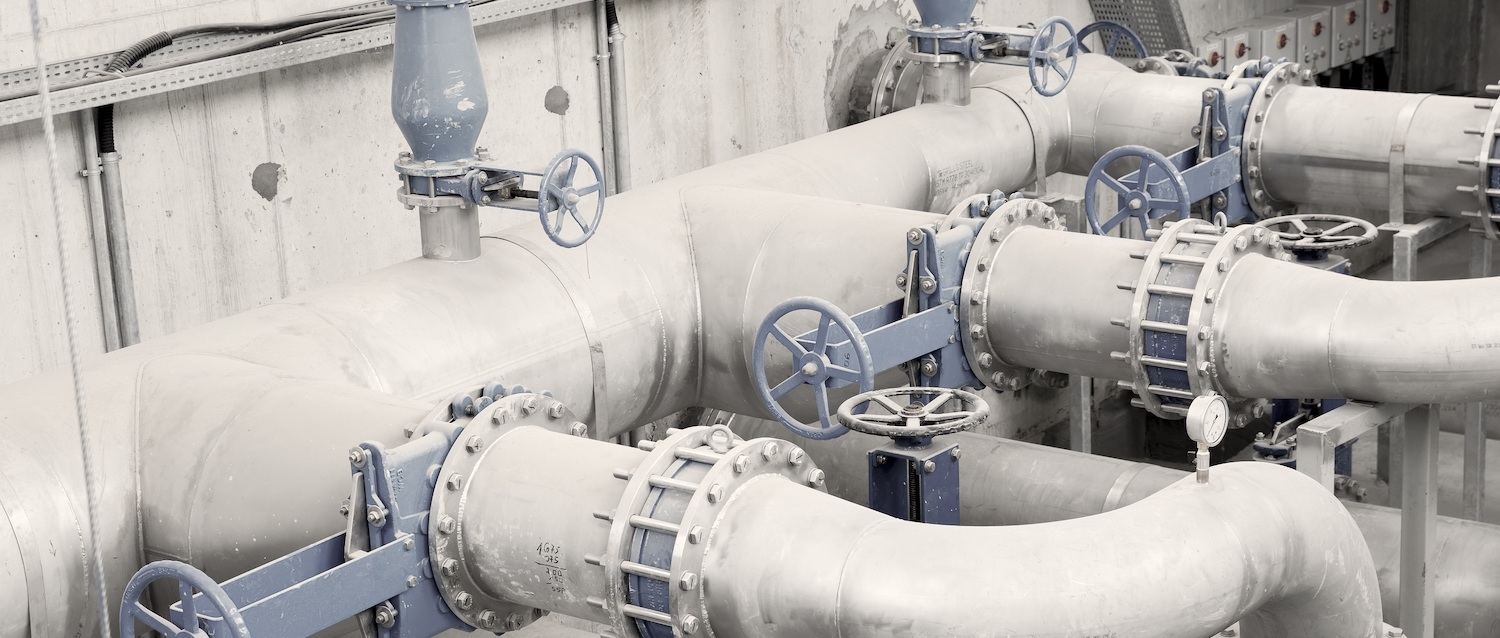

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
How Do Oil Pipelines Function in B2B Contexts?
Oil pipelines are engineered for high-pressure transportation of crude oil and refined products over long distances. Constructed primarily from steel, they are designed to minimize leaks and withstand environmental factors. For businesses in the energy sector, the choice of pipeline system can greatly affect logistics and cost efficiency. Buyers should assess factors such as pipeline diameter, pressure ratings, and the potential environmental impact, as regulatory scrutiny is often stringent.
What Are the Advantages of Gas Pipelines for Energy Distribution?
Gas pipelines are essential for the safe and efficient transport of natural gas, often featuring insulation to prevent heat loss and ensure safety. They serve a critical role in energy distribution for residential and industrial applications. B2B buyers need to evaluate the pipeline’s capacity, pressure rating, and installation costs. Safety features, such as monitoring systems for leaks, are also vital considerations, especially in regions where natural gas is a primary energy source.
Why Choose Slurry Pipelines for Mining and Waste Management?
Slurry pipelines are specialized systems designed to transport a mixture of solids and liquids, commonly used in mining operations and waste management. These pipelines require robust materials and pumping systems to handle the abrasive nature of the slurry. For B2B buyers, the efficiency of slurry transport can lead to significant cost savings in logistics. However, maintenance can be more demanding due to wear and tear, necessitating a thorough evaluation of operational capacity and material durability.
In What Situations Are Pneumatic Pipelines Most Effective?
