Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sts transfer
Navigating the complexities of Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer operations presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the demand for efficient and safe cargo transfer solutions grows, understanding the intricacies of STS operations becomes vital. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the various types of STS operations, their applications, and the essential procedures that ensure safe and effective cargo transfer.
From vetting suppliers to understanding the cost implications, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It addresses the critical aspects of operational safety, regulatory compliance, and logistical efficiency that are crucial for successful STS operations. By equipping buyers with actionable insights and best practices, we aim to enhance their ability to navigate the global market for STS transfer services.
Whether you are a procurement officer in a multinational corporation or a logistics manager seeking to optimize your supply chain, this guide will provide you with the knowledge needed to leverage STS operations effectively. Understanding the significance of these operations not only mitigates risks but also opens up opportunities for cost savings and operational efficiencies in your shipping endeavors.
Inhoudsopgave
- Top 5 Sts Transfer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sts transfer
- Understanding sts transfer Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of sts transfer
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sts transfer’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for sts transfer
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sts transfer
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sts transfer’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sts transfer Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sts transfer With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sts transfer
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sts transfer Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sts transfer
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sts transfer
- Belangrijke disclaimer en gebruiksvoorwaarden
Understanding sts transfer Types and Variations
| Type Naam | Belangrijkste onderscheidende kenmerken | Primaire B2B-toepassingen | Korte voor- en nadelen voor kopers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional STS | Involves two vessels transferring cargo side-by-side at sea. | Bulk oil and gas transportation | Voordelen: Efficient for large volumes; Minpunten: Weather-dependent, potential for spills. |
| Emergency STS | Conducted in urgent situations to transfer cargo from compromised vessels. | Crisis management, spill prevention | Voordelen: Quick response to emergencies; Minpunten: Higher risk due to compromised conditions. |
| Bunkering STS | Focuses on transferring fuel from bunker vessels to operational ships. | Refueling operations for vessels | Voordelen: Reduces port time; Minpunten: Requires precise coordination and timing. |
| Lightering STS | Transfers cargo from larger vessels to smaller ones for port access. | Ports with draught restrictions | Voordelen: Geeft toegang tot ondiepe poorten; Minpunten: Involves additional handling and potential delays. |
