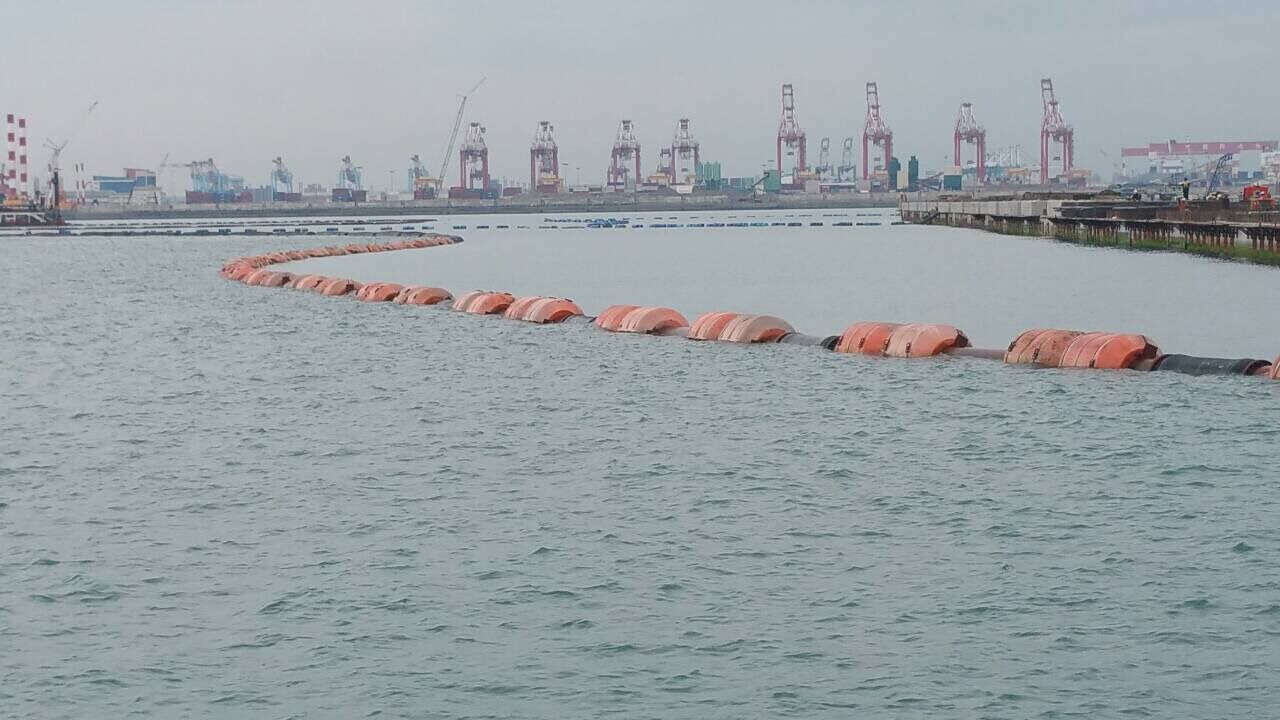
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for floating pipeline
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing floating pipelines presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These pipelines, essential for applications ranging from dredging to offshore oil and gas operations, must be durable, flexible, and capable of withstanding the dynamic conditions of marine environments. Buyers often grapple with selecting the right type of floating pipeline that meets their specific operational needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability.
This comprehensive guide aims to navigate the complexities of floating pipeline procurement by exploring various types—including HDPE and modular systems—alongside their diverse applications. We will delve into critical aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the latest innovations in floating pipeline technology. By providing actionable insights and expert advice, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you are involved in large-scale infrastructure projects or specialized marine operations, understanding the nuances of floating pipelines is crucial. This resource will empower you to identify suitable suppliers, assess product quality, and ultimately enhance the efficiency of your operations in a competitive global marketplace.
Inhoudsopgave
- Top 8 Floating Pipeline Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for floating pipeline
- Understanding floating pipeline Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of floating pipeline
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘floating pipeline’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for floating pipeline
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for floating pipeline
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘floating pipeline’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for floating pipeline Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing floating pipeline With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for floating pipeline
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the floating pipeline Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of floating pipeline
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for floating pipeline
- Belangrijke disclaimer en gebruiksvoorwaarden
Understanding floating pipeline Types and Variations
| Type Naam | Belangrijkste onderscheidende kenmerken | Primaire B2B-toepassingen | Korte voor- en nadelen voor kopers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Floating Pipeline | Comprised of steel pipes with buoyancy units for support. | Offshore oil & gas, dredging operations | Voordelen: Durable, strong; Minpunten: Heavier, potential corrosion issues. |
| HDPE Floating Pipeline | Made from high-density polyethylene, lightweight and flexible. | Water transport, dredging in challenging terrains | Voordelen: Corrosion-resistant, lightweight; Minpunten: Beperkte temperatuurbestendigheid. |
| Modular Floating Pipeline | Built in sections, allowing for easy assembly and transport. | Temporary water transport, construction projects | Voordelen: Versatile, easy to install; Minpunten: May require more maintenance. |
| Rubber Hose Floating Pipeline | Flexible hoses with floats, designed for high mobility. | Emergency water supply, irrigation systems | Voordelen: Highly flexible, easy to deploy; Minpunten: Less durable than rigid pipes. |
| Composite Floating Pipeline | Combines materials for enhanced performance and flexibility. | Marine applications, environmental projects | Voordelen: Lightweight, resistant to chemicals; Minpunten: Can be expensive. |
What are the Characteristics of Steel Floating Pipelines?
Steel floating pipelines are notable for their robustness, constructed from steel pipes supported by buoyancy units. This design is particularly advantageous in offshore oil and gas applications, where durability is paramount. Buyers should consider the weight and potential corrosion issues, as these pipelines may require additional protective coatings. Their strength makes them suitable for high-pressure applications, but the heavier weight can complicate transportation and installation.
How Do HDPE Floating Pipelines Stand Out?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) floating pipelines are lightweight and flexible, making them ideal for various applications, including water transport and dredging in difficult terrains. Their corrosion resistance is a significant advantage, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs. However, buyers should be aware of their limitations regarding temperature extremes, which could affect performance in certain environments. Overall, HDPE pipelines offer a balance of durability and adaptability for many B2B applications.
Why Choose Modular Floating Pipelines?
Modular floating pipelines are designed in sections, allowing for straightforward assembly and transport. This flexibility makes them suitable for temporary water transport and construction projects where quick deployment is necessary. Buyers should consider the ease of installation and versatility of these pipelines, although they may require more frequent maintenance than traditional options. Their modular nature allows for customization, making them appealing for businesses with specific needs.
What are the Advantages of Rubber Hose Floating Pipelines?
Rubber hose floating pipelines are characterized by their flexibility and mobility, making them ideal for emergency water supply and irrigation systems. Their design allows for easy deployment in varied environments. However, while they are highly adaptable, they may not be as durable as rigid pipelines, which could impact long-term use. Buyers should weigh the immediate benefits of flexibility against potential durability concerns when considering this option.
How Do Composite Floating Pipelines Enhance Performance?
Composite floating pipelines combine various materials to provide enhanced performance and flexibility, making them suitable for marine applications and environmental projects. Their lightweight nature and chemical resistance are significant benefits, but buyers should be prepared for potentially higher costs. Understanding the specific requirements of a project can help in evaluating whether the investment in composite pipelines is justified, especially when performance in challenging conditions is essential.
Key Industrial Applications of floating pipeline
| Industrie/sector | Specific Application of Floating Pipeline | Waarde/Voordeel voor het bedrijf | Belangrijkste overwegingen bij de inkoop voor deze toepassing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Offshore oil extraction and transport | Enhanced operational efficiency in challenging marine environments | Material durability, resistance to corrosion, and buoyancy features |
| Dredging | Sediment removal and transportation of materials | Improved project timelines and reduced environmental impact | Flexibility, modularity, and ease of installation |
| Water Management | Water transport in flood-prone or arid regions | Reliable water supply management during variable conditions | Adaptability to terrain, UV resistance, and cost-effectiveness |
| Environmental Protection | Wastewater discharge and treatment | Compliance with environmental regulations and reduced ecological footprint | Quality of materials, installation services, and maintenance support |
| Mijnbouw | Slurry transport from remote locations | Cost-effective transport of materials over long distances | Pipeline diameter, flow regime compatibility, and local regulations |
How is Floating Pipeline Used in Oil and Gas Applications?
