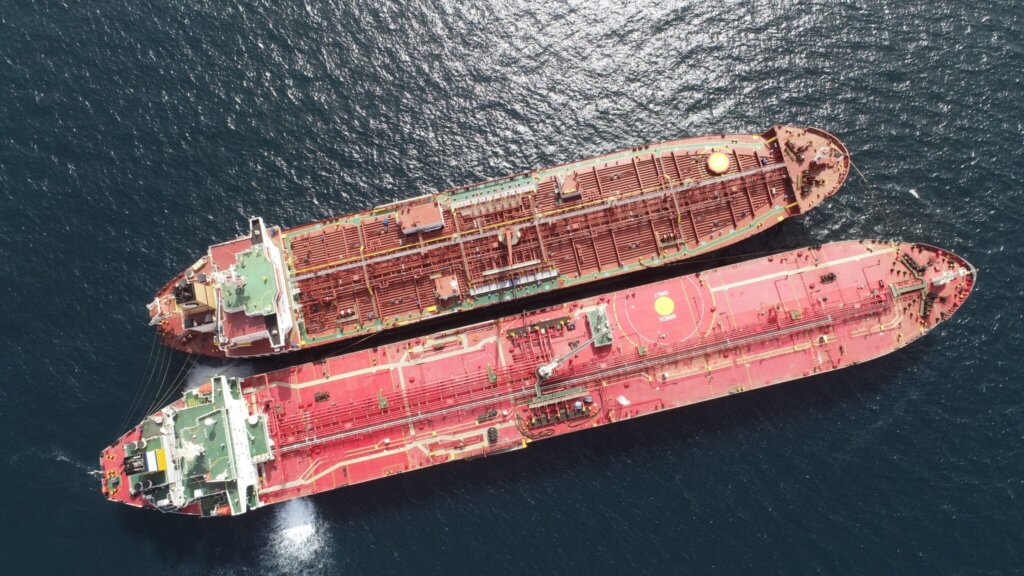
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sts in shipping
In the complex landscape of maritime logistics, navigating the global market for ship-to-ship (STS) operations presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers. Ensuring the safe and efficient transfer of bulk cargo, such as crude oil and liquefied gas, is critical, especially for businesses operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As vessel sizes increase and port limitations become more stringent, the demand for STS services continues to rise. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource to help you understand the nuances of STS operations, covering essential aspects such as types of STS transfers, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By providing actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory compliance. Whether you’re based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or elsewhere, understanding the intricacies of STS can significantly impact your supply chain efficiency and cost-effectiveness. From navigating regulatory frameworks to establishing robust safety protocols, each section is designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to streamline your shipping operations and mitigate risks associated with STS transfers. Embrace the opportunities that come with effective STS management and position your business for success in the global marketplace.
Indice dei contenuti
- Top 4 Sts In Shipping Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sts in shipping
- Understanding sts in shipping Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of sts in shipping
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sts in shipping’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for sts in shipping
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sts in shipping
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sts in shipping’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sts in shipping Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sts in shipping With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sts in shipping
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sts in shipping Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sts in shipping
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sts in shipping
- Disclaimer importante e condizioni d'uso
Understanding sts in shipping Types and Variations
| Nome del tipo | Caratteristiche distintive principali | Applicazioni primarie B2B | Brevi pro e contro per gli acquirenti |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional STS | Transfers between two tankers in open water; often static | Oil and gas transportation | Pro: Cost-effective, time-saving. Contro: Weather-dependent, requires skilled crew. |
| Bunkering STS | Refueling operations at sea using a bunker barge | Marine fuel supply for vessels | Pro: Reduces port delays, efficient. Contro: Risk of spills, requires stringent safety measures. |
| Emergency STS | Conducted during crises, such as vessel compromise | Rescue operations, pollution prevention | Pro: Rapid response, minimizes environmental impact. Contro: High risk, requires specialized equipment. |
| Lightering STS | Offloading cargo to smaller vessels to meet port restrictions | Bulk cargo transport, especially in shallow ports | Pro: Enables access to ports, cost-efficient. Contro: Increased logistical complexity, potential delays. |
| STS for Liquid Gases | Specialized for transferring liquefied gases | Chemical transport, LNG shipping | Pro: Safe handling of hazardous materials. Contro: High regulatory compliance, specialized training required. |
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional STS Operations?
Conventional STS operations involve the transfer of cargo between two tankers moored side-by-side in open waters. This method is primarily used for transporting crude oil and liquefied gas. The process can be conducted while the vessels are static or moving slowly, making it versatile for different maritime conditions. B2B buyers should consider the operational costs, the need for skilled crew, and the potential impact of adverse weather conditions when opting for this type of STS.
How Does Bunkering STS Improve Marine Fuel Supply Efficiency?
Bunkering STS refers to the process of transferring fuel from a bunker vessel to a larger ship at sea. This operation eliminates the need for ships to dock at ports for refueling, thereby reducing time and costs associated with port delays. B2B buyers in the shipping industry should weigh the efficiency gains against the risks of spills and the need for stringent safety protocols. The choice of reliable bunker suppliers is also crucial to ensure compliance with international regulations.

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
In What Situations Is Emergency STS Most Beneficial?
Emergency STS operations are critical during crises, such as when a vessel is compromised or leaking cargo. This type of STS allows for rapid cargo transfer to prevent environmental disasters and minimize losses. For B2B buyers, the speed and effectiveness of emergency STS can be a decisive factor in crisis management. However, the high-risk nature of these operations necessitates specialized equipment and trained personnel, which can increase costs.
Why Is Lightering STS Important for Accessing Shallow Ports?