Pneumatic pipelines utilize air pressure to transport bulk materials, making them particularly useful in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. These systems are valued for their cleanliness and efficiency, as they minimize contamination risks. Buyers should consider the types of materials to be transported, as pneumatic systems are not universally applicable. The initial setup cost can be high, but operational costs are often lower, making it a compelling option for businesses focused on hygiene and efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of pipeline systems
| Industria/Settore | Specific Application of pipeline systems | Valore/Beneficio per l'azienda | Considerazioni chiave sull'approvvigionamento per questa applicazione |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petrolio e gas | Transportation of crude oil and natural gas | Efficient, cost-effective transport over long distances | Compliance with international safety standards, pipeline material durability, and corrosion resistance |
| Water Supply and Wastewater | Delivery of potable water and sewage management | Reliable infrastructure for public health and sanitation | Local regulations, pipe material compatibility, and installation logistics |
| Mining and Minerals | Slurry transport of ores and minerals | Reduces environmental impact and operational costs | Material handling capabilities, pipeline diameter, and pumping systems |
| Agricoltura | Irrigation systems using water pipelines | Enhances crop yield through efficient water distribution | Pipe sizing for pressure and flow rates, weather resistance, and local sourcing availability |
| Chemicals and Petrochemicals | Transfer of various chemicals and fluids | Safe and efficient movement of hazardous materials | Regulatory compliance, material safety data sheets (MSDS), and leak detection systems |
How Are Pipeline Systems Used in Oil and Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas sector, pipeline systems are essential for the transportation of crude oil and natural gas from extraction points to refineries and distribution centers. These pipelines are designed to handle high pressures and corrosive substances, making them vital for operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector must prioritize compliance with international safety standards and seek materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, particularly in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia where infrastructure challenges may arise.
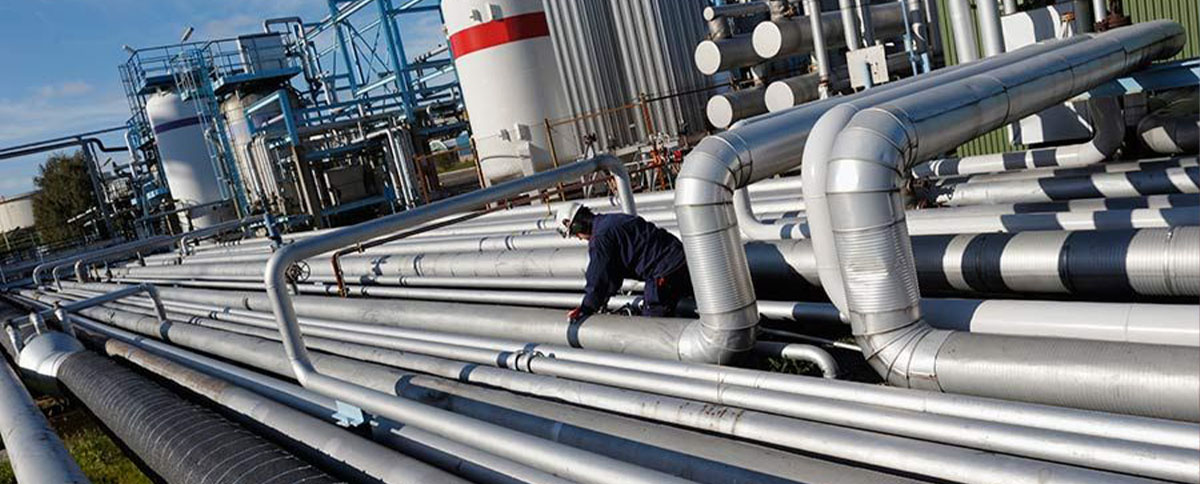

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
What Role Do Pipeline Systems Play in Water Supply and Wastewater Management?
Pipeline systems are crucial for delivering potable water to urban and rural areas, as well as managing sewage disposal. They ensure a reliable supply of clean water, which is fundamental for public health. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, understanding local regulations and the compatibility of pipe materials is essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of water infrastructure.
How Are Pipeline Systems Implemented in Mining and Minerals Transport?
In mining, pipeline systems facilitate the transport of slurry, a mixture of water and finely crushed ore, from mines to processing facilities. This method reduces the environmental impact compared to traditional transport methods like trucks. Buyers must consider the pipeline’s diameter and material handling capabilities to optimize operational efficiency and minimize costs, especially in remote mining locations across South America and Africa.
How Do Agriculture Industries Utilize Pipeline Systems for Irrigation?
Pipeline systems are increasingly adopted in agriculture for efficient irrigation. They allow for the controlled distribution of water across large fields, enhancing crop yields and conserving water resources. Buyers need to evaluate pipe sizing to ensure adequate pressure and flow rates, and must also consider local climate conditions to select materials that can withstand environmental stressors.