In the oil and gas sector, floating pipelines are essential for offshore extraction and transportation of hydrocarbons. They provide a stable and flexible solution for moving oil from drilling platforms to processing facilities, especially in regions with rough seas. This application solves the challenge of maintaining pipeline integrity under dynamic marine conditions. Buyers should consider the material’s resistance to corrosion and the buoyancy features to ensure longevity and reliability in these harsh environments.
What Role Does Floating Pipeline Play in Dredging?
Floating pipelines are integral to dredging operations, facilitating the efficient removal and transport of sediment and materials. Their modular design allows for easy installation and adaptation to various project scales, significantly improving project timelines and reducing environmental impact. For B2B buyers, sourcing pipelines that offer flexibility and modularity is crucial, as these features enable quick adjustments to project specifications and minimize downtime.
How Do Floating Pipelines Benefit Water Management?
In regions prone to flooding or experiencing drought, floating pipelines provide a reliable means of transporting water. They can be deployed in challenging terrains where traditional pipelines may fail, ensuring consistent water supply management. Buyers must prioritize adaptability to varying terrain conditions, UV resistance for longevity, and overall cost-effectiveness when sourcing these pipelines for water management projects.
What is the Importance of Floating Pipeline in Environmental Protection?
Floating pipelines are increasingly used for wastewater discharge and treatment, helping industries comply with stringent environmental regulations. By ensuring that waste is transported away from sensitive ecological areas, these pipelines contribute to a reduced ecological footprint. B2B buyers should focus on the quality of materials used, the availability of installation services, and the support for ongoing maintenance to ensure compliance and operational efficiency.
How is Floating Pipeline Utilized in Mining Operations?
In the mining sector, floating pipelines facilitate the transport of slurry from remote locations to processing facilities. This method is particularly beneficial for transporting materials over long distances, providing a cost-effective solution that minimizes environmental disruption. Buyers must consider factors such as pipeline diameter and flow regime compatibility to optimize performance and comply with local regulations, ensuring efficient operations in mining projects.
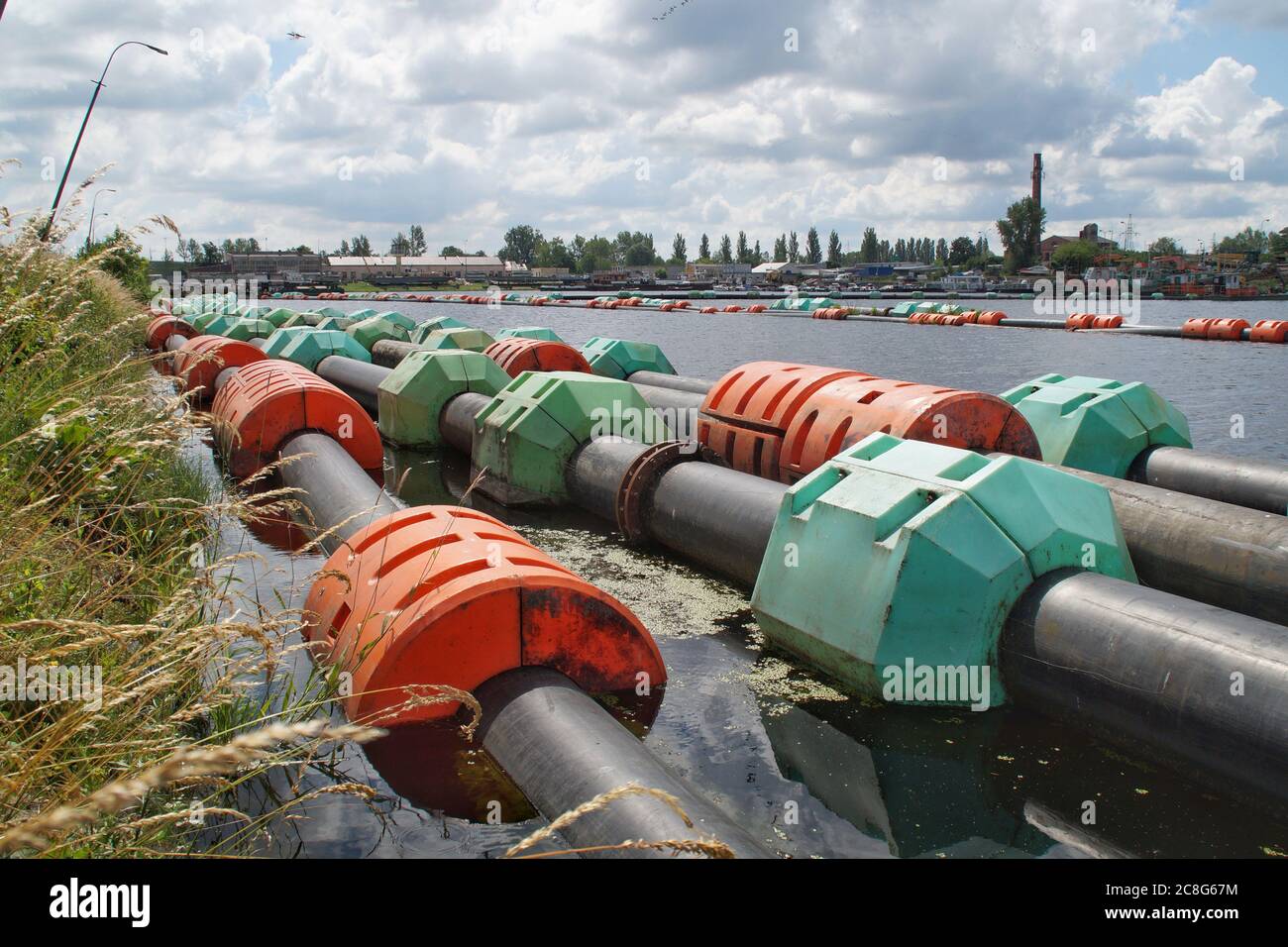
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘floating pipeline’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Unpredictable Sea Conditions
Het probleem: Many B2B buyers in the offshore oil and gas sector face the challenge of deploying floating pipelines in areas with unpredictable sea conditions. Strong currents, waves, and sudden weather changes can lead to misalignment, damage, or even total failure of the pipeline system. This not only jeopardizes the project timeline but can also escalate costs due to potential repairs or replacements. Additionally, the financial implications of halted operations can be significant, especially for companies that rely on consistent flow rates for their profitability.
De oplossing: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize the selection of floating pipelines designed for flexibility and durability. Sourcing pipelines with integrated buoyancy units and flexible joints can enhance the system’s ability to withstand dynamic sea conditions. It is essential to collaborate with manufacturers who provide custom solutions tailored to specific environmental challenges. Furthermore, conducting thorough site assessments using advanced modeling software can help predict how the pipeline will behave under various conditions. Regular maintenance checks and real-time monitoring systems can also be implemented to ensure any potential issues are identified and addressed swiftly, thus maintaining operational integrity.
Scenario 2: High Installation and Maintenance Costs
Het probleem: Another prevalent pain point for international buyers is the high cost associated with the installation and ongoing maintenance of floating pipelines. Many projects require significant upfront capital for installation, and unexpected maintenance needs can lead to budget overruns. Companies in regions like Africa or South America, where financial resources may be limited, often struggle to balance quality and cost-effectiveness in their pipeline solutions.