Lightering STS is essential for transferring cargo from larger vessels to smaller ones, particularly in ports with draught restrictions. This method allows larger tankers to offload part of their cargo in deeper waters, enabling smaller vessels to access the port. B2B buyers should consider the logistical complexities and potential delays associated with lightering operations, as well as the cost efficiencies gained from improved port access.
What Makes STS for Liquid Gases Different from Other Types?
STS operations for liquid gases, such as LNG and chemicals, are specialized due to the hazardous nature of the materials involved. This type of STS requires rigorous safety protocols and equipment designed to handle high-pressure and low-temperature conditions. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with expertise in handling these materials and ensure compliance with international safety regulations, as the consequences of spills or accidents can be severe both environmentally and financially.
Key Industrial Applications of sts in shipping
| Industria/Settore | Specific Application of sts in shipping | Valore/Beneficio per l'azienda | Considerazioni chiave sull'approvvigionamento per questa applicazione |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petrolio e gas | Transfer of crude oil between large tankers at sea | Reduces port congestion and associated costs | Compliance with international safety regulations, equipment reliability, and experienced crew availability. |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Lightering of hazardous chemicals to smaller vessels | Enhances safety by minimizing onshore risks | Need for specialized equipment and adherence to safety protocols. Verify supplier certifications. |
| Maritime Logistics | Bunkering operations for fuel supply at sea | Saves time and reduces operational costs | Ensure availability of high-quality fuel and reliable delivery schedules. |
| Energia rinnovabile | Transfer of biofuels from production vessels | Supports sustainable energy initiatives | Focus on suppliers with eco-friendly practices and compliance with environmental regulations. |
| Bulk Cargo Shipping | STS operations for transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG) | Expands shipping capabilities and market access | Evaluate vessel compatibility and adherence to international LNG transfer standards. |
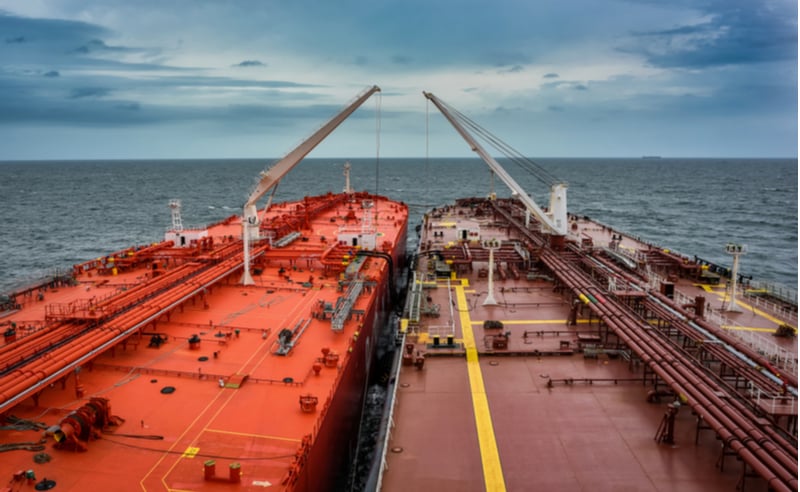
How is STS in Shipping Used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, STS operations are primarily used for the transfer of crude oil between large tankers, often in open sea locations to avoid congestion at ports. This method allows for the efficient handling of large volumes of cargo without the need for costly port berthing. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations is crucial. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from experienced operators who can provide robust safety records and reliable equipment.
What Role Does STS Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
In chemical manufacturing, STS is utilized for lightering hazardous chemicals to smaller vessels, thereby minimizing risks associated with onshore storage and transfer. This application is vital in regions where infrastructure may be limited. Buyers must ensure that suppliers have specialized equipment designed for hazardous materials and adhere to safety protocols to mitigate risks. Certification and compliance with local and international regulations should be key considerations in sourcing decisions.
How Does STS Enhance Maritime Logistics?
Maritime logistics benefit from STS through efficient bunkering operations, allowing vessels to refuel at sea rather than at port. This approach significantly reduces downtime and operational costs, especially for companies operating in busy shipping lanes. For businesses in Africa and South America, it is essential to source high-quality fuel and establish reliable delivery schedules to ensure seamless operations. Buyers should also assess the supplier’s ability to meet international fuel standards.
What is the Importance of STS in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, STS is increasingly used for transferring biofuels from production vessels to distribution points. This application supports sustainable energy initiatives by facilitating the transport of eco-friendly fuels without the environmental risks associated with traditional methods. Buyers should focus on suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations, which is particularly important in Europe where green initiatives are prioritized.

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
How is STS Used for Bulk Cargo Shipping?
For bulk cargo shipping, STS operations are essential for transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG) efficiently. This method allows for the transfer of LNG from large carriers to smaller vessels that can access ports with draught restrictions. International buyers must evaluate vessel compatibility and ensure adherence to international LNG transfer standards to mitigate risks. Sourcing from experienced operators with proven track records in LNG handling is critical for maintaining safety and efficiency in operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sts in shipping’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance in STS Operations
Il problema: B2B buyers often encounter significant challenges related to compliance with international regulations during STS operations. The shipping industry is heavily regulated, with guidelines set by bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and MARPOL. Buyers may struggle to ensure that their operations meet these standards, risking fines, operational delays, or even legal repercussions. Additionally, the complexity of different regulations across regions can lead to confusion, particularly for companies operating in multiple jurisdictions.