What Are the Applications of Pipeline Systems in Chemicals and Petrochemicals?
In the chemicals and petrochemicals industry, pipeline systems are used to transfer various hazardous fluids and chemicals safely. These systems must adhere to stringent safety regulations and include advanced leak detection technologies. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who provide comprehensive material safety data sheets (MSDS) and demonstrate a commitment to safety compliance, particularly in regions with strict environmental regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pipeline systems’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delayed Project Timelines Due to Inefficient Pipeline Systems
Il problema: B2B buyers often face significant delays in their project timelines due to inefficient pipeline systems. This inefficiency can stem from inadequate planning, poor material selection, or outdated technology. For instance, a construction company in Nigeria may find that its water pipeline installation is lagging behind schedule because the chosen materials are not suitable for the local climate, leading to unexpected corrosion or breakdown. Such delays not only inflate costs but can also result in lost contracts and damage to the company’s reputation.
La soluzione: To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough research on materials and technologies tailored to the specific environmental conditions of their projects. For instance, opting for high-grade, corrosion-resistant materials like ductile iron or PVC can significantly extend the lifespan of pipelines, reducing maintenance costs and project delays. Additionally, leveraging advanced technologies such as automated pipeline monitoring systems can help in early detection of potential issues, allowing for timely interventions. Buyers should also consider collaborating with local experts who understand the regional challenges and can provide insights on best practices in pipeline installation and maintenance.
Scenario 2: Regulatory Compliance and Safety Concerns in Pipeline Operations
Il problema: Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory compliance and safety standards presents a major challenge for B2B buyers involved in pipeline systems. In regions like the Middle East, stringent regulations govern the transportation of hazardous materials. A company operating gas pipelines may struggle to keep up with evolving regulations, risking fines and operational shutdowns. Moreover, safety breaches not only threaten public safety but can also lead to costly legal battles and severe reputational damage.
La soluzione: To mitigate these risks, it is crucial for buyers to stay informed about local and international regulatory requirements. Engaging with compliance specialists or legal advisors who specialize in pipeline operations can provide valuable guidance. Furthermore, investing in training programs for employees on safety protocols and regulatory standards can enhance operational safety. Implementing a robust monitoring system that tracks compliance and safety metrics can also help in identifying potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that the company remains compliant while prioritizing safety.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Maintenance Practices
Il problema: Many B2B buyers encounter high operational costs stemming from inefficient maintenance practices of pipeline systems. For instance, a mining company in South America might experience frequent breakdowns in their slurry pipelines due to a lack of regular inspections and maintenance. These breakdowns not only incur repair costs but also disrupt production schedules, leading to significant financial losses.
La soluzione: To address these challenges, buyers should implement a proactive maintenance strategy that emphasizes regular inspections and predictive maintenance. Utilizing technologies such as IoT sensors can provide real-time data on pipeline conditions, allowing for early detection of issues that could lead to failures. Establishing a comprehensive maintenance schedule based on pipeline usage and environmental factors will also help in reducing downtime and extending the life of the systems. Additionally, training maintenance staff on the latest technologies and best practices can further enhance efficiency and reduce costs associated with pipeline upkeep.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pipeline systems
When selecting materials for pipeline systems, B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in pipeline construction: steel, ductile iron, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and concrete. Each material presents unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact application suitability, particularly in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Properties of Steel in Pipeline Systems?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in pipeline systems, particularly for transporting oil and gas. Its key properties include high tensile strength, excellent pressure resistance, and good temperature tolerance, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. Steel pipelines can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, which is crucial for transporting hydrocarbons.
Pros: Steel pipelines are durable and can last for decades with proper maintenance. They are also highly resistant to impact and provide a secure barrier against leaks.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, which can lead to failures if not properly managed through coatings or cathodic protection. Additionally, steel can be more expensive than other materials, both in terms of initial cost and maintenance.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
Impatto sull'applicazione: Steel is particularly compatible with hydrocarbons and high-temperature fluids, making it a preferred choice for oil and gas pipelines.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Buyers must ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A53 or API 5L, which govern the quality and specifications of steel pipes. In regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, local regulations may also dictate specific requirements for pipeline materials.
How Does Ductile Iron Perform in Pipeline Systems?
Ductile iron is another popular choice, especially for water and wastewater applications. It offers excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when coated, and can handle high pressures.
Pros: Ductile iron is known for its strength and flexibility, making it less likely to crack under stress. It also has a long service life and is relatively easy to install.