De oplossing: To address these financial concerns, buyers should focus on investing in high-density polyethylene (HDPE) floating pipelines, which offer a balance of strength and affordability. HDPE pipes are resistant to corrosion and have lower maintenance needs compared to traditional materials. Additionally, buyers should consider modular pipeline systems that allow for easier installation and replacement, reducing labor costs and time. Seeking partnerships with suppliers who offer comprehensive installation and maintenance packages can further alleviate financial strain, providing a clearer picture of total cost ownership. Lastly, utilizing predictive maintenance technologies can help anticipate issues before they arise, ensuring budget adherence.
Scenario 3: Compliance with Environmental Regulations
Het probleem: Compliance with environmental regulations is a critical issue for B2B buyers, especially in regions where strict laws govern marine and coastal ecosystems. Floating pipelines, if not designed or operated properly, can pose risks of leaks or damage to sensitive environments. Companies face potential fines and reputational damage, creating a pressing need to ensure their pipeline systems align with environmental standards.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
De oplossing: To navigate these regulatory challenges, buyers must work closely with suppliers who are well-versed in environmental compliance. It is vital to choose floating pipeline solutions made from environmentally friendly materials that minimize ecological impact. Incorporating leak detection systems and spill prevention technologies can further enhance compliance efforts. Additionally, engaging in transparent communication with local regulatory bodies during the planning phase can provide clarity on necessary permits and environmental assessments. By proactively addressing these concerns, companies can safeguard their operations while fostering goodwill with local communities and regulators.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for floating pipeline
What Are the Key Materials for Floating Pipelines?
When selecting materials for floating pipelines, it’s crucial to consider various factors such as performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in floating pipeline applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Key Properties:
HDPE is known for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for a range of applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F) and has a pressure rating that varies based on wall thickness.
Pros & Cons:
HDPE is lightweight and easy to handle, which reduces installation costs. Its resistance to corrosion ensures longevity, but it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications. Additionally, while HDPE is cost-effective, its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment for welding and joining.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
Invloed op de toepassing:
HDPE is ideal for transporting water and slurry in dredging and offshore oil applications. However, it may not be compatible with certain aggressive chemicals, necessitating careful media compatibility checks.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or ISO. In Europe, particularly Germany, adherence to DIN standards is critical, as is considering the environmental impact of plastic materials.
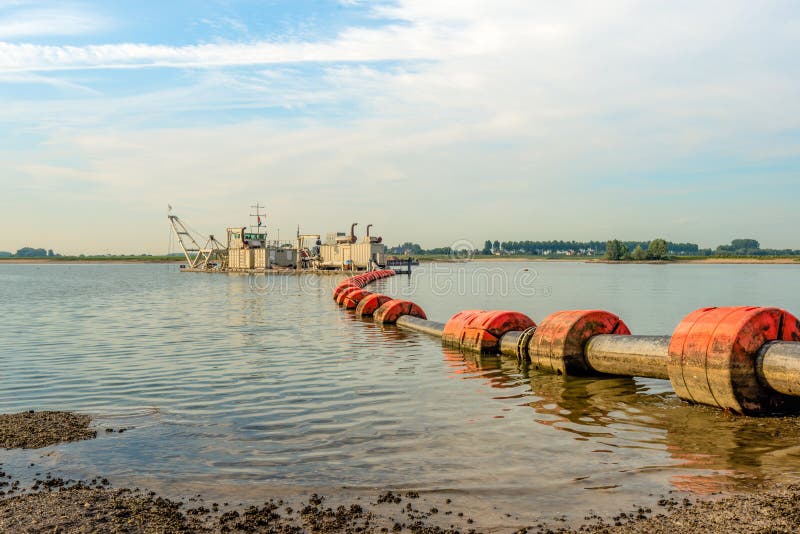
2. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel pipelines offer high strength and can withstand extreme pressures and temperatures. They are typically rated for high-pressure applications and can endure harsh environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s durability is unmatched, making it suitable for long-term use in challenging environments. However, it is prone to corrosion unless coated or treated, which can increase costs. The manufacturing process can be labor-intensive, adding to the overall expense.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
Invloed op de toepassing:
Steel is often used for transporting oil and gas in offshore environments. Its robustness allows for the handling of high-pressure fluids, but corrosion resistance must be addressed, especially in saline environments.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Compliance with international standards such as API and ASTM is essential for steel pipelines. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who adhere to these standards to ensure quality and reliability.
3. Polyurethane (PU)
Key Properties:
Polyurethane is known for its flexibility and resistance to abrasion and impact. It can operate effectively in a temperature range of -30°C to 80°C (-22°F to 176°F) and is often used in applications requiring high elasticity.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of PU is its excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for abrasive materials. However, it can be more expensive than HDPE and may have limitations in high-pressure applications.
Invloed op de toepassing:
PU is often used in dredging operations where flexibility and durability are essential. Its compatibility with various media, including slurries and chemicals, makes it versatile.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Buyers should verify that PU products meet relevant standards, such as ASTM D624 for rubber-like materials. In regions like Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is also crucial.
4. Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE)
Key Properties:
UHMWPE offers exceptional abrasion resistance and low friction properties. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and is known for its high impact strength.
Pros & Cons:
The advantage of UHMWPE is its long service life and low maintenance requirements. However, it is often more expensive than traditional materials like HDPE and can be challenging to weld, which may complicate installation.
Invloed op de toepassing:
UHMWPE is particularly effective in applications involving abrasive slurries, making it a preferred choice for dredging and mining operations.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
International buyers must ensure that UHMWPE products comply with specific industry standards such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like South America and Africa, understanding local regulations related to plastic materials is vital.
Summary Table
| Materiaal | Typical Use Case for Floating Pipeline | Belangrijkste voordeel | Belangrijkste nadeel/beperking | Relatieve kosten (laag/gemiddeld/hoog) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Water transport, dredging | Lichtgewicht en corrosiebestendig | Limited high-temperature suitability | Medium |
| Steel | Oil and gas transport | High strength and pressure resistance | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Hoog |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Dredging operations | Excellent wear resistance | Higher cost, limited high-pressure use | Medium-High |
| Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Abrasive slurry transport | Long service life and low maintenance | More expensive, welding challenges | Hoog |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a comprehensive resource for B2B buyers in diverse international markets, helping them make informed decisions regarding floating pipeline materials.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for floating pipeline
Floating pipelines are crucial components in various industries, including dredging, offshore oil and gas operations, and water transport. Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is essential for B2B buyers who seek reliable and efficient pipeline solutions. This section delves into the intricacies of manufacturing floating pipelines and the quality control measures that ensure their reliability and performance.
What Are the Main Stages of Floating Pipeline Manufacturing?
How Is Material Prepared for Floating Pipeline Production?
The manufacturing of floating pipelines begins with material preparation. Typically, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) are the materials of choice due to their resistance to corrosion and buoyancy properties. The materials are sourced in bulk and undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet industry standards.
The preparation phase involves cutting the raw materials into specific dimensions suitable for the intended pipeline design. This step may also include pre-treatment processes such as cleaning and drying to eliminate contaminants that could affect the integrity of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Floating Pipelines?
The forming stage involves several key techniques, including extrusion and molding. In extrusion, raw material pellets are melted and formed into long, continuous pipes through a die. This method allows for uniform thickness and strength across the length of the pipeline.
Alternatively, molding techniques, such as blow molding, may be utilized for creating custom shapes or fittings. This approach is particularly beneficial for producing specialized components like buoyancy units or connectors that enhance the functionality of the floating pipeline system.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Floating Pipelines?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly stage begins. Floating pipelines are typically modular, allowing for easy transportation and installation. During assembly, sections of the pipeline are connected using bolts, quick coupling devices, or other fastening methods.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
This modular design not only simplifies logistics but also enables flexibility in design modifications. Each connection point is meticulously aligned and secured to withstand the stresses of marine environments, such as waves and currents.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Floating Pipelines?
The finishing stage includes several processes aimed at enhancing the durability and performance of the pipelines. This often involves surface treatments to increase resistance to UV radiation, abrasion, and marine growth.
Additionally, final inspections are performed to ensure that the pipeline meets the specified dimensions and performance criteria. The finished product is then subjected to a thorough cleaning process to remove any residues from the manufacturing phase before it is packaged for shipment.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Standard for Floating Pipelines?