La soluzione: To effectively navigate regulatory compliance, buyers should invest in comprehensive training programs for their crews, focusing on the latest international regulations and best practices in STS operations. It is also crucial to develop a robust STS Operation Plan that outlines procedures, safety protocols, and compliance checklists tailored to the specific regions in which they operate. Collaborating with experienced maritime consultants or legal experts can provide valuable insights into region-specific requirements, helping companies stay ahead of compliance issues. Regular audits and reviews of operational practices against regulatory standards will further ensure adherence and mitigate risks.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Safety During STS Transfers
Il problema: Safety concerns during STS operations are a major pain point for B2B buyers. The inherent risks of equipment malfunctions, adverse weather conditions, and the potential for cargo spills can create anxiety about the safety of the crew and the environment. Buyers often find themselves grappling with how to implement the necessary safety measures effectively while also managing the logistical aspects of STS operations.
La soluzione: To enhance safety during STS transfers, buyers should prioritize the implementation of a comprehensive risk management strategy. This includes conducting thorough pre-transfer safety checks, utilizing advanced technology such as automated monitoring systems for equipment status, and ensuring that all personnel are well-trained in emergency response procedures. Establishing clear communication protocols between the mother and daughter vessels can prevent misunderstandings that might lead to accidents. Additionally, investing in high-quality equipment and safety gear, such as durable marine hoses and reliable fenders, will minimize the risks associated with STS operations.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Efficiency in STS Operations
Il problema: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of managing costs associated with STS operations. While STS can save time and money compared to traditional port berthing, the operational costs can still escalate due to delays, equipment failures, or inefficient planning. Buyers may struggle to find the balance between cost savings and maintaining high operational standards, leading to budget overruns that impact their bottom line.
La soluzione: To achieve cost efficiency, buyers should adopt a proactive approach to planning and logistics. This involves meticulous scheduling of STS operations to avoid peak times when costs are higher. Implementing a detailed STS operation plan that includes contingency measures can help manage unexpected delays or complications. Moreover, leveraging data analytics to assess past STS operations can reveal patterns and areas for improvement, allowing buyers to make informed decisions about resource allocation. Building strong relationships with reliable service providers can also lead to negotiated rates and reduced operational costs, making STS operations more financially viable.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sts in shipping
What Are the Key Materials Used in STS Operations for Shipping?
In the realm of Ship to Ship (STS) operations, selecting the right materials is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in STS operations, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Stainless Steels Perform in STS Applications?
Proprietà chiave: Stainless steel is known for its high corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine environments. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures, which is essential during cargo transfer operations.
Pro e contro: The durability of stainless steel is one of its strongest points, as it can last for many years with minimal maintenance. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, which may impact budget considerations for buyers. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impatto sull'applicazione: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including crude oil and liquefied gases, making it a versatile choice for STS operations.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. The higher initial investment may be justified by the long-term savings on maintenance and replacements.
What Role Does Polypropylene Play in STS Operations?
Proprietà chiave: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer with excellent chemical resistance and a low density, which makes it lightweight and easy to handle.
Pro e contro: Its cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage, especially for large-scale operations. However, polypropylene has a lower temperature tolerance compared to metals, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications.
Impatto sull'applicazione: Polypropylene is suitable for transferring non-corrosive liquids, making it ideal for specific cargo types. However, its compatibility with certain chemicals must be assessed to avoid degradation.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards to ensure the material meets operational requirements. The lower cost can be appealing, but long-term performance should be evaluated against potential risks.
Why Is Carbon Steel Commonly Used in STS Operations?
Proprietà chiave: Carbon steel is known for its strength and toughness, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. It has a good balance of ductility and hardness.
Pro e contro: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its low cost, making it accessible for many operations. However, it is prone to corrosion, especially in marine environments, which can lead to higher maintenance costs over time.
Impatto sull'applicazione: Carbon steel is often used in structural components of STS operations, but its susceptibility to rust means that protective coatings or regular maintenance are essential.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Buyers should ensure that carbon steel components are treated to withstand harsh marine conditions. Compliance with international standards is also crucial to avoid potential liabilities.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance STS Operations?
Proprietà chiave: Composite materials, typically made from a combination of fibers and resins, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to corrosion.
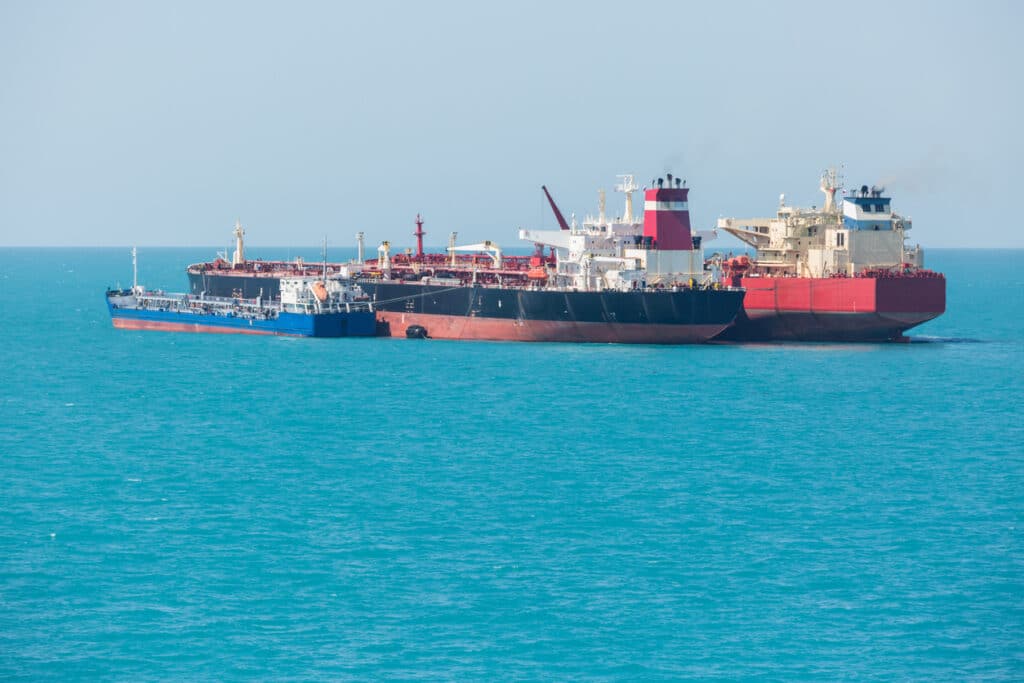

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
Pro e contro: Their lightweight nature can improve fuel efficiency during operations. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers.