Cons: While ductile iron is robust, it can be heavier than alternatives like PVC, which may increase transportation and installation costs. Additionally, it can be more expensive than traditional cast iron.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
Impatto sull'applicazione: Ductile iron is well-suited for transporting water and sewage due to its resistance to corrosion and ability to handle varying pressure levels.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Compliance with standards such as ISO 2531 is crucial. Buyers in regions like South America should be aware of local standards that may affect material selection and installation practices.
What are the Advantages of Using PVC in Pipeline Systems?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is commonly used for non-pressurized applications such as drainage and irrigation. Its key properties include lightweight construction, ease of installation, and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and easy to work with, making it a popular choice for smaller diameter pipelines. It is also resistant to chemicals and does not corrode, which enhances its longevity.
Cons: However, PVC has limitations in high-pressure applications and can become brittle in extreme temperatures. Its lower tensile strength compared to metals may also be a concern in certain applications.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
Impatto sull'applicazione: PVC is ideal for transporting water and wastewater but is less suitable for high-pressure gas or oil applications.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D1785 and be aware of local regulations regarding the use of PVC in pipeline systems, particularly in regions like Europe where environmental standards may be stringent.
How Does Concrete Compare in Pipeline Systems?
Concrete is often used for large-diameter pipelines, particularly in municipal water systems and sewage treatment plants. Its key properties include high compressive strength and durability.
Pros: Concrete pipes are resistant to corrosion and can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for underground applications. They also have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance.
Cons: The main limitation of concrete is its weight, which can complicate transportation and installation. Additionally, concrete pipes are not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impatto sull'applicazione: Concrete is best suited for gravity-flow applications in water and sewage systems, where high pressure is not a primary concern.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Compliance with standards such as ASTM C76 is essential. Buyers in the Middle East may also need to consider the impact of local soil conditions on the choice of concrete for pipeline systems.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pipeline Systems
| Materiale | Typical Use Case for pipeline systems | Vantaggio chiave | Svantaggi/limitazioni principali | Costo relativo (basso/medio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio | Oil and gas transportation | High strength and pressure resistance | Suscettibile alla corrosione | Alto |
| Ductile Iron | Water and wastewater applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Heavier and more expensive than PVC | Medio |
| PVC | Drainage and irrigation | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited in high-pressure applications | Basso |
| Concrete | Municipal water and sewage systems | High durability and low maintenance | Heavy and unsuitable for high pressure | Medio |
In summary, the choice of material for pipeline systems is critical and should be based on specific application needs, environmental conditions, and compliance with local standards. Understanding the pros and cons of each material will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and regulatory obligations.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pipeline systems
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Pipeline Systems?
The manufacturing process of pipeline systems involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, durable pipes suitable for various applications. These stages are:
-
Preparazione del materiale: The initial stage begins with the selection of appropriate materials, typically metals like steel or cast iron. For pipelines transporting gas or oil, high-strength steel is preferred for its durability. The raw materials undergo inspections to verify their specifications and chemical compositions.
-
Formazione: This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into pipe form. Techniques such as extrusion, rolling, or welding are commonly employed. In the case of steel pipes, sections are often welded together using high-frequency or submerged arc welding methods to create long, continuous lengths of pipe. Ensuring proper weld quality is crucial, as it directly impacts the integrity of the pipeline.
-
Montaggio: Once formed, the pipes are assembled with additional components like valves, fittings, and flanges. This stage also includes the installation of cathodic protection systems to prevent corrosion, which is especially important in environments with high moisture or saline conditions.
-
Finitura: The final stage involves surface treatment processes such as coating or galvanization. These treatments enhance corrosion resistance and improve the lifespan of the pipelines. Quality control checks are conducted to ensure that all finishes meet the required specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Pipeline Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of pipeline systems, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. The following aspects are crucial for effective QA:
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding international quality standards is essential in verifying supplier capabilities. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, including pipeline manufacturing. It emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
-
Standard API: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards specifically for oil and gas pipelines, ensuring safety and reliability.
-
Marchio CE: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Pipeline Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are vital to monitor the manufacturing process at various stages:
-
Controllo qualità in entrata (CQI): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring materials meet specified standards is crucial to prevent defects in the final product.
-
Controllo qualità in corso d'opera (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections and tests are conducted to monitor the quality of the product at various stages. This may include weld inspections, dimensional checks, and non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or radiographic testing.
-
Controllo qualità finale (CQC): Once the manufacturing process is complete, a final inspection is performed before the pipes are dispatched. This includes pressure testing, visual inspections, and verification of surface finishes.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Pipeline Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the safety and reliability of pipeline systems:
-
Test idrostatici: This method involves filling the pipeline with water and pressurizing it to identify leaks. It is a widely accepted practice for verifying the integrity of pipelines.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and radiographic testing are used to detect internal and external defects without damaging the material.