Which International Standards Govern Floating Pipeline Quality?
Quality assurance is paramount in the production of floating pipelines, and adherence to international standards is critical. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Furthermore, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are essential for pipelines used in oil and gas applications.
These standards set the benchmark for material quality, manufacturing processes, and overall product performance, which are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of floating pipelines.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Pipeline Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Inkomende kwaliteitscontrole (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure compliance with specified standards. Materials that do not meet the quality criteria are rejected.
-
Kwaliteitscontrole tijdens het proces (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular checks are conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensional accuracy. This ensures that any deviations from the specifications are addressed promptly.
-
Finale kwaliteitscontrole (FQC): After assembly, the complete pipeline undergoes rigorous testing to verify its integrity and performance. This may include pressure testing, buoyancy assessments, and inspection for surface defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Floating Pipelines?
Testing methods are vital for validating the quality and performance of floating pipelines. Common tests include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: This method assesses the pipeline’s ability to withstand internal pressure without leaking, ensuring its suitability for transporting liquids.
- Buoyancy Testing: Essential for floating pipelines, this test confirms that the pipeline remains afloat under specified conditions.
- Environmental Resistance Testing: This involves exposing the pipeline materials to various environmental conditions, such as saltwater and UV radiation, to evaluate their durability over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Audit Suppliers’ Quality Control?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are several steps to consider:
-
Request Certification Documents: Buyers should ask for copies of relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, API) to ensure the supplier meets industry standards.
-
Leveranciersaudits uitvoeren: On-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturer’s quality control practices. Buyers should assess the QC checkpoints, testing methods, and overall production environment.
-
Review Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of quality control tests, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports offer transparency and assurance of product quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: For added assurance, buyers can employ independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place.
Wat zijn de nuances op het gebied van kwaliteitscontrole voor internationale B2B-kopers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate unique challenges in quality assurance. Regulatory differences, varying standards, and logistical considerations can complicate procurement processes.
It’s crucial for buyers to understand the specific quality requirements relevant to their region and industry. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about these requirements and conducting thorough due diligence can mitigate risks associated with quality assurance.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for floating pipelines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and finishing processes, alongside rigorous quality control standards, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful project outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘floating pipeline’
To effectively source floating pipelines for your projects, a structured approach is essential. This checklist provides international B2B buyers with actionable steps to ensure a successful procurement process tailored to your specific needs and operational environments.
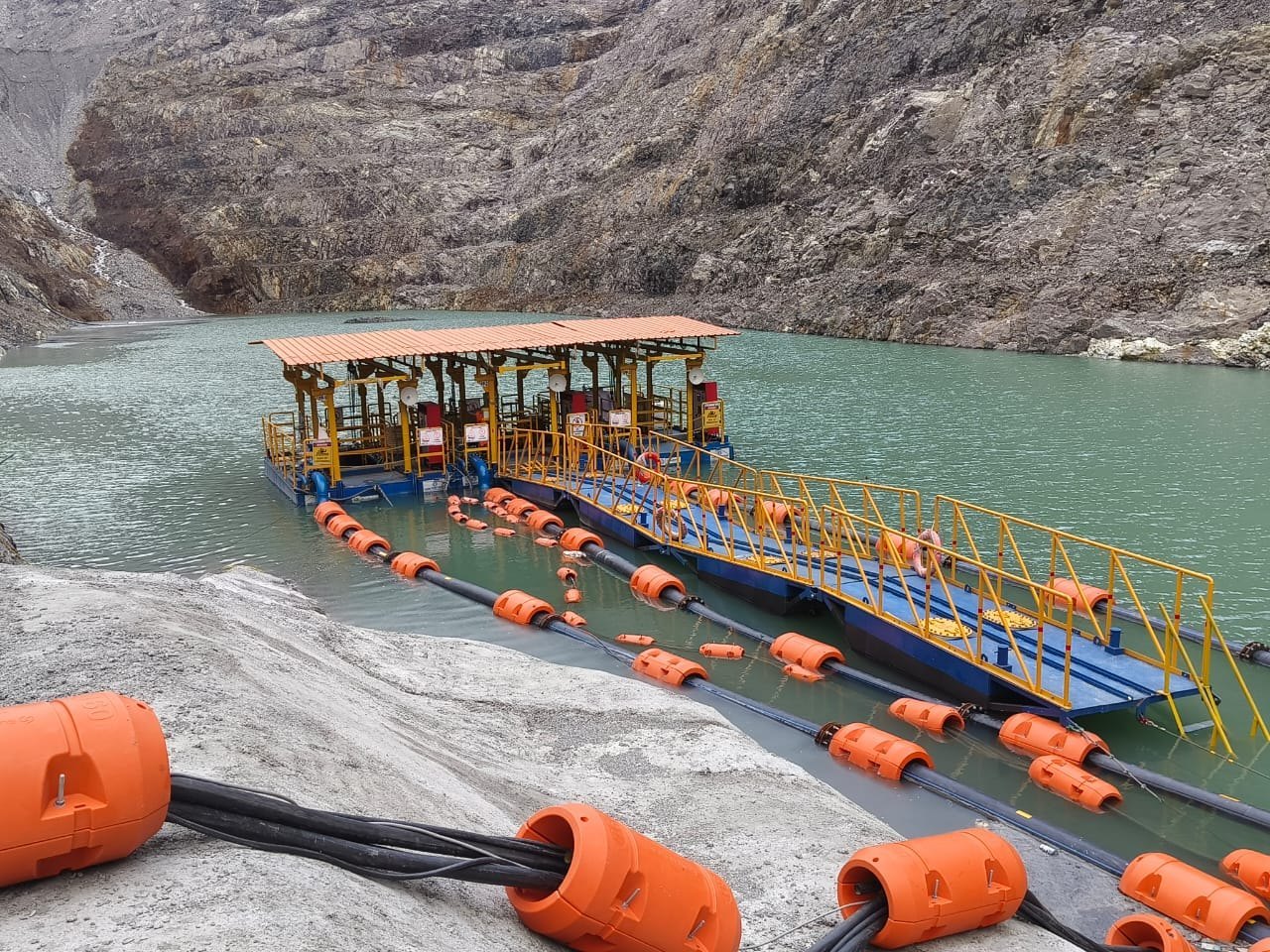

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
Stap 1: Je technische specificaties definiëren
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the floating pipeline you need. This includes parameters such as pipe material (e.g., HDPE, steel), diameter, length, and buoyancy requirements. Defining these specifications helps prevent costly miscommunications and ensures that the pipeline can withstand local environmental conditions, such as sea currents and temperature variations.
Stap 2: Onderzoek markttrends en toepassingen
Understanding the current market trends and common applications for floating pipelines is crucial. Investigate the specific industries where floating pipelines are utilized—such as dredging, oil and gas, and water transport. This knowledge will guide you in selecting a product that meets industry standards and is suitable for your operational context, especially in regions like Africa and South America where conditions can vary significantly.
Stap 3: Potentiële leveranciers evalueren
Before making a commitment, it is vital to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers who have operated in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering floating pipelines and ensure they have the necessary certifications to meet international quality and safety standards.
- Key Questions to Ask:
- What is your experience with floating pipelines in my industry?
- Can you provide references from previous projects?
Stap 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Ensure that you are comparing similar products and specifications to avoid any discrepancies. Be aware of hidden costs that may not be immediately apparent, such as shipping fees, installation costs, and maintenance services.