Impatto sull'applicazione: Composites are particularly useful in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in hoses and lightweight structures.
Considerazioni per gli acquirenti internazionali: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet international safety and performance standards. The initial investment may be higher, but the long-term benefits in performance and maintenance can be significant.

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
Summary Table of Material Selection for STS in Shipping
| Materiale | Typical Use Case for STS in Shipping | Vantaggio chiave | Svantaggi/limitazioni principali | Costo relativo (basso/medio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio inox | Hoses and structural components | High corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | Alto |
| Polipropilene | Non-corrosive liquid transfer | Cost-effective | Limited temperature tolerance | Basso |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components | Low cost | Prone to corrosion | Basso |
| Composite Materials | Lightweight hoses and structures | High strength-to-weight ratio | Complex manufacturing process | Medio |
This analysis provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions on material selection for STS operations. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
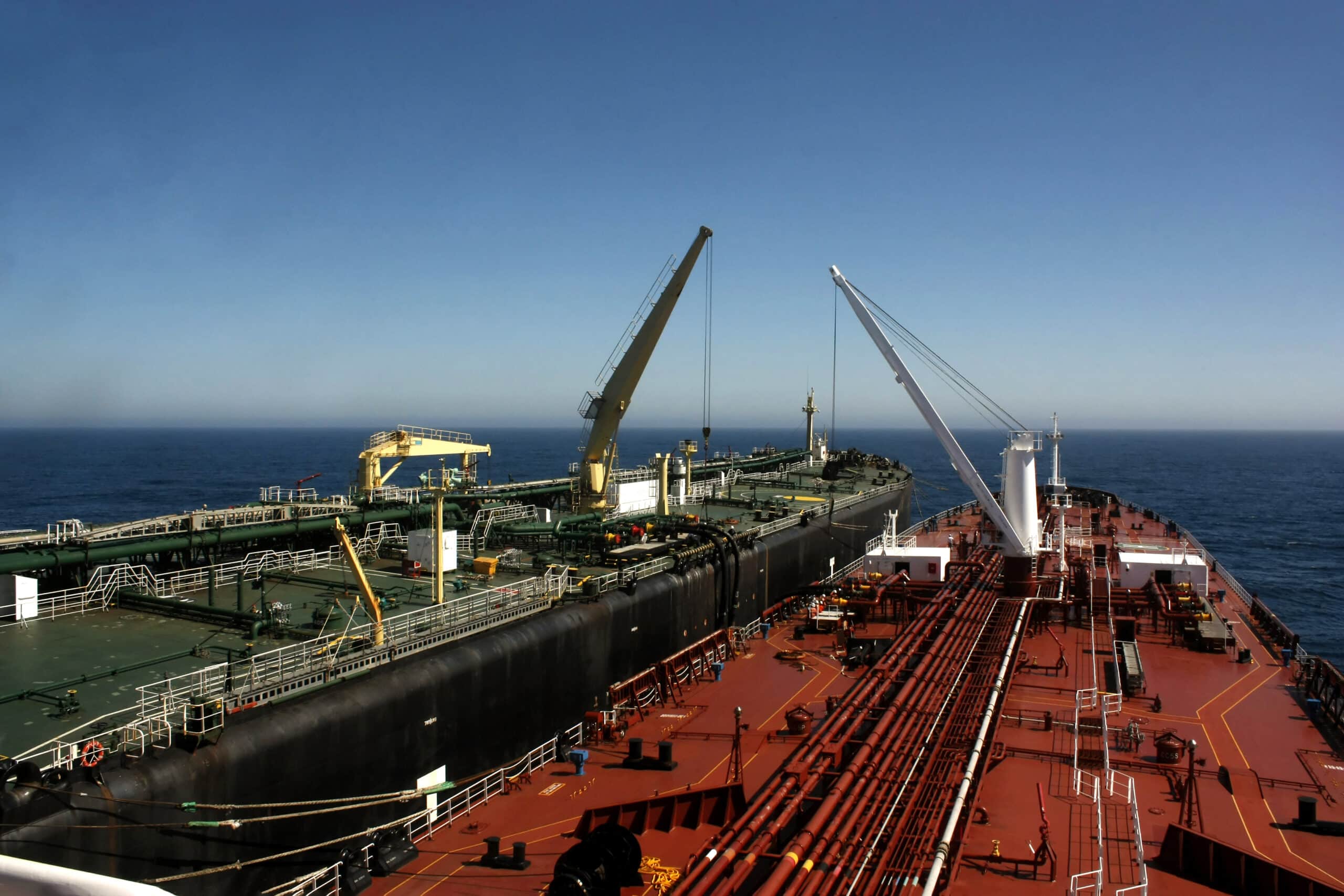
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sts in shipping
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for STS Equipment?
When it comes to the production of equipment used in Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer operations, several key stages are involved. Understanding these stages helps international B2B buyers make informed decisions about the suppliers they choose.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Processed for STS Equipment?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality raw materials such as steel, rubber, and specialized polymers are sourced, as they are critical for the performance and durability of hoses, fenders, and other equipment. The selection of materials must comply with international standards to ensure reliability under varying marine conditions.