-
Chemical Analysis: Conducted to ensure that the material properties meet the specified requirements, chemical analysis is crucial for maintaining the quality of the raw materials used.
Come possono gli acquirenti B2B verificare il controllo qualità dei fornitori?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some strategies:
-
Audit dei fornitori: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. This provides insight into the supplier’s capabilities and commitment to quality.
-
Richiesta di rapporti sulla qualità: Buyers should request detailed quality control reports from suppliers. These reports should outline the testing methods used, results of inspections, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Ispezioni di terzi: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies can perform audits and testing, ensuring compliance with international standards.
Quali sono le sfumature del controllo qualità per gli acquirenti internazionali?
Quality control nuances vary depending on the region and specific industry requirements. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to consider:

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that must be adhered to. Understanding these local requirements is crucial for compliance and successful project execution.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can differ significantly across cultures. Building strong relationships with suppliers and understanding their operational practices can enhance collaboration and ensure quality.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International buyers must be aware of logistics challenges that may impact the delivery of materials and components. Ensuring that suppliers have robust logistics capabilities is vital for timely project completion.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in pipeline systems is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, testing methods, and verification strategies, buyers can ensure they source reliable and high-quality pipeline systems that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pipeline systems’
The procurement of pipeline systems is a critical aspect for businesses engaged in the transportation of liquids, gases, or other materials. This guide provides a clear checklist to help international B2B buyers effectively navigate the sourcing process, ensuring they select the right systems for their operational needs.
Fase 1: Definire le specifiche tecniche
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for ensuring that the pipeline systems meet your operational requirements. Consider the type of fluid or gas being transported, pressure levels, and environmental conditions. Specifics like pipe diameter, material type (steel, PVC, etc.), and flow rates should be documented to facilitate accurate supplier quotes.
Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
Fase 2: Condurre ricerche di mercato
Thorough market research helps identify potential suppliers and understand current trends in pipeline technology. Look into various manufacturers’ reputations, product offerings, and customer reviews. This insight will guide you in selecting suppliers who not only meet your technical specifications but also align with your business values and sustainability goals.
Fase 3: Valutare i potenziali fornitori
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Assess their experience with projects of comparable scope and complexity to ensure they can meet your specific needs.
- Check Certifications: Ensure suppliers have the necessary certifications for quality and safety standards relevant to your region, such as ISO or API certifications.
- Review Past Projects: Look for examples of successful installations or projects that demonstrate the supplier’s capability and reliability.
Passo 4: Request Proposals and Compare
Solicit proposals from shortlisted suppliers based on your defined specifications. Compare not only the pricing but also the terms of service, warranty offerings, and delivery timelines. This comparison will help you identify the best value proposition, which is critical for long-term operational success.
Passo 5: Valutare i servizi di assistenza e manutenzione post-vendita
Pipeline systems require ongoing maintenance and support to ensure operational efficiency. Inquire about the after-sales services offered by suppliers, including installation assistance, training for your staff, and availability of spare parts. A supplier that provides strong post-purchase support can significantly enhance your operational resilience.
Passo 6: Negotiate Contract Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize the contract terms. Ensure that all expectations regarding delivery schedules, payment terms, warranties, and liabilities are clearly outlined. A well-structured contract can prevent future disputes and ensure accountability.
Passo 7: Plan for Installation and Compliance
Prepare for the installation phase by coordinating with your chosen supplier to establish timelines and logistical requirements. Additionally, ensure that all installation processes comply with local regulations and safety standards. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and enhance the longevity of your pipeline systems.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing pipeline systems, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pipeline systems Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Pipeline Systems Sourcing?
When sourcing pipeline systems, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
-
I materiali: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials include steel, ductile iron, PVC, and concrete, each with varying costs and durability. Steel, while strong and suitable for high-pressure applications, is often more expensive than PVC or concrete.
-
Lavoro: Labor costs can vary based on the region and the complexity of the installation. Skilled labor is essential for welding and assembling pipelines, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Spese generali di produzione: This encompasses costs associated with running production facilities, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. High overhead can lead to increased prices for buyers.
-
Utensili: Specialized tools are required for pipeline construction and maintenance. The initial investment in tooling can be significant, influencing the final pricing structure.
-
Controllo qualità (CQ): Ensuring that pipeline systems meet safety and regulatory standards involves rigorous QC processes. These costs can add to the overall price but are essential for long-term reliability.
-
Logistica: Transportation of materials to the installation site can be a substantial cost factor, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and local regulations can influence logistics expenses.