| Chemical STS | Specialized for transferring chemicals, requiring strict safety protocols. | Chemical transport and logistics | Voordelen: Ensures safe handling of hazardous materials; Minpunten: Higher regulatory compliance costs. |
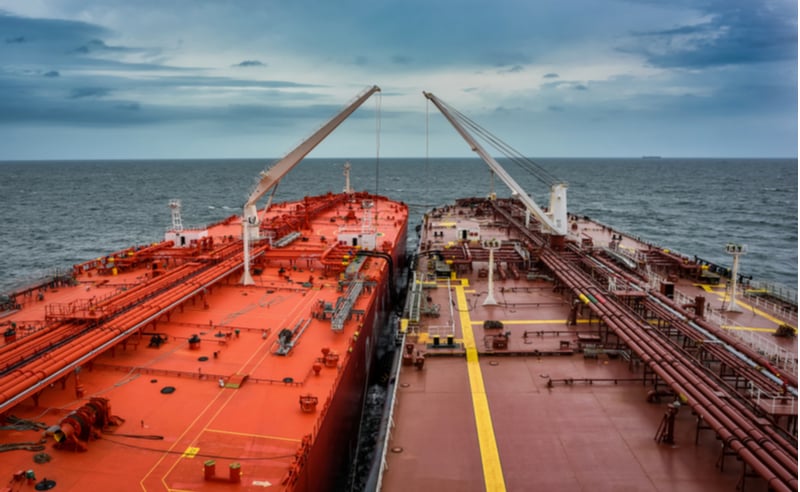
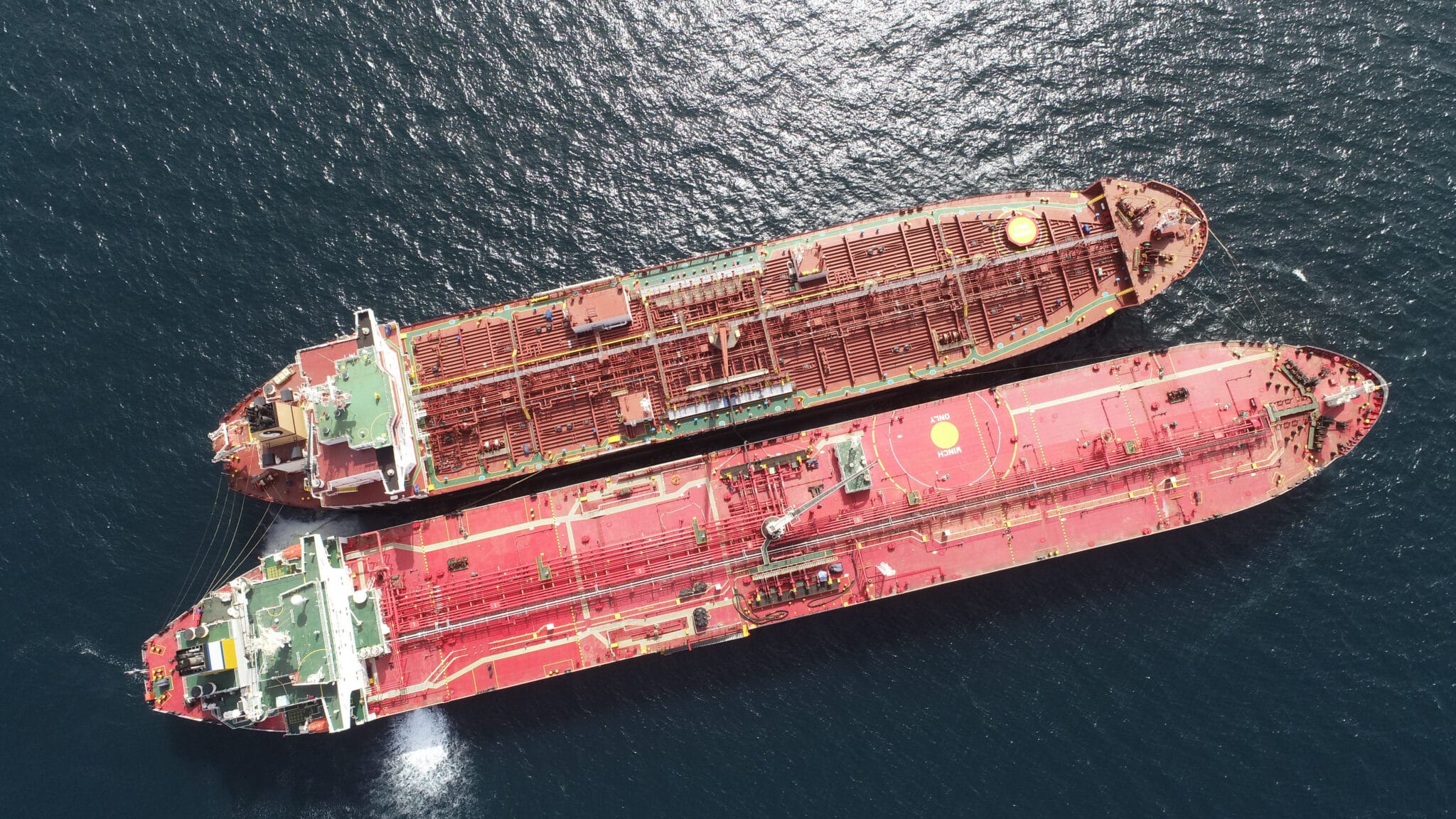
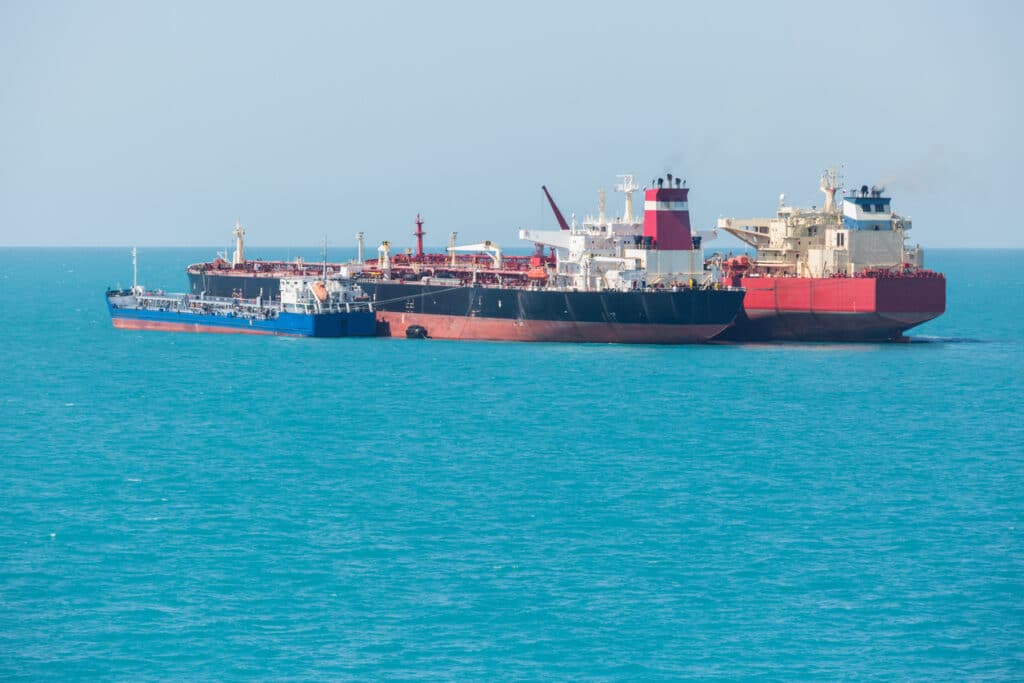
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional STS Transfers?
Conventional STS transfers are the most common type, where two vessels moor side-by-side to facilitate the transfer of cargo, typically bulk oil or gas. This method is advantageous for large volumes, as it allows for efficient and rapid transfer without the need for port facilities. However, buyers must consider the weather conditions, as operations are susceptible to adverse weather, which can lead to delays and potential spills if not managed properly.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
When Is Emergency STS Transfer Necessary?
Emergency STS transfers are critical in situations where a vessel is compromised, such as leaking cargo or mechanical failure. This type of transfer aims to mitigate environmental risks and ensure the safe retrieval of valuable cargo. For B2B buyers, the urgency of these operations can be beneficial, but the associated risks are higher due to the compromised nature of the vessels involved. Buyers should prioritize service providers with proven emergency protocols and experienced personnel.
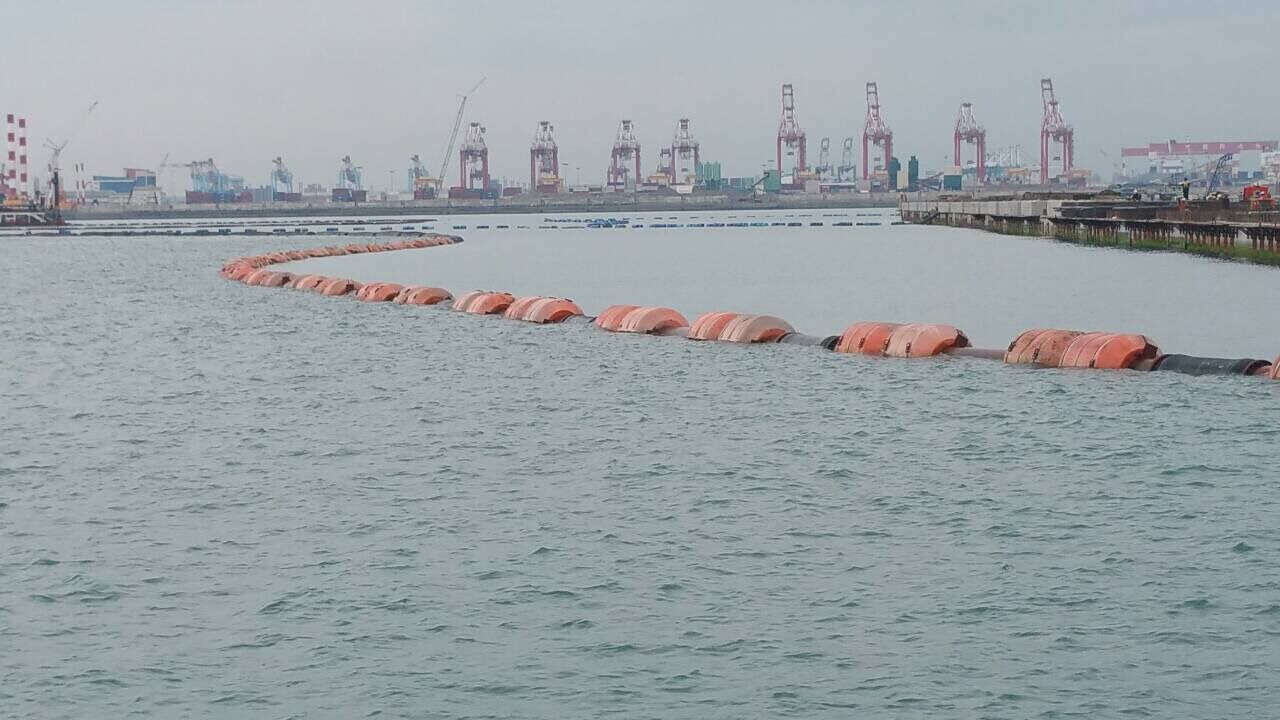
How Does Bunkering STS Work?