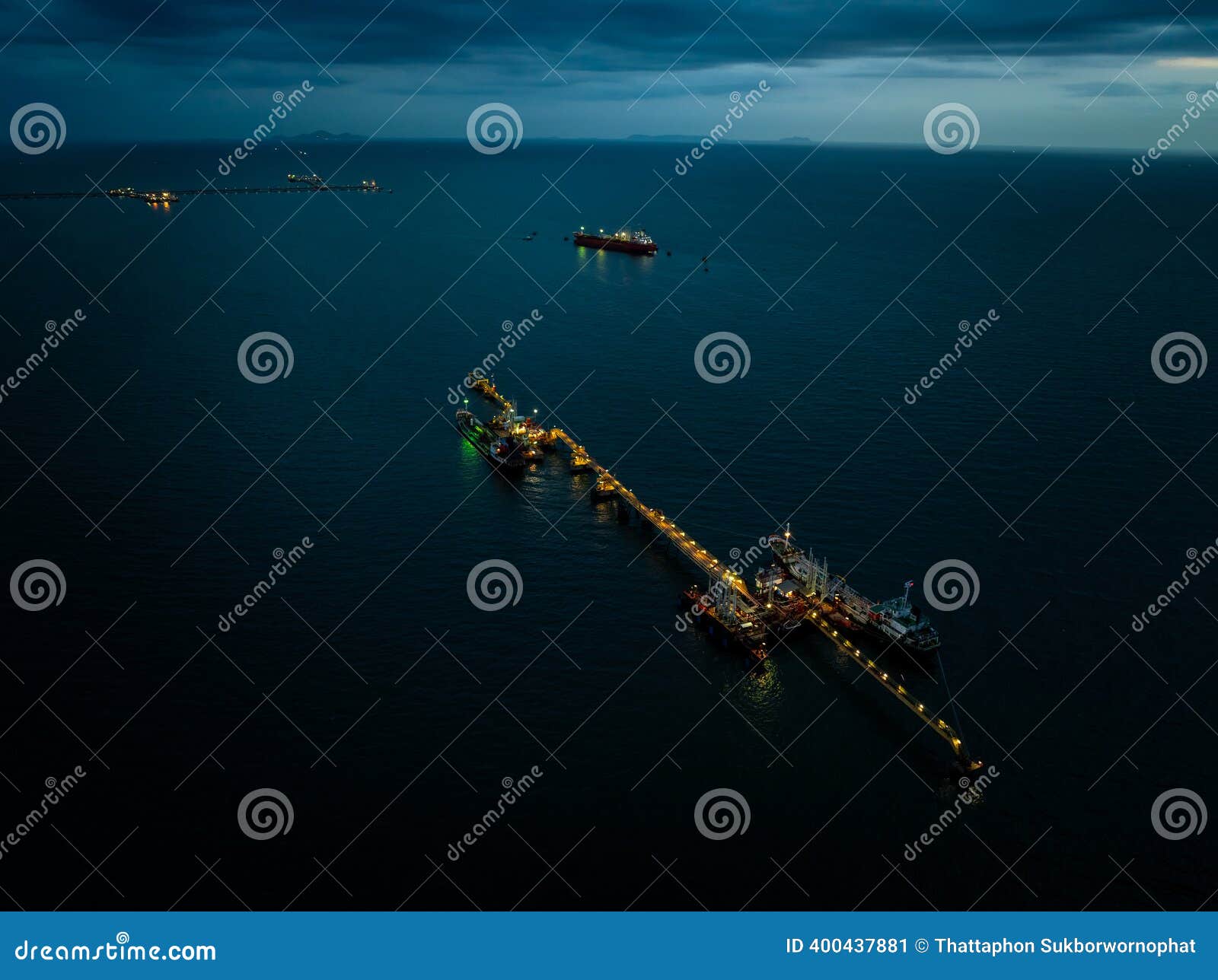
Stap 5: Assess Quality Assurance Processes
Investigate the quality assurance processes employed by your potential suppliers. A reputable supplier should have robust quality control measures in place to ensure that their floating pipelines meet or exceed industry standards. This may include testing for durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
- Things to Check:
- Are there third-party certifications?
- What testing protocols do you follow?
Stap 6: Understand After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Inquire about the after-sales support and maintenance services provided by the supplier. A reliable supplier should offer comprehensive support that includes installation guidance, maintenance schedules, and troubleshooting assistance. This can be particularly important in remote locations where access to technical support may be limited.
Stap 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve selected a supplier, review and finalize the purchase agreement carefully. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, payment conditions, and warranty details, are clearly outlined. A well-defined agreement can help prevent disputes and ensure that both parties have aligned expectations regarding the procurement process.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the sourcing of floating pipelines, ensuring that your procurement process is efficient and aligned with your operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for floating pipeline Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Floating Pipeline Sourcing?
When sourcing floating pipelines, it is essential to understand the comprehensive cost structure involved. The primary cost components include:
-
Materialen: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Floating pipelines are often made from HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) or UHMWPE (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene), known for their durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. The market price of these materials fluctuates, affecting procurement costs.
-
Arbeid: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the pipeline assembly and the location of manufacturing. Regions with lower labor costs can provide a competitive advantage, but it is crucial to balance this with the skill level required for installation and maintenance.
-
Productie Overhead: This includes costs related to the operation of manufacturing facilities, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these overheads.
-
Gereedschap: Specialized tooling is often required for the production of floating pipelines. The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for customized or large-scale orders.
-
Kwaliteitscontrole (QC): Ensuring that pipelines meet industry standards and certifications is critical. QC costs should be factored into the pricing, as rigorous testing and compliance with international standards enhance product reliability.
-
Logistiek: Transporting floating pipelines can be expensive, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a crucial role in logistics costs.
-
Marge: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and risks. Understanding the average market margins can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Floating Pipeline Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of floating pipelines:
-
Volume/MOQ (minimum bestelhoeveelheid): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their needs carefully to take advantage of bulk pricing.
-
Specificaties en aanpassingen: Custom specifications may lead to increased costs. Buyers must clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materialen en kwaliteitscertificaten: The choice of material and the availability of quality certifications can significantly impact pricing. Higher quality materials and recognized certifications justify higher costs due to increased durability and reliability.
-
Factoren van leveranciers: Supplier reputation, production capabilities, and historical performance can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect overall costs.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Floating Pipelines?
Navigating the procurement landscape for floating pipelines requires strategic approaches:
-
Negotiation Strategies: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating with multiple suppliers. Request quotes and be transparent about your budget constraints to foster competitive pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational costs, and lifespan when assessing the value of a pipeline.
-
Prijsnuances voor internationale kopers: When sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions. This understanding can help prevent budget overruns.
-
Utilize Local Expertise: Engage local experts or consultants familiar with regional suppliers and regulations. Their insights can lead to better sourcing decisions and cost savings.
Disclaimer over indicatieve prijzen
Prices for floating pipelines can vary widely based on the above factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing aligned with their project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing floating pipeline With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Pipeline Solutions
In the dynamic landscape of pipeline solutions, businesses often seek alternatives to floating pipelines for transporting fluids in challenging environments. Floating pipelines are designed to operate effectively in aquatic settings, but other methods can also provide viable solutions depending on specific operational needs and contexts. This analysis will explore how floating pipelines compare to submerged pipelines and land-based pipelines, offering insights to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Vergelijkende tabel
| Vergelijkingsaspect | Floating Pipeline | Submerged Pipeline | Land-Based Pipeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prestaties | High flexibility; suitable for dynamic water conditions | Stable but limited to fixed locations; vulnerable to seabed conditions | Reliable for short distances; easier to monitor and maintain |
| Kosten | Moderate to high initial investment; costs can increase with installation complexity | Generally lower material costs; higher installation costs due to underwater work | Lower upfront costs; may require additional equipment for flow management |
| Gemak van implementatie | Requires specialized vessels for deployment; modular design aids in flexibility | Complex installation; requires skilled labor and equipment for sinking | Straightforward installation; less technical expertise required |
| Onderhoud | Requires regular inspections and adjustments; vulnerable to environmental conditions | Maintenance can be challenging due to underwater location | Easier access for repairs and upgrades; regular maintenance is simpler |
| Beste gebruikscasus | Ideal for offshore oil/gas, dredging, and temporary installations | Suitable for permanent installations in stable seabeds | Best for short-distance transport on land; effective in stable environments |
Gedetailleerd overzicht van alternatieven
Submerged Pipeline
Submerged pipelines are typically welded together and sunk to the seabed, making them a stable option for transporting fluids over longer distances. The primary advantage of this method is its lower material costs compared to floating pipelines. However, installation is complex and labor-intensive, which can significantly increase overall costs. Furthermore, maintenance poses a challenge as accessing submerged lines often requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Land-Based Pipeline
Land-based pipelines are the most straightforward option, utilizing standard piping systems laid onshore. They are generally less expensive to install and maintain due to easier access for repairs. However, land-based solutions are limited in terms of distance and may require additional infrastructure for flow management. These pipelines are ideal for stable environments where the risk of environmental disruption is low, making them suitable for short-distance transport.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pipeline Solution
Selecting the appropriate pipeline solution involves careful consideration of the specific operational context, including environmental conditions, project duration, and budget constraints. Floating pipelines offer unmatched flexibility in aquatic environments, while submerged pipelines provide stability for permanent installations. Conversely, land-based pipelines are the most cost-effective for shorter distances. B2B buyers should assess their unique requirements and weigh the pros and cons of each option to determine which solution aligns best with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for floating pipeline
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Floating Pipelines?