Before manufacturing begins, materials undergo inspection to verify their quality and specifications. This may include chemical analysis, tensile strength testing, and dimensional verification to ensure they meet industry requirements.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in STS Equipment Manufacturing?
Forming is the next crucial stage where raw materials are shaped into usable components. Various techniques are employed, including:
- Stampaggio: For fenders and hoses, rubber and polymers are often molded into specific shapes to provide the necessary buoyancy and flexibility.
- Welding: Steel components are welded together to create robust structures for support frames and other equipment. The welding processes used must adhere to stringent safety and quality standards to ensure structural integrity.
- Machining: Precision machining is utilized to ensure that all parts fit together correctly, especially for connections and joints that must withstand high pressure during cargo transfer.
How Is Assembly Conducted for STS Equipment?
Once individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage involves:
- Component Integration: Various parts, such as hoses, fittings, and valves, are assembled to create a complete system. This requires skilled labor to ensure that all connections are secure and leak-proof.
- System Testing: Before finalizing the assembly, each system undergoes a series of tests to verify its functionality. This may include pressure testing, flow testing, and operational simulations to ensure the equipment can perform under real-world conditions.
What Finishing Processes Are Necessary for STS Equipment?
The final stage is finishing, where the equipment is prepared for delivery. This includes:
- Trattamento della superficie: To enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, components may undergo surface treatments such as galvanizing or painting.
- Ispezione della qualità: Each unit is thoroughly inspected for defects, ensuring that it meets all operational and safety standards before it is shipped to the customer.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for STS Equipment?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of manufacturing STS equipment, especially given the high stakes involved in maritime operations. To ensure the reliability and safety of products, manufacturers implement a multi-tiered QC process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for STS Equipment?
B2B buyers should be aware of the international standards that govern quality assurance in manufacturing. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management system standard that ensures manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards for oil and gas equipment, are essential for ensuring compliance with safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process and typically include:
- Controllo qualità in entrata (CQI): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before being processed.
- Controllo qualità in corso d'opera (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, operators conduct inspections to verify that processes are followed correctly, and products meet design specifications.
- Controllo qualità finale (CQC): Before shipping, each piece of equipment undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all operational criteria and is free of defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for STS Equipment?
Several testing methods are employed to guarantee the performance and safety of STS equipment:
- Test idrostatici: This method is used to test hoses and connections under pressure to identify any leaks or weaknesses.
- Ultrasonic Testing: Employed for weld integrity, this non-destructive testing method detects internal flaws in materials.
- Ispezione visiva: A thorough visual check ensures that all components are assembled correctly and meet aesthetic and functional requirements.
Come possono gli acquirenti B2B verificare il controllo qualità dei fornitori?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential. Here are actionable steps to ensure that the chosen supplier maintains high standards:
What Role Do Audits Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting regular audits is one of the most effective methods for ensuring compliance with quality standards. Buyers should request audits of the supplier’s manufacturing processes, which can be performed by third-party organizations or by the buyers themselves. These audits assess adherence to ISO and other relevant standards.

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
How Important Are Quality Reports and Certifications?
Buyers should request quality reports and certifications from suppliers. These documents provide insight into the supplier’s quality management systems and demonstrate compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or API can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
Why Is Third-Party Inspection Valuable for International Buyers?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance processes. This is particularly valuable for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as it helps mitigate risks associated with international procurement.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances regarding quality control and certification. Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements, and understanding these can be critical to ensuring compliance and operational success.
- Cultural Differences: Buyers must be aware of cultural differences that may affect communication and quality expectations. Establishing clear guidelines and expectations can help bridge these gaps.
- Conformità normativa: Familiarizing oneself with the regulatory landscape in the supplier’s country can prevent unexpected compliance issues during importation.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for STS equipment is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, finishing, and stringent QC protocols, buyers can ensure that they procure reliable and safe equipment for their operations.
Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sts in shipping’
Introduzione
In the dynamic world of maritime logistics, procuring Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer services requires careful planning and execution. This guide offers a step-by-step checklist tailored for B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can ensure a seamless and compliant STS operation that meets your business needs.
Fase 1: Identify Your Cargo Type
Understanding the specific type of cargo you intend to transfer is crucial. Different cargoes, such as crude oil, liquefied gas, or chemicals, have unique handling requirements and regulations. Ensure that your chosen STS service provider has the necessary expertise and equipment to handle your specific cargo type safely.
Fase 2: Evaluate Regulatory Compliance
Before initiating an STS operation, verify that your supplier adheres to international maritime regulations, including those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL). Compliance not only mitigates risks but also safeguards your reputation and avoids potential legal issues.
Fase 3: Assess Technical Capabilities
Examine the technical capabilities of potential STS service providers. This includes their equipment, such as fenders, hoses, and pumping systems, which should meet industry standards for safety and efficiency. Additionally, inquire about their operational procedures and contingency plans for adverse weather or equipment failure.
Passo 4: Review Safety Protocols
Safety is paramount in STS operations. Ensure that the provider has robust safety protocols in place, including emergency response plans and crew training certifications. Request documentation that outlines their safety record and any incident history to gauge their reliability and commitment to safe operations.
Passo 5: Check for Experienced Personnel
The success of an STS transfer often hinges on the expertise of the personnel involved. Verify that the operation will be overseen by a qualified person in overall advisory control (POAC), such as a ship captain or a designated STS superintendent. Their experience will help navigate potential challenges during the transfer.
Passo 6: Confirm Insurance and Liability Coverage
Ensure that your STS service provider carries adequate insurance coverage, including liability for environmental damage and cargo loss. This is crucial for protecting your investment and mitigating financial risks. Request copies of their insurance certificates and understand the terms of their coverage.