-
Margine: Supplier profit margins can vary widely. Understanding typical margins in your industry can help in negotiations.
What Influences Pricing for Pipeline Systems?
Several factors can affect the pricing of pipeline systems beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume e quantità minima d'ordine (MOQ): Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better prices.
-
Specifiche e personalizzazione: Customized solutions that meet specific project requirements can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard solutions.
-
Qualità dei materiali e certificazioni: Higher quality materials and certifications, such as ISO or API standards, can lead to increased costs but may be necessary for compliance and safety.
-
Fattori di fornitura: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but offer better warranties and service.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly impact the total cost. Buyers should understand terms such as FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to manage shipping expenses effectively.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pipeline Pricing?
Negotiation is a key skill in securing favorable pricing for pipeline systems. Here are some practical tips for buyers:
-
Ricerca e benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand typical pricing and costs. Benchmarking against similar projects can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Costo totale di proprietà (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operation, and potential downtime. Presenting a TCO analysis can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Volume Leverage: If planning multiple projects, leveraging future volume can help negotiate better terms and discounts from suppliers.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate with buyers they trust.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in pipeline systems sourcing:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Currency exchange rates can impact pricing. Buyers should account for potential fluctuations when budgeting for purchases.
-
Conformità normativa: Different countries have varying regulations regarding pipeline materials and installation. Compliance costs can influence overall pricing.
-
Cultural Negotiation Styles: Understanding regional negotiation customs can help in effectively communicating with suppliers and achieving favorable outcomes.
-
Shipping and Tariffs: Be aware of international shipping costs and any applicable tariffs that could affect total expenses.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for pipeline systems can vary significantly based on the above factors and market conditions. The information provided here serves as a guideline and may not reflect actual prices. It is advisable for buyers to obtain detailed quotations from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pipeline systems With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Pipeline Systems
In the realm of transporting liquids, gases, and other materials, pipeline systems are a well-established solution. However, various alternative methods and technologies exist that can achieve similar objectives. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers who seek the most efficient and cost-effective solution tailored to their unique operational needs. This section compares pipeline systems with two viable alternatives: truck transportation e rail transport, providing insights into their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Tabella di confronto
| Aspetto di confronto | Pipeline Systems | Truck Transportation | Rail Transport |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prestazioni | High throughput, continuous flow | Flexible routes, variable speed | High capacity, consistent schedules |
| Costo | High initial investment, low operating costs | Moderate capital, high operational costs | Moderate capital, low operational costs |
| Facilità di implementazione | Complex installation, long-term commitment | Quick setup, adaptable to needs | Requires infrastructure investment |
| Manutenzione | Moderate, specialized tools needed | Low, general maintenance | Moderate, regular inspections needed |
| Il miglior caso d'uso | Long-distance, high-volume transport | Short to medium distances, flexible delivery | Bulk materials over long distances |
Ripartizione dettagliata delle alternative
Truck Transportation: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
Truck transportation is a flexible and adaptable alternative to pipeline systems. It allows for the delivery of materials directly to various locations without the need for extensive infrastructure. One of the significant advantages is its ability to navigate various terrains and reach remote areas, making it ideal for short to medium distances. However, operational costs can be high due to fuel, driver wages, and vehicle maintenance. Additionally, trucks may encounter traffic and weather-related delays, impacting delivery schedules.
Rail Transport: How Does It Compare?
Rail transport is another viable alternative, particularly suited for bulk materials over long distances. It benefits from lower operational costs per ton-mile compared to trucks, making it an economical choice for large shipments. Rail infrastructure can handle heavy loads and has a lower environmental impact compared to road transport. However, the initial investment in rail infrastructure can be substantial, and it lacks the flexibility of trucks, requiring specific routes and schedules. Delays can also occur due to congestion on the rail networks.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating pipeline systems against alternatives such as truck transportation and rail transport, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, including the volume and type of materials being transported, distance, and budget constraints. Pipeline systems excel in high-volume, long-distance transport, while trucks offer flexibility for varied routes, and rail provides cost-effective bulk transport. By assessing these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their logistical goals and operational efficiencies, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and profitability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pipeline systems
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pipeline Systems?
Understanding the essential technical properties of pipeline systems is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating the suitability of materials and designs for specific applications. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Grado del materiale
The material grade of pipes determines their strength, durability, and suitability for different fluids and pressures. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and PVC. For example, carbon steel is preferred for oil and gas transport due to its high tensile strength and resistance to pressure. Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring long-term operational efficiency and compliance with industry standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in dimensions of the pipes and fittings. This specification is critical for ensuring that components fit together correctly during installation. Tight tolerances are essential for high-pressure applications, as they minimize the risk of leaks and failures. For buyers, understanding tolerance levels can help in assessing the quality and reliability of the pipeline systems.