Floating pipelines are specialized infrastructure solutions designed for various applications, including dredging, offshore oil and gas operations, and water transport in challenging environments. Understanding the essential technical properties of these pipelines is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions.
1. Materiële rang
The material grade of a floating pipeline significantly influences its durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. Common materials include High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE). These materials are chosen for their corrosion resistance and lightweight characteristics, making them suitable for floating applications. Selecting the right material is vital for ensuring long-term performance and minimizing maintenance costs.
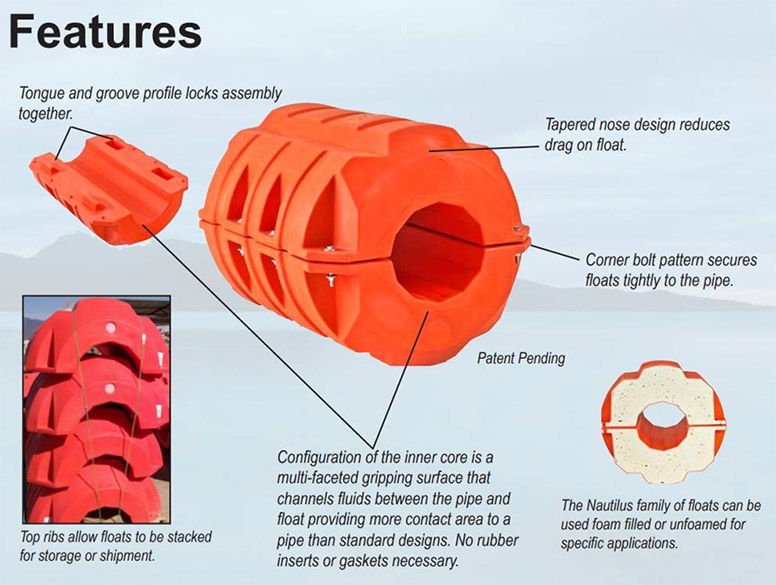
2. Buoyancy Units
Buoyancy units are integral to floating pipelines, providing the necessary lift to keep the pipeline above water. These units are typically made from lightweight materials and are designed to withstand harsh marine conditions. Understanding the specifications of buoyancy units, including their size and load capacity, is crucial for ensuring the pipeline’s stability and functionality. Proper buoyancy design can prevent sagging or submersion, which could lead to operational failures.
3. Flexibility and Joint Design
Flexibility is a critical property of floating pipelines, allowing them to adapt to ocean currents and wave movements. This is often achieved through the incorporation of flexible joints or ball joints at regular intervals. The design of these joints is essential to accommodate movement without compromising the integrity of the pipeline. B2B buyers should consider the joint design when evaluating potential suppliers, as it directly impacts the pipeline’s longevity and performance.
4. Tolerance Specifications
Tolerance specifications refer to the allowable deviations in dimensions and performance characteristics of the pipeline components. These tolerances are crucial in ensuring that all parts fit together seamlessly and function as intended. For floating pipelines, maintaining strict tolerances can prevent leaks and operational disruptions. Buyers should verify the tolerance specifications from suppliers to ensure compatibility with their project requirements.
5. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the pipeline can safely handle. This is especially important in applications involving fluid transport under varying pressure conditions. A higher pressure rating can enhance the pipeline’s versatility, allowing it to be used in a broader range of applications. Buyers must assess the pressure requirements of their specific applications to select an appropriate pipeline.
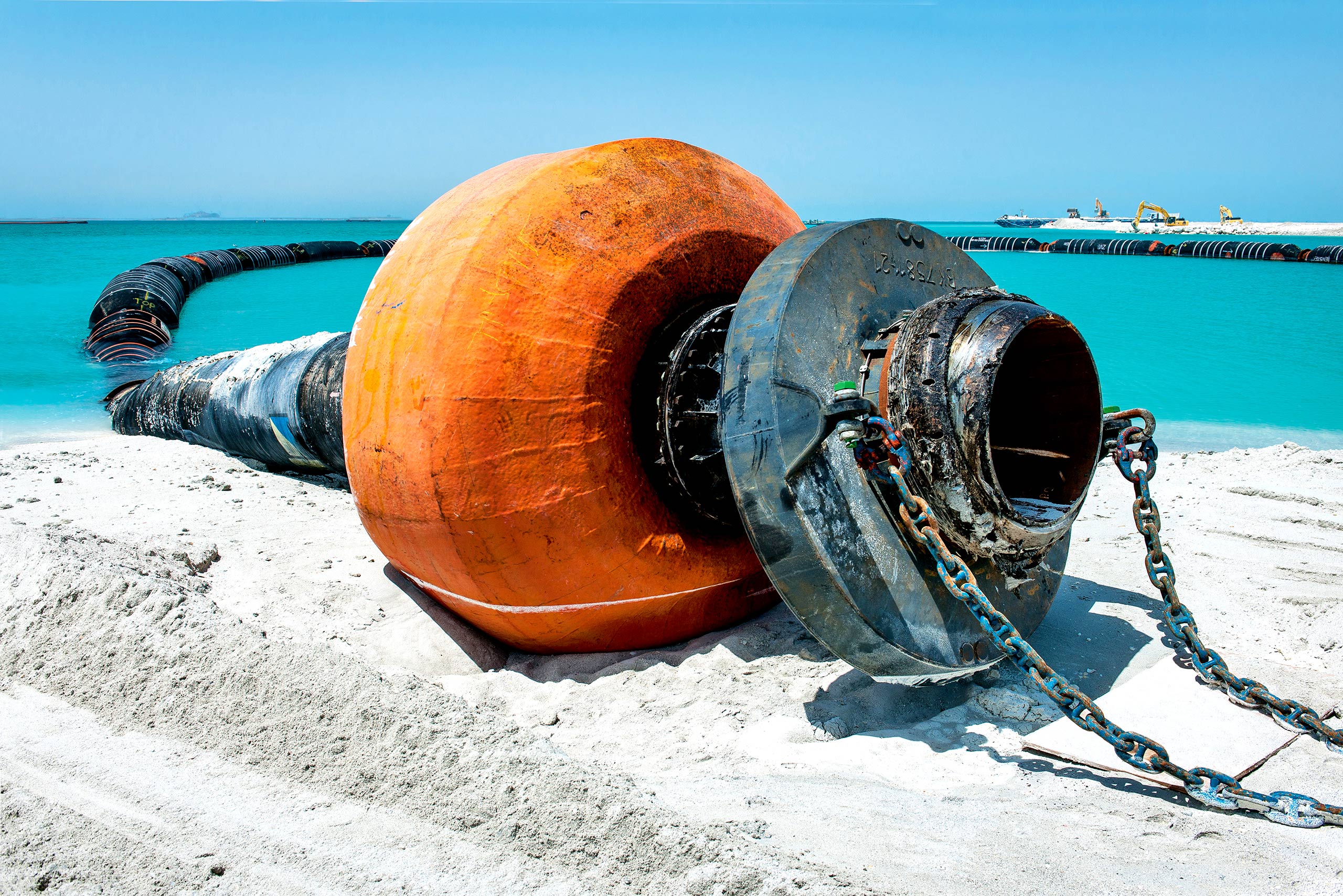
What Are Common Trade Terminology Terms in the Floating Pipeline Industry?