Passo 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital for the success of STS operations. Establish clear lines of communication between your team, the STS provider, and any relevant port authorities. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, which will facilitate smoother operations and quicker resolution of any issues that may arise.
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of procuring STS services, ensuring that their operations are efficient, compliant, and safe.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sts in shipping Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in STS Shipping Sourcing?
When evaluating the cost structure of Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations in shipping, several critical components come into play. The primary cost factors include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
I materiali: The materials involved in STS operations predominantly include specialized hoses, fenders, and safety equipment. The quality and specifications of these materials can significantly affect pricing. Higher-grade materials may lead to increased upfront costs but can reduce long-term liabilities associated with safety failures or equipment malfunctions.
-
Lavoro: Labor costs encompass the wages for skilled crew members who conduct the STS transfers, including the operation of equipment and safety checks. Given the specialized nature of this work, labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and the expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Overhead costs related to the maintenance of equipment and facilities also contribute to the overall pricing. Tooling costs are incurred if specialized tools are needed for specific STS operations, which can be a considerable expense for companies that engage in these operations infrequently.
-
Controllo qualità (CQ): Ensuring compliance with international safety and environmental standards involves QC measures that can add to the operational costs. This includes adherence to guidelines set by organizations like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and MARPOL.
-
Logistica: Logistics costs cover the transportation of equipment and personnel to and from the STS operation site. This can include vessel positioning and the need for support vessels, which can be particularly costly in remote locations.
-
Margine: The profit margin applied by service providers can vary based on market demand, competition, and perceived value. Understanding this margin is essential for buyers aiming to negotiate favorable terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact STS Operations?
Several factors can influence the pricing of STS operations, making it essential for international B2B buyers to understand these elements:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) and overall volume of operations can significantly impact pricing. Larger volumes often lead to discounts and more favorable terms, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their STS needs.
-
Specifiche e personalizzazione: Tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customized solutions against their budget constraints.
-
Materiali e certificazioni di qualità: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications can affect both the cost and the reliability of STS operations. Buyers should consider the long-term implications of lower-quality materials versus the upfront savings.
-
Fattori di fornitura: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can also play a role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide assurances of quality and compliance that can mitigate risks.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping transactions. The choice of Incoterms can influence logistics costs and the overall price structure.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better STS Pricing?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, negotiating STS pricing can be intricate. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Buyers should engage in discussions about payment terms, delivery schedules, and potential volume discounts. Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to more favorable conditions.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: When assessing STS operations, consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial price. This includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Familiarize yourself with the local market conditions and economic factors that may influence pricing. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help them identify when a price is fair or inflated.
Conclusion and Disclaimer on Pricing
The costs associated with STS operations can vary widely based on numerous factors, and it is vital for buyers to conduct thorough research. The information provided in this analysis is indicative and should be used as a guide rather than a definitive pricing framework. Each STS operation will present unique circumstances that can significantly influence costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sts in shipping With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Ship-to-Ship (STS) Transfers in Shipping
When considering the logistics of maritime shipping, particularly for bulk liquids like crude oil and liquefied gas, Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfers represent a highly specialized solution. However, various alternatives can provide different advantages depending on operational requirements and contexts. This section outlines several viable alternatives to STS operations, focusing on their comparative performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
Tabella di confronto
| Aspetto di confronto | STS In Shipping | Floating Storage Units (FSUs) | Barge Transfers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prestazioni | High efficiency for bulk transfers; operational flexibility | Moderate; limited by storage capacity | Variable; dependent on barge capacity and distance |
| Costo | Moderate to high; influenced by ship size and operational complexity | High initial investment; lower operational costs over time | Generally low; cost-effective for short distances |
| Facilità di implementazione | Requires specialized equipment and training | Complex setup; requires appropriate permits | Relatively easy; fewer regulatory hurdles |
| Manutenzione | High; requires regular inspections and adherence to safety protocols | Moderate; ongoing maintenance for storage facilities | Low; routine checks suffice |
| Il miglior caso d'uso | Large vessels needing offshore transfer | Long-term storage near production sites | Short-distance transfer to ports or refineries |
Understanding Floating Storage Units (FSUs)
Floating Storage Units (FSUs) serve as a viable alternative to STS operations, providing a solution for the long-term storage of liquid cargo at sea. FSUs can accommodate large volumes and reduce the need for multiple transfers. However, the initial investment in FSUs can be significant, and they typically require a more complex setup and regulatory compliance. Once operational, though, FSUs can lead to lower long-term operational costs, especially for companies needing to store large quantities of oil or gas offshore.
Evaluating Barge Transfers
Barge transfers are another alternative that facilitates the movement of bulk liquids, especially over shorter distances. This method is generally more cost-effective and easier to implement than STS operations, with fewer regulatory hurdles. However, barge transfers may lack the efficiency of STS for large-scale operations, particularly when transferring large quantities at once. Additionally, barges are limited by their capacity and may not be suitable for all types of cargo, particularly those requiring immediate transfer or those that are highly volatile.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
For international B2B buyers navigating the complexities of maritime logistics, choosing the right solution requires careful consideration of operational needs, budget constraints, and the specifics of the cargo being transferred. STS operations offer high efficiency for bulk transfers but come with higher costs and maintenance demands. In contrast, FSUs and barge transfers present alternative options that may be more suitable for specific scenarios, such as long-term storage or short-distance transport. Ultimately, buyers should assess their unique circumstances and weigh the pros and cons of each method to determine the most effective solution for their shipping needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sts in shipping
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to STS Operations in Shipping?