Bunkering STS is a specialized operation focusing on the transfer of fuel from bunker vessels to operational ships at sea. This method allows vessels to refuel without entering port, significantly reducing downtime and associated costs. Buyers should evaluate the efficiency of the bunkering process and the reliability of suppliers, as timely fuel delivery is crucial for maintaining operational schedules. Coordination and timing are essential, making it vital to work with experienced partners.
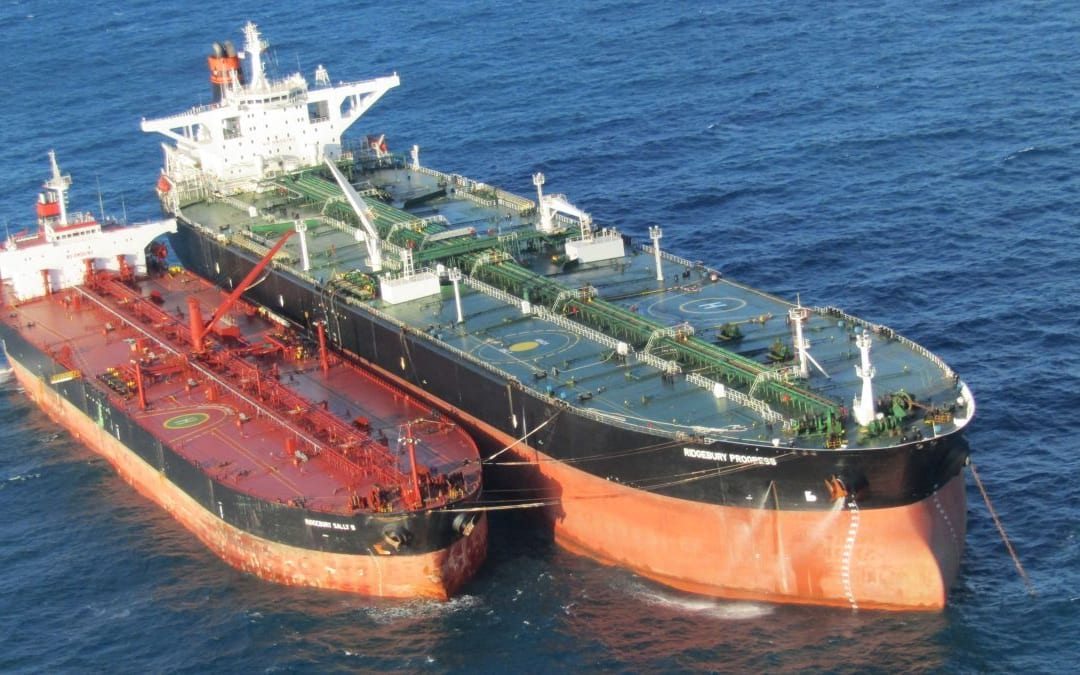
What Is the Purpose of Lightering STS?