Navigating the floating pipeline industry requires familiarity with specific trade terminology that can influence procurement processes and negotiations.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of floating pipelines, understanding who the OEM is can help buyers gauge the quality and reliability of the product. Buyers often prefer OEM products for their proven track record and adherence to industry standards.
2. MOQ (minimale bestelhoeveelheid)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it directly impacts inventory management and costs. Understanding the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchasing strategy and avoid excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Offerteaanvraag)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the floating pipeline sector, an RFQ helps clarify technical specifications and pricing structures, enabling buyers to make informed decisions based on competitive offers.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases of floating pipelines, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation.
5. Doorlooptijd
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and resource allocation. Buyers should consider lead times when evaluating suppliers to ensure timely project execution.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes and optimize their procurement strategies in the floating pipeline industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the floating pipeline Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Floating Pipeline Sector?
The floating pipeline sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increasing demand for offshore oil and gas extraction, coupled with the need for efficient water transportation in areas with challenging geographical conditions, is propelling market expansion. Emerging economies in Africa and South America are particularly notable as they seek to develop their natural resources and infrastructure, creating significant opportunities for international B2B buyers.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the industry landscape. Innovations in materials such as High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) are leading to the development of lightweight, durable, and flexible pipelines that can withstand harsh marine environments. The adoption of modular pipeline systems is another trend, allowing for quicker assembly and disassembly, which is crucial for temporary projects or in response to changing environmental conditions.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer not just product quality but also competitive pricing and reliable supply chains. The integration of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is becoming common, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and streamline their purchasing processes. As a result, companies that invest in e-commerce solutions and digital marketing are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving market.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping B2B Relationships in the Floating Pipeline Sector?
As global awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the floating pipeline sector. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices. This includes the use of recyclable materials, such as HDPE, which not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to clients aiming to achieve sustainability goals.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now more informed and concerned about the sourcing origins of the materials used in floating pipelines. Transparency in the supply chain fosters trust and enhances brand reputation, making it a critical factor in supplier selection. Companies that obtain ‘green’ certifications or adhere to environmental standards are better positioned to attract business from conscientious buyers.
Moreover, the implementation of eco-friendly practices not only aids in regulatory compliance but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. By reducing waste and improving efficiency, companies can lower operational costs, which is an attractive proposition for B2B buyers looking to maximize their ROI.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Floating Pipeline Technology?
Floating pipeline technology has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially, floating pipelines were limited to basic designs that lacked flexibility and durability. However, advancements in materials science and engineering have transformed the industry, leading to the introduction of modular systems that enhance adaptability and resilience.
The shift towards using synthetic materials like HDPE has been a game-changer, providing superior buoyancy, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as modern floating pipelines can meet the diverse needs of various sectors, including dredging, offshore oil and gas operations, and water transport.
As the floating pipeline sector continues to grow and innovate, understanding its historical context helps international B2B buyers appreciate the advancements that have shaped the current landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions when sourcing products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of floating pipeline
-
How do I solve logistical challenges when sourcing floating pipelines internationally?
Logistical challenges in sourcing floating pipelines can be addressed by partnering with suppliers who have a proven track record in international shipping and customs clearance. Ensure your supplier can provide detailed shipping documentation and support with import/export regulations specific to your country. Consider working with freight forwarders experienced in handling large industrial equipment. It’s also beneficial to establish clear communication regarding timelines, shipping methods, and any potential delays due to customs or transport issues to avoid disruptions in your project schedule. -
What is the best material for floating pipelines used in diverse environments?
The best material for floating pipelines largely depends on the specific application and environmental conditions. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is widely regarded for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for offshore operations and areas with fluctuating water levels. Additionally, consider Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) for high abrasion resistance and durability in challenging conditions. Always assess the specific requirements of your project, including chemical compatibility and pressure ratings, before making a decision. -
How can I vet suppliers for floating pipelines effectively?
To effectively vet suppliers for floating pipelines, start by researching their industry reputation and customer reviews. Request case studies or references from past projects to evaluate their experience in similar applications. Check for certifications that reflect quality standards, such as ISO 9001, and ensure they comply with international shipping regulations. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facility, if feasible, to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes firsthand. -
What customization options are available for floating pipelines?
Most suppliers offer various customization options for floating pipelines, including size, buoyancy features, and connection methods. Depending on your project’s specific requirements, you can request modifications such as reinforced joints, specialized coatings for chemical resistance, or tailored buoyancy units. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the procurement process to ensure they can meet your specifications while adhering to industry standards and safety regulations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for floating pipelines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for floating pipelines can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specifications of the order. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred meters for standard products to larger quantities for customized pipelines. It’s essential to communicate your project needs clearly with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and project timelines. Some suppliers may also offer flexible options for smaller projects or trial orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing floating pipelines?
Payment terms for floating pipeline procurement can vary widely depending on the supplier’s policies and your location. Typically, suppliers may require a deposit of 30% to 50% upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after installation. It’s advisable to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and discuss any potential payment incentives for early settlement. Always ensure the terms are documented in a formal purchase agreement to protect both parties. -
How is quality assurance handled in the production of floating pipelines?
Quality assurance (QA) in the production of floating pipelines typically involves several stages, including material inspection, in-process monitoring, and final testing. Reputable suppliers will conduct rigorous testing for factors such as pressure resistance, buoyancy, and durability under simulated environmental conditions. Request documentation of QA processes and any certifications that the manufacturer holds. Additionally, inquire about their approach to handling defects or non-conformance issues, which can affect your project’s success. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when transporting floating pipelines?
When transporting floating pipelines, consider factors such as the size and weight of the pipes, the mode of transport, and the route taken. Ensure that your logistics provider is equipped to handle oversized shipments and can navigate local regulations regarding transport permits. Additionally, assess the potential for damage during transit; protective packaging and secure loading methods are crucial. Establish a clear timeline for delivery, accounting for any potential delays due to customs or regional transport constraints.
Top 8 Floating Pipeline Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IADC Dredging – Floating Pipelines
Domein: iadc-dredging.com
Geregistreerd: 1998 (27 jaar)
Inleiding: Pipelines fall into three main categories: floating pipelines, submerged or “sinker” lines, and land or “shore” lines. Floating pipelines are formed of steel pipes supported by buoyancy units or made of buoyant material, designed to be flexible to endure sea movement. They are modular and connected by bolts or quick coupling devices. Submerged pipelines are welded together, floated into place, and…
2. Pedredge Pipe – HDPE Floating Pipelines
Domein: pedredgepipe.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Inleiding: HDPE floating pipelines are used in dredging, offshore oil and gas operations, and water transport in challenging terrains. They utilize high-density polyethylene (HDPE) for buoyancy and stability, making them suitable for freshwater and saltwater environments. The pipelines consist of HDPE pipes and pipe floats, designed to float on water surfaces. They are lightweight, durable, and cost-effectiv…
3. BIS Floats – FPS Modular Line
Domein: bisfloats.nl
Geregistreerd: 2005 (20 jaar)
Inleiding: BIS FPS MODULAR LINE is a customizable floating pipeline system that utilizes steel or HDPE pipes in combination with dredger hoses and BIS-RING-FLOATS®. It aims to achieve an optimal balance between technical performance and investment costs.