In the context of Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient cargo transfers. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Material Grade of Hoses
The hoses used in STS operations must meet stringent material grade standards. Typically constructed from high-grade rubber or composite materials, these hoses are designed to withstand high pressure and corrosive substances like crude oil and liquefied gas. The right material grade ensures durability and safety, mitigating the risk of leaks or ruptures during transfer. -
Draught Capacity
Draught capacity refers to the maximum depth of water a vessel requires to float. This is particularly important in STS operations, as vessels often need to transfer cargo to comply with port draught restrictions. Understanding the draught capacity helps buyers plan STS operations effectively, ensuring that vessels can safely navigate to their intended destinations without grounding. -
Transfer Rate
The transfer rate indicates the volume of cargo that can be moved from one vessel to another over a specific period. This metric is vital for B2B buyers as it impacts operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. A higher transfer rate can reduce time at sea and lower associated costs, making it a key consideration when planning STS operations. -
Safety Protocols and Compliance Standards
Compliance with international safety protocols, such as those outlined by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), is non-negotiable. Buyers should ensure that all equipment and procedures meet these standards to minimize risks associated with STS operations, including spills and collisions. Understanding these protocols helps in selecting service providers who prioritize safety and regulatory compliance. -
Emergency Response Capability
The ability of vessels and their crews to respond to emergencies during STS operations is a critical property. This includes having the necessary equipment and training for spill containment and equipment failure scenarios. Buyers should assess the emergency response plans of potential partners to ensure that they are prepared for any unforeseen incidents.
What Are Common Trade Terms in STS Shipping?
Navigating the complexities of STS operations also requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of STS operations, buyers often seek OEMs for specialized equipment like hoses and pumps to ensure reliability and compatibility with their vessels. -
MOQ (quantità minima d'ordine)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers looking to procure equipment or services for STS operations, as it can influence purchasing decisions and inventory management. -
RFQ (Richiesta di offerta)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to invite suppliers to submit price quotes for specific goods or services. In STS shipping, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to gather competitive pricing and evaluate potential partners based on cost and service offerings. -
Incoterms (Termini commerciali internazionali)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers during transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and the obligations involved in STS operations. -
Lightering
Lightering is another term used interchangeably with STS operations, referring specifically to the transfer of cargo from larger vessels to smaller ones. This term is important for buyers to understand as it highlights the operational strategy employed to facilitate cargo movement efficiently.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in shipping can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety in STS operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sts in shipping Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the STS Shipping Market?
The Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer market is increasingly shaped by global economic shifts, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. One significant driver is the growing demand for energy resources, particularly crude oil and liquefied natural gas (LNG), in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. These regions are experiencing rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to increased energy consumption. As a result, international B2B buyers are seeking efficient and cost-effective shipping solutions, making STS operations a strategic choice to avoid port congestion and high berthing fees.
Moreover, advancements in maritime technology are enhancing the safety and efficiency of STS operations. The implementation of automated systems for cargo transfer and real-time monitoring solutions is gaining traction. These innovations not only streamline operations but also improve compliance with international safety regulations, attracting more international buyers to engage in STS transfers.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting STS Operations?
As the global shipping industry grapples with environmental challenges, sustainability has become a critical focus for B2B buyers. The impact of STS operations on marine ecosystems cannot be overlooked, as spills and equipment failures pose significant risks. Therefore, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to stringent environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.

Illustrative image related to sts in shipping
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with businesses seeking partners who share their values regarding environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which outlines effective environmental management systems, are becoming essential for companies looking to establish credibility in the marketplace. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate their suppliers based on their sustainability practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and technologies in STS operations. This not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of STS Operations in Shipping?
The evolution of STS operations dates back to the early 20th century when lightering was first introduced as a solution for transferring cargo from large tankers to smaller vessels, particularly in ports with draught restrictions. Initially employed in the oil industry, the practice has expanded to accommodate other bulk commodities such as LNG and chemicals.
Over the years, regulatory frameworks have evolved, with organizations like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) establishing guidelines to enhance safety and environmental protection during STS operations. Today, STS transfers are integral to the shipping industry, providing an efficient means of transporting large volumes of cargo across challenging maritime environments. Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it underscores the importance of adhering to regulations and best practices in contemporary STS operations.
Conclusione
Navigating the complexities of the STS shipping market requires a keen understanding of the dynamics at play, particularly for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By recognizing market drivers, embracing sustainability, and appreciating the historical evolution of STS operations, businesses can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sts in shipping
-
How do I ensure the safety of STS operations?
To ensure the safety of Ship to Ship (STS) operations, it is crucial to adhere to international safety guidelines provided by organizations like the International Maritime Organization (IMO). This includes having a well-documented STS Operation Plan that outlines procedures, responsibilities, and emergency protocols. Additionally, appointing a qualified Person in Overall Advisory Control (POAC) is essential to oversee the operation. Regular equipment checks, crew training, and communication drills can further mitigate risks associated with equipment malfunctions and environmental hazards during the transfer process. -
What are the typical costs associated with STS operations?
The costs associated with STS operations can vary based on several factors, including vessel size, cargo type, and location of the transfer. Key expenses include vessel chartering, port fees, and insurance, along with potential costs for specialized equipment and crew. It is advisable to obtain detailed quotations from service providers and consider additional costs such as demurrage if operations exceed planned timelines. By conducting thorough budgeting and planning, buyers can better manage these costs and avoid unexpected expenses during STS operations. -
What are the primary reasons for conducting STS transfers?