Lightering STS operations are employed when larger vessels need to offload cargo to smaller vessels to comply with port draught restrictions. This process is essential for accessing ports that cannot accommodate larger vessels, allowing for seamless logistics and supply chain management. While lightering can facilitate access to more ports, it involves additional handling, which could introduce delays. Buyers should assess the logistical capabilities of their partners to ensure smooth operations.
Why Are Chemical STS Transfers Unique?
Chemical STS transfers are distinct due to the stringent safety protocols required for handling hazardous materials. This type of transfer is essential for the chemical industry, where regulatory compliance and safety are paramount. Buyers in this sector must ensure that their service providers adhere to all safety guidelines and possess the necessary certifications. The added regulatory compliance can lead to higher costs, but it is essential for maintaining safety and environmental standards.
Key Industrial Applications of sts transfer
| Industrie/sector | Specific Application of sts transfer | Waarde/Voordeel voor het bedrijf | Belangrijkste overwegingen bij de inkoop voor deze toepassing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Olie & gas | Lightering operations for large tankers | Enables large vessels to offload cargo in deep water, avoiding port congestion | Compliance with international safety standards and regulations |
| Maritieme logistiek | Bunkering operations at sea | Reduces downtime and costs associated with port bunkering | Availability of certified bunkering vessels and equipment |
| Chemische Productie | Transfer of hazardous materials | Ensures safe and efficient transfer of chemicals, minimizing risk of spills | Need for specialized equipment and trained personnel |