3. Wall Thickness
Wall thickness affects the pipe’s ability to withstand internal pressure and external forces. Thicker walls provide greater strength and resistance to corrosion but may also increase weight and cost. Buyers must balance the need for durability with economic factors, ensuring that the selected wall thickness meets operational requirements without incurring unnecessary expenses.
4. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum internal pressure a pipe can safely handle. This property is essential for determining the appropriate pipeline system for various fluids, including water, gas, and hazardous materials. Buyers should evaluate the pressure requirements of their applications to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a critical property for pipeline materials, particularly in environments with aggressive chemicals or moisture. Materials such as stainless steel and certain plastics offer enhanced resistance to corrosion. Selecting corrosion-resistant materials can significantly extend the lifespan of pipeline systems, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
6. Temperature Rating
The temperature rating specifies the maximum and minimum temperatures that the pipeline can withstand without compromising integrity. This property is particularly important in industries like oil and gas, where temperature fluctuations can be extreme. Buyers should consider the temperature conditions of their applications to ensure that the selected pipeline systems can perform reliably.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
What Are Common Trade Terms in Pipeline Systems?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can facilitate smoother negotiations and better decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms relevant to pipeline systems:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the pipeline industry, OEMs provide crucial components such as valves, pumps, and fittings. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure quality in their pipeline systems.
2. MOQ (quantità minima d'ordine)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and purchasing strategies. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better deals and plan their procurement processes efficiently.
3. RFQ (Richiesta di offerta)
An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of pipeline systems, an RFQ helps buyers compare offers and select the most favorable terms. Crafting a clear RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and better supplier relationships.
4. Incoterms (Termini commerciali internazionali)
Incoterms are a set of standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B transactions involving pipeline systems, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks during transport. Familiarity with Incoterms can enhance negotiation processes and reduce misunderstandings.
5. Tempo di esecuzione
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the pipeline industry, lead times can vary significantly based on material availability and production schedules. Buyers should consider lead times when planning projects to ensure timely delivery and avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals, enhancing their procurement processes in the pipeline sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pipeline systems Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Pipeline Systems Market?
The pipeline systems market is currently experiencing robust growth driven by several key global factors. The increasing demand for energy, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, is propelling investments in oil and gas infrastructure. The global shift towards renewable energy sources, such as hydrogen and biofuels, is also reshaping pipeline requirements, as companies seek to adapt their systems for new types of energy transport. Additionally, the need for efficient water and sewage systems in rapidly urbanizing regions in Africa and South America is creating significant opportunities for pipeline suppliers.
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing the sourcing landscape in the pipeline sector. Innovations such as smart pipeline monitoring systems, which utilize IoT and AI for predictive maintenance, are becoming standard. These technologies enhance safety and reduce downtime, appealing to international buyers looking to optimize operations. Furthermore, 3D printing and advanced materials are being adopted for pipeline manufacturing, providing cost-effective and customized solutions for specific regional needs.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Pipeline Industry?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority for businesses in the pipeline systems sector. The environmental impact of pipeline construction and operation is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. Ethical sourcing is vital, as buyers demand transparency in supply chains. This includes ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that suppliers adhere to environmental regulations.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is gaining traction. For instance, companies are exploring eco-friendly alternatives to traditional materials, such as recycled plastics and low-carbon steel. Additionally, suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards, like ISO 14001, are becoming more appealing to B2B buyers, especially in Europe where regulatory pressures are high. By prioritizing sustainability, companies not only mitigate risks but also enhance their brand reputation, which is crucial in competitive markets.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
What Is the Historical Context of Pipeline Development Relevant to Today’s Market?
The evolution of pipeline systems dates back thousands of years, with ancient civilizations using rudimentary forms to transport water. The modern pipeline industry began in the 19th century with the introduction of steel pipes, which allowed for the long-distance transportation of oil and gas. Significant technological advancements, such as the welding of pipe sections and the development of sophisticated leak detection systems, have transformed the industry, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Today, this historical context is essential for understanding current market dynamics. The lessons learned from past pipeline failures and environmental incidents have led to stricter regulations and a greater emphasis on safety and sustainability. This historical awareness informs B2B buyers about the importance of selecting reliable suppliers who prioritize innovation and compliance, ensuring that they are not only meeting current demands but are also prepared for future challenges in the pipeline systems sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pipeline systems
-
How do I solve issues related to pipeline corrosion?