STS transfers are typically conducted for several key reasons, including draught restrictions that prevent large vessels from entering ports, cost efficiency by reducing time spent at port, and emergency responses to compromised vessels. These operations enable the transfer of bulk cargoes like crude oil and liquefied gas in a more flexible manner, allowing larger vessels to offload cargo to smaller vessels that can dock at port. Understanding the motivations behind STS operations can help buyers make informed decisions regarding their shipping strategies. -
How do I vet suppliers for STS services?
When vetting suppliers for STS services, it’s essential to assess their experience and reputation within the industry. Check for certifications that comply with international standards, such as ISO and MARPOL compliance. Request references from previous clients and evaluate their safety records and operational efficiency. It is also beneficial to conduct site visits and engage in discussions about their operational procedures, equipment quality, and crew qualifications to ensure they align with your safety and operational standards. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for STS services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for STS services can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the cargo being transferred. Many service providers may set MOQs based on vessel capacities or operational efficiency considerations. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to determine their flexibility regarding MOQs. Understanding your supply chain requirements will help you negotiate better terms and ensure that you can meet your operational needs without incurring unnecessary costs. -
What payment terms are common for STS operations?
Payment terms for STS operations can differ among suppliers but typically involve upfront deposits, milestone payments, or payment upon completion of the service. It’s crucial to negotiate clear terms before finalizing any agreements. Consider factors such as currency, payment methods (like wire transfers or letters of credit), and the timeline for payments. Establishing transparent payment terms can mitigate potential disputes and ensure a smooth transaction process, which is especially important in international trade scenarios. -
How can I customize STS services to fit my shipping needs?
Customizing STS services involves discussing your specific requirements with the supplier, including the type of cargo, transfer volume, and preferred scheduling. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions that can include specialized equipment or unique operational procedures based on your cargo’s characteristics. Engaging in open communication about your expectations and challenges will enable suppliers to propose effective strategies that align with your logistics needs, enhancing the overall efficiency of your shipping operations. -
What are the logistics considerations for STS operations?
Logistics considerations for STS operations include planning the transfer location, scheduling the operation to minimize delays, and coordinating with all parties involved, such as port authorities and vessel operators. It is important to assess weather conditions and sea state to ensure safe operations. Additionally, understanding local regulations and ensuring compliance with customs and environmental guidelines are crucial for successful operations. Effective logistics planning will help streamline the STS process and enhance the reliability of your shipping schedule.
Top 4 Sts In Shipping Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Breakaway Couplings – STS Transfer Solutions
Dominio: breakawaycouplings.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduzione: Ship to Ship (STS) transfer, also known as lightering, involves two storage tankers mooring side-by-side to transfer cargo, typically crude oil and liquefied gas, in open sea or at the outer port limit. Key procedures include lowering fenders, berthing ships, connecting hoses, and transferring cargo. Regulatory guidelines from the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and MARPOL ensure safety …
2. Marine Insight – Ship-to-Ship Transfer Essentials
Dominio: marineinsight.com
Registrato: 2010 (15 anni)
Introduzione: Ship-to-Ship Transfer (STS) refers to the transfer of cargo, such as oil or gas, between two merchant tanker vessels positioned alongside each other. Key requirements for conducting STS operations include: adequate training of staff, proper STS equipment in good condition, pre-planning of operations, attention to vessel differences, permission from port authorities, knowledge of cargo properties, …
3. Britannia Pandi – Ship to Ship Transfers
Dominio: britanniapandi.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduzione: This company, Britannia Pandi – Ship to Ship Transfers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Marine Pilot – Ship to Ship Transfer Services
Dominio: marinepilot-eg.com
Registrazione: 2020 (5 anni)
Introduzione: Marine Pilot provides Ship to Ship (STS) transfer services for the oil and shipping industries, facilitating the transfer of various cargoes including crude oil, white and black products, LPG, and bulk cargoes. The operations can occur between vessels of any size, either while stationary or underway, requiring proper coordination, equipment, and approval. Key requirements for STS operations includ…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sts in shipping
In the evolving landscape of international shipping, strategic sourcing of Ship to Ship (STS) operations stands as a pivotal element for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the intricacies of STS operations not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces costs associated with traditional port berthing. By leveraging STS for bulk cargo transfers, companies can circumvent draught restrictions and streamline their supply chain processes.
The importance of adhering to regulatory guidelines and ensuring safety protocols cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with experienced operators who can navigate the complexities of STS transfers, ensuring compliance while minimizing risks associated with equipment failure or environmental hazards.
As the global market continues to grow, the demand for efficient and safe cargo transfer solutions will only increase. International B2B buyers are encouraged to invest in strategic sourcing for STS operations to gain a competitive edge. Embracing innovation and best practices in this area can lead to improved profitability and sustainability in shipping. Engage with industry experts and explore opportunities that align with your business goals to enhance your operational capabilities in the maritime sector.
Disclaimer importante e condizioni d'uso
⚠️ Disclaimer importante
Le informazioni fornite in questa guida, compresi i contenuti relativi ai produttori, alle specifiche tecniche e all'analisi di mercato, hanno uno scopo puramente informativo ed educativo. Non costituiscono una consulenza professionale in materia di acquisti, né una consulenza finanziaria o legale.
Pur avendo compiuto ogni sforzo per garantire l'accuratezza e la tempestività delle informazioni, non siamo responsabili di eventuali errori, omissioni o informazioni non aggiornate. Le condizioni di mercato, i dettagli aziendali e gli standard tecnici sono soggetti a modifiche.
Gli acquirenti B2B devono condurre una due diligence indipendente e approfondita. prima di prendere qualsiasi decisione di acquisto. Per questo è necessario contattare direttamente i fornitori, verificare le certificazioni, richiedere campioni e chiedere una consulenza professionale. Il rischio di affidarsi alle informazioni contenute in questa guida è esclusivamente a carico del lettore.