| Renewable Energy | Transfer of biofuels | Facilitates the movement of renewable energy products, supporting sustainability goals | Sourcing eco-friendly and compliant transfer systems |
| Shipping & Transportation | Efficient cargo redistribution | Enhances supply chain efficiency by redistributing cargo between vessels | Logistics planning and coordination with experienced STS operators |
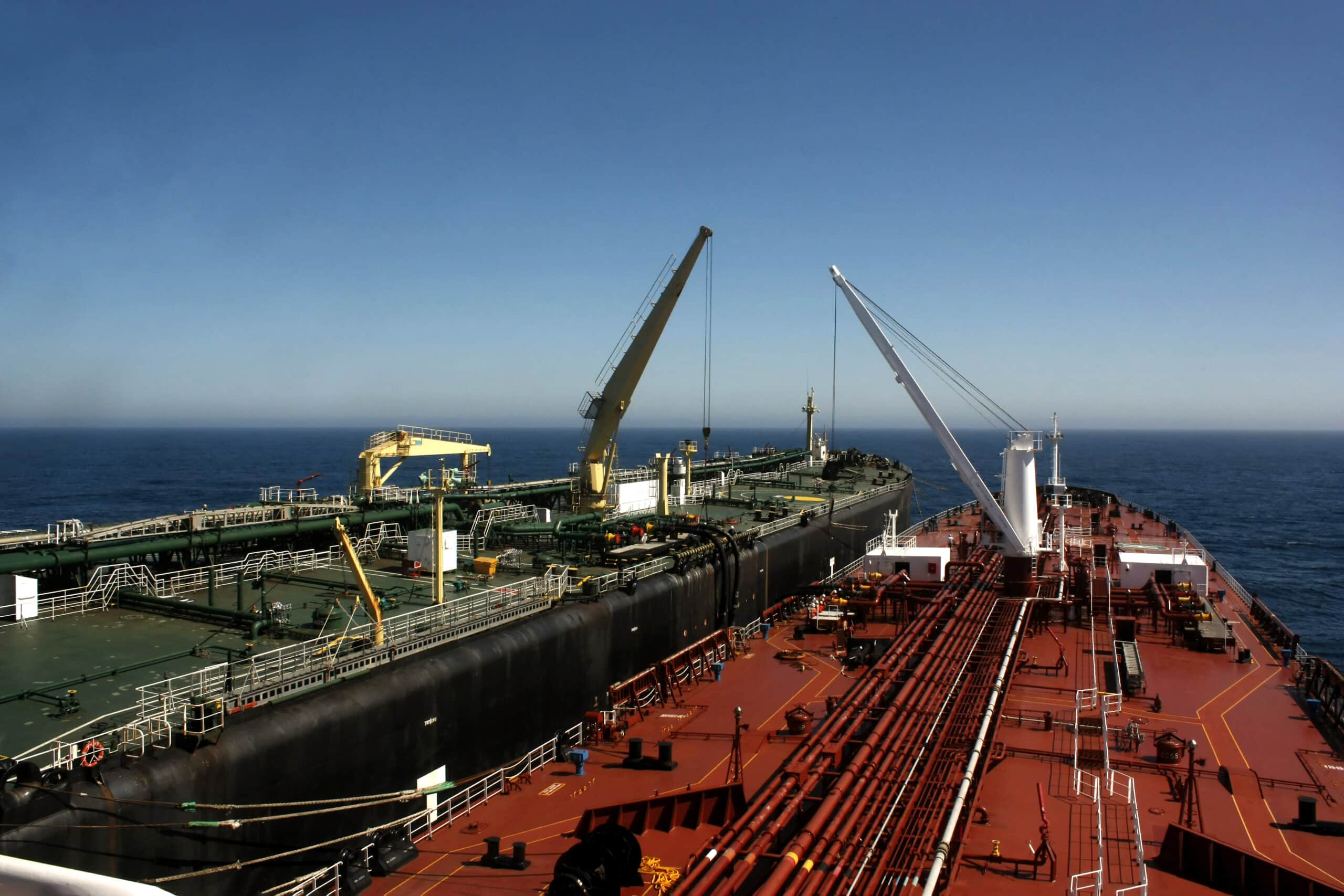
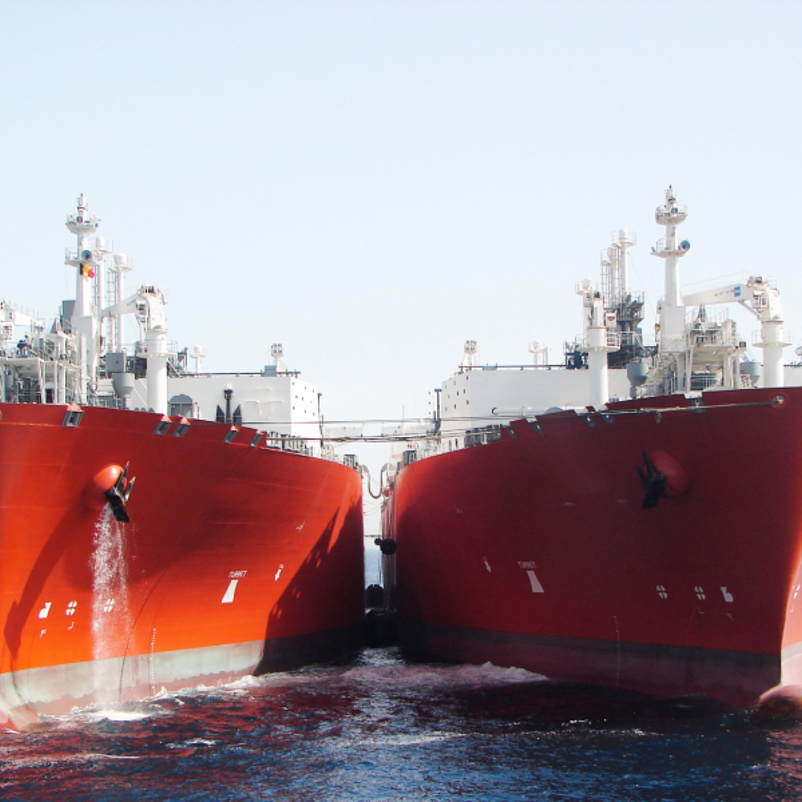
How is STS Transfer Utilized in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, STS transfer is crucial for lightering operations, where large tankers offload crude oil or liquefied natural gas in deep waters. This process helps vessels comply with port draught restrictions, enabling them to reach ports without incurring hefty fees or delays. International buyers must ensure that their operations adhere to the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) safety regulations and have a robust STS operation plan to mitigate risks associated with spills and equipment malfunctions.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
What Role Does STS Transfer Play in Maritime Logistics?
Within maritime logistics, STS transfer facilitates efficient bunkering operations at sea, allowing ships to refuel without docking at ports. This practice significantly reduces vessel downtime and associated costs, making it a preferred method for shipping companies. Buyers should prioritize sourcing certified bunkering vessels equipped with the latest technology to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and to optimize operational efficiency.
How is STS Transfer Applied in Chemical Manufacturing?