4. Sangir – Dredging Pipe Floats
Domein: sangir.com
Geregistreerd: 2011 (14 jaar)
Inleiding: {“product_name”: “Dredging Pipe Floats”, “material”: “European high-impact marine-grade, UV-stabilized PE materials”, “features”: [“strong construction”, “flexibility”, “long-lasting performance”, “eco-friendly PU foam for buoyancy”, “galvanized accessories for extended service life”, “lightweight”, “easy installation”, “superb flexibility for rough sea conditions”], “applications”: [“dredging ope…
5. Neptune™ – Pipe Floats
Domein: pipefloat.com
Geregistreerd: 2011 (14 jaar)
Inleiding: Neptune™ is the leading manufacturer of pipe floats (Dredge Floats or Float Collars) in the United States. Key features include:
– Made from rotationally-molded polyethylene plastic with UV inhibitors.
– Designed for safety and usability.
– Features: Clamp Tite™ (prevents pipeline slips), EzGlide™ (allows wind and water to pass), Snap-N-Lock (solves transportation and storage issues).
– Pipe F…
6. EZ Connect – Pipeline Floats
Domein: ezconnectfloats.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Inleiding: Pipeline floats, also known as dredge pipe floats, are specialized devices used in the oil and gas industry to support and protect underwater pipelines. They are typically cylindrical or spherical structures made of durable materials such as steel or polyethylene. The primary purpose of pipeline floats is to provide buoyancy, preventing pipelines from sinking or resting on the seabed, while mainta…
7. Locs – Pipeline Floaters
Domein: locs.cz
Geregistreerd: 2017 (8 jaar)
Inleiding: Pipeline Floaters are designed for transporting slurry (a mixture of water and soil or rock) using hydraulic dredger equipment. They connect the working dredge to the shore slurry pipeline, allowing for operational maneuvers and supporting line structures for securing supply and control cables. Key features include:
– Made of polyethylene through rotational molding, hollow inside with optional fo…
8. Vicking Kayaks – Durable LLDPE Channel Floating Barrier
Domein: vickingkayaks.com
Geregistreerd: 2014 (11 jaar)
Inleiding: {“Product Name”:”Durable LLDPE Channel Floating Barrier Plastic Pipeline Buoy”,”Material”:”UV-stabilised polyethylene”,”Size”:”800mm x 500mm”,”Weight”:”14kg”,”Buoyancy”:”150kg”,”Colour”:”Red”,”Warranty”:”12 Months”,”Place of Origin”:”Zhejiang, China”,”Environmental Protection Material”:”New food grade polyethylene material filled with water-closed foam”,”Product Advantages”:”High shell strength, s…
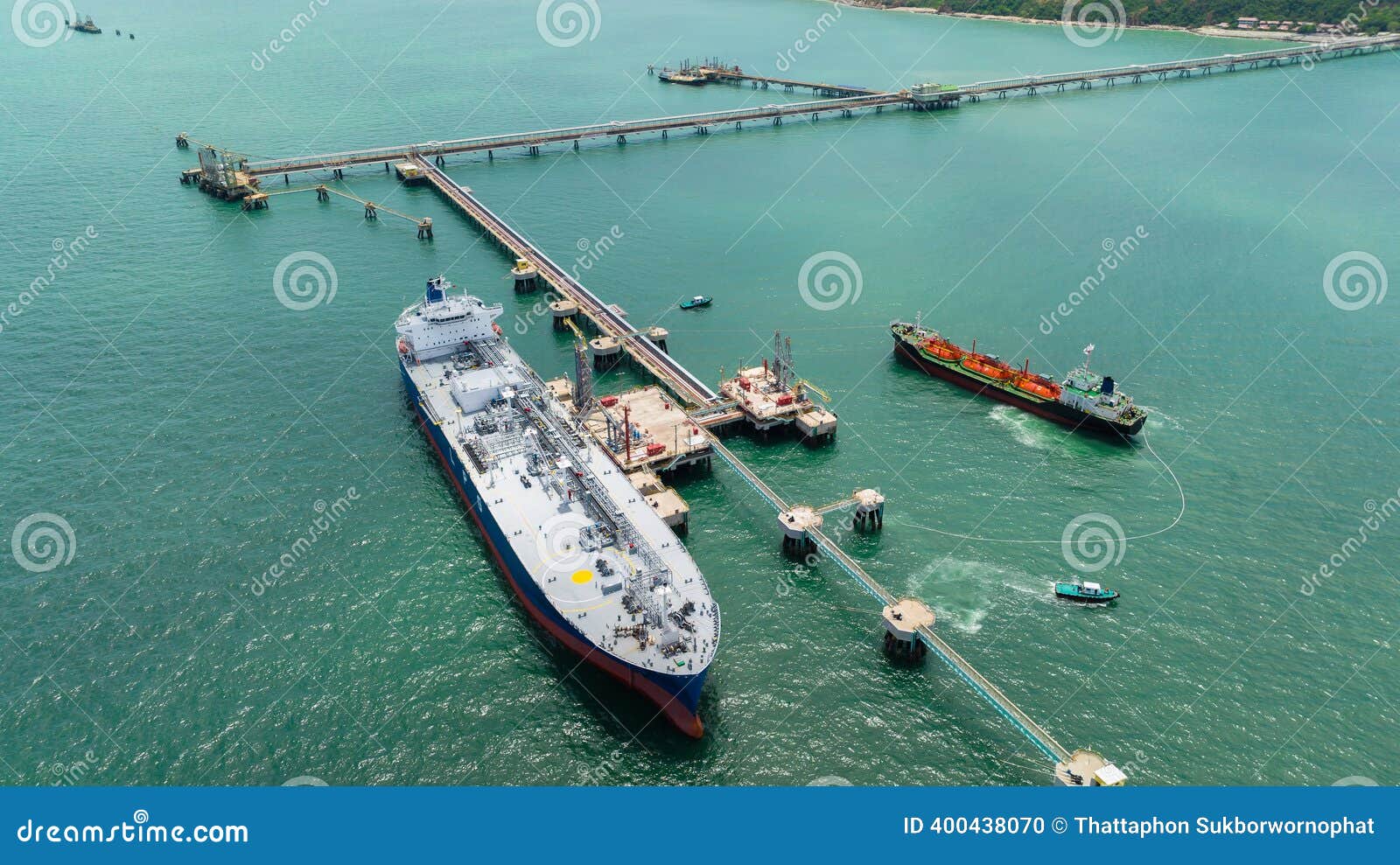
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for floating pipeline
In the rapidly evolving landscape of floating pipelines, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement processes. Key takeaways highlight the importance of selecting high-quality materials, such as HDPE and UHMWPE, which offer durability and flexibility in challenging marine environments. The adaptability of floating pipelines, especially in dredging and offshore operations, makes them indispensable in regions with fluctuating water levels and complex terrains.
Investing in a reliable supplier network not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with pipeline failures. Buyers should prioritize partnerships that emphasize innovation and sustainability, ensuring that their projects align with global environmental standards and practices.

Illustrative image related to floating pipeline
Looking ahead, the demand for floating pipelines is set to increase, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. This presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers to leverage strategic sourcing as a means of gaining a competitive edge. Embrace this moment to explore advanced solutions and establish partnerships that will drive success in your upcoming projects.
Belangrijke disclaimer en gebruiksvoorwaarden
⚠️ Belangrijke disclaimer
De informatie in deze gids, inclusief inhoud over fabrikanten, technische specificaties en marktanalyses, is uitsluitend bedoeld voor informatieve en educatieve doeleinden. Het is geen professioneel aankoopadvies, financieel advies of juridisch advies.
Hoewel we al het mogelijke hebben gedaan om de nauwkeurigheid en actualiteit van de informatie te garanderen, zijn we niet verantwoordelijk voor eventuele fouten, weglatingen of verouderde informatie. Marktomstandigheden, bedrijfsgegevens en technische normen kunnen veranderen.
B2B-kopers moeten hun eigen onafhankelijke en grondige due diligence uitvoeren voordat je een aankoopbeslissing neemt. Dit houdt in dat u rechtstreeks contact moet opnemen met leveranciers, certificeringen moet controleren, monsters moet aanvragen en professioneel advies moet inwinnen. Het risico van het vertrouwen op informatie in deze gids wordt uitsluitend gedragen door de lezer.