Corrosion in pipelines can lead to significant operational challenges and safety hazards. To mitigate this, consider implementing cathodic protection systems, which use electrical currents to prevent corrosion. Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance using advanced technologies like smart pigs can detect corrosion early. Selecting corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or lined pipes, is also crucial. Collaborating with experienced suppliers who provide comprehensive quality assurance (QA) services will ensure that the materials meet international standards. -
What is the best material for oil pipeline systems?
The best material for oil pipeline systems is typically high-strength steel, which offers durability and resistance to high pressures. However, the choice may depend on factors like the environmental conditions, the type of oil being transported, and budget constraints. For regions prone to corrosion, consider using alloyed steels or pipes with protective linings. It’s essential to work with suppliers who understand local conditions and can provide tailored solutions that comply with international safety regulations. -
How can I ensure compliance with international pipeline standards?
To ensure compliance with international pipeline standards, start by familiarizing yourself with the relevant regulations in your target market, such as API (American Petroleum Institute) standards or ISO (International Organization for Standardization) guidelines. Collaborate with suppliers who have certifications and a proven track record of adhering to these standards. Regular audits and inspections by third-party entities can further verify compliance, ensuring that your pipeline systems are safe and reliable for operation. -
What factors should I consider when vetting pipeline suppliers?
When vetting pipeline suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications, and reputation. Review their past projects and customer testimonials to gauge their reliability and quality. Assess their financial stability to ensure they can fulfill large orders and provide ongoing support. Additionally, inquire about their supply chain practices and logistics capabilities, especially for international shipments, to avoid delays and ensure timely delivery. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for pipeline systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for pipeline systems can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type and complexity of the product. Generally, larger orders may yield better pricing and terms. However, it’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility on MOQs, especially for new customers or special projects. Understanding your pipeline requirements will help you negotiate favorable terms. -
What payment terms are typical in international pipeline procurement?
Typical payment terms in international pipeline procurement can range from advance payment to net 30 or net 60 days after delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for large orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment. -
How can I customize pipeline systems for specific applications?
Customizing pipeline systems involves understanding your unique application requirements, including pressure ratings, fluid characteristics, and environmental conditions. Collaborate closely with your supplier to discuss the specific adaptations needed, such as material selection, diameter adjustments, or additional features like insulation. Many suppliers have engineering teams that can assist in the design and provide prototypes to ensure the final product meets your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing pipelines internationally?
When sourcing pipelines internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure compliance with local import/export laws. Plan for potential delays by building extra time into your project schedule. Additionally, evaluate the supplier’s ability to provide comprehensive logistics support, including tracking and insurance options, to safeguard your investment during transit.
A Look at Pipeline Systems Manufacturers & Suppliers
Could not verify enough suppliers for pipeline systems to create a list at this time.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pipeline systems
In today’s global marketplace, strategic sourcing for pipeline systems is not just an operational necessity but a critical component for achieving competitive advantage. By leveraging the right suppliers and technologies, businesses can ensure the integrity, efficiency, and sustainability of their pipeline infrastructure. Key takeaways for international buyers include the importance of understanding local regulations, fostering relationships with reliable suppliers, and investing in advanced technologies that enhance pipeline safety and performance.
As regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to develop their energy and water infrastructures, the demand for innovative pipeline solutions will only increase. Buyers should prioritize partnerships that emphasize quality, reliability, and environmental responsibility.

Illustrative image related to pipeline systems
Looking ahead, the future of pipeline systems lies in smart technologies and sustainable practices. Engaging with suppliers who are committed to these values will not only optimize operations but also contribute to broader environmental goals. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to take decisive action—explore partnerships that align with your strategic sourcing objectives and position your organization at the forefront of the pipeline industry.
Disclaimer importante e condizioni d'uso
⚠️ Disclaimer importante
Le informazioni fornite in questa guida, compresi i contenuti relativi ai produttori, alle specifiche tecniche e all'analisi di mercato, hanno uno scopo puramente informativo ed educativo. Non costituiscono una consulenza professionale in materia di acquisti, né una consulenza finanziaria o legale.
Pur avendo compiuto ogni sforzo per garantire l'accuratezza e la tempestività delle informazioni, non siamo responsabili di eventuali errori, omissioni o informazioni non aggiornate. Le condizioni di mercato, i dettagli aziendali e gli standard tecnici sono soggetti a modifiche.
Gli acquirenti B2B devono condurre una due diligence indipendente e approfondita. prima di prendere qualsiasi decisione di acquisto. Per questo è necessario contattare direttamente i fornitori, verificare le certificazioni, richiedere campioni e chiedere una consulenza professionale. Il rischio di affidarsi alle informazioni contenute in questa guida è esclusivamente a carico del lettore.