The chemical manufacturing industry leverages STS transfer for the safe movement of hazardous materials between vessels. This method minimizes the risk of spills and accidents, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations. For international buyers, it is essential to partner with suppliers who have specialized equipment and trained personnel capable of handling hazardous cargo, as well as adhering to local and international safety standards.
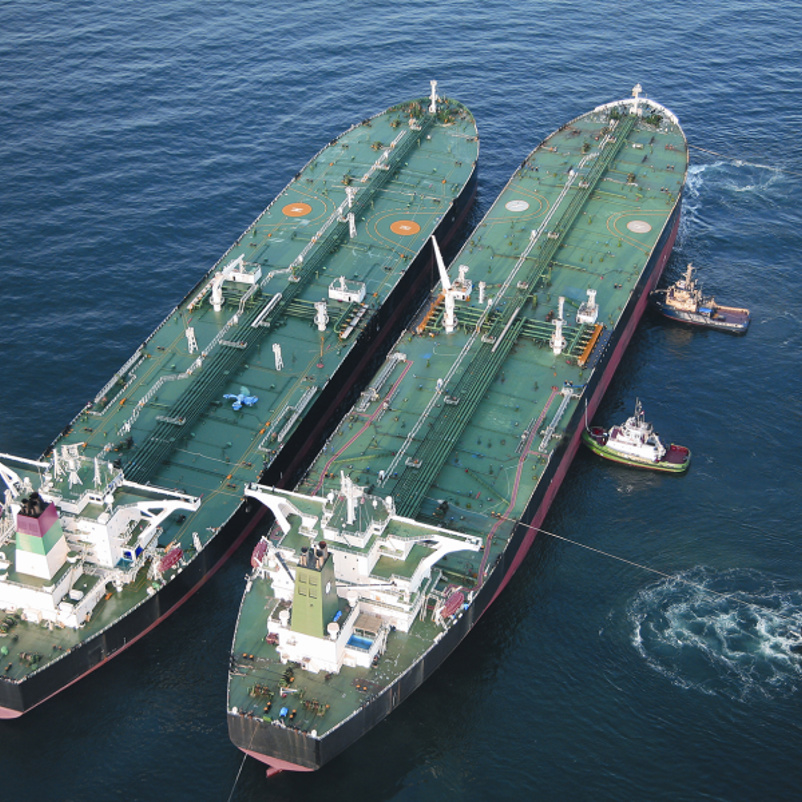
What Benefits Does STS Transfer Offer to Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, STS transfer is employed for the movement of biofuels, which supports the transition to sustainable energy sources. This process allows for the efficient transfer of biofuels from production facilities to distribution points, thereby enhancing supply chain responsiveness. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing eco-friendly and compliant transfer systems to align with their sustainability initiatives and regulatory requirements.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
How Does STS Transfer Improve Efficiency in Shipping & Transportation?
Shipping and transportation companies utilize STS transfer to redistribute cargo between vessels, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency. This application is particularly beneficial when dealing with oversized cargo that may not fit into standard port facilities. B2B buyers must consider logistics planning and coordination with experienced STS operators to ensure smooth operations and compliance with all safety protocols, thus safeguarding their investments and cargo integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sts transfer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance Challenges in STS Transfers
Het probleem:
B2B buyers often struggle with the complex regulatory landscape surrounding STS (Ship-to-Ship) transfers, especially when operating across international waters. Each region may have different compliance requirements set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and local maritime authorities. Buyers may find themselves at risk of incurring fines or facing operational delays if they fail to comply with these regulations, particularly regarding pollution prevention and safety protocols. This can lead to financial losses and damage to their company’s reputation.
De oplossing:
To effectively navigate regulatory compliance, it is crucial for buyers to invest in comprehensive training for their crew and operational staff. This training should cover the specific regulations applicable to each region where STS operations will occur. Additionally, establishing a robust compliance management system that includes regular audits and updates on regulatory changes is vital. Buyers should also consider partnering with legal experts or maritime consultants who specialize in international shipping regulations. This proactive approach will ensure that all necessary documentation, such as oil record books and STS operation plans, are meticulously maintained, thus minimizing the risk of non-compliance.
Scenario 2: Managing Equipment Malfunctions During STS Transfers
Het probleem:
Equipment malfunctions during STS transfers can be a significant pain point for buyers, potentially leading to operational delays and safety hazards. A malfunction could occur due to inadequate maintenance of transfer equipment, such as hoses and pumps, or from miscommunication between the two vessels. Such issues can result in cargo spills, which not only pose environmental risks but also lead to costly cleanup operations and legal liabilities.
De oplossing:
To mitigate the risk of equipment malfunctions, buyers should implement a rigorous maintenance schedule for all equipment involved in STS operations. This includes regular inspections and testing of hoses, pumps, and safety equipment to ensure they meet operational standards. Furthermore, employing advanced communication technologies can enhance coordination between vessels during the transfer process. It is also advisable to have contingency plans in place, such as backup equipment and trained personnel on standby, to address any unexpected issues that may arise during operations. By prioritizing equipment reliability and effective communication, buyers can significantly reduce the likelihood of malfunctions and their associated risks.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Time Delays in STS Operations
Het probleem:
International B2B buyers often face time delays in STS operations, which can lead to increased costs and missed market opportunities. These delays can stem from various factors, including adverse weather conditions, inefficient logistical coordination, and the complex nature of the transfer process itself. For companies operating in fast-paced markets, such delays can significantly impact their competitive edge and profitability.
De oplossing:
To overcome time delays, buyers should streamline their logistical processes by employing detailed planning and scheduling for STS operations. Utilizing advanced software solutions for real-time tracking and management can enhance visibility and coordination between vessels. Additionally, creating a flexible operational strategy that accounts for weather fluctuations and other potential disruptions can help minimize delays. Buyers should also engage with reliable service providers that have a proven track record of efficiency in STS operations. By focusing on operational efficiency and adaptability, B2B buyers can reduce delays and enhance their overall performance in the marketplace.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sts transfer
What Materials Are Best for Ship-to-Ship (STS) Transfers?
In the realm of Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfers, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in STS operations, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures. It is particularly effective in environments where exposure to seawater and various cargoes is a concern.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for long-term applications, but it comes at a higher cost compared to alternatives like carbon steel. Manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized techniques, which may increase lead times.
Invloed op de toepassing:
Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including crude oil and liquefied gases, making it suitable for diverse cargo types. Its resistance to corrosion ensures a longer lifespan for equipment involved in STS operations.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with ASTM and DIN standards for stainless steel grades. In markets like Africa and South America, sourcing local suppliers who can meet these standards may be beneficial.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and ability to withstand mechanical stress. However, it has lower corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel, making it less suitable for prolonged exposure to harsh marine environments.
Pros & Cons:
Carbon steel is more cost-effective than stainless steel, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can lead to increased maintenance costs and shorter equipment lifespan.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
Invloed op de toepassing:
While carbon steel can be used for certain cargoes, it is less suitable for corrosive materials. Its compatibility with non-corrosive bulk cargoes makes it a viable option for specific STS applications.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding material specifications and corrosion protection measures. Compliance with JIS standards may be particularly relevant for buyers in Asia.
3. Polyurethane
Key Properties:
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. It can withstand a range of temperatures and is often used in hoses and seals for STS operations.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of polyurethane makes it easy to handle, and its flexibility allows for easier installation. However, it may not be as durable as metal alternatives, particularly in high-pressure applications.
Invloed op de toepassing:
Polyurethane is ideal for transferring various liquid cargoes, including chemicals and oils. Its resistance to abrasion and chemicals ensures reliable performance in STS operations.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Buyers should ensure that the polyurethane products meet relevant international standards for chemical compatibility. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from manufacturers who adhere to ISO certifications can enhance reliability.
4. Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber is commonly used in fenders and hoses for STS operations due to its excellent shock absorption and flexibility. It can handle a wide range of temperatures but may degrade over time when exposed to certain chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber is cost-effective and provides excellent cushioning during vessel berthing. However, its susceptibility to wear and tear, especially in harsh marine environments, can lead to frequent replacements.
Invloed op de toepassing:
Rubber is suitable for applications involving various liquids but may not be ideal for corrosive substances. Its compatibility with standard marine applications makes it a common choice for STS operations.
Overwegingen voor internationale kopers:
Buyers should consider local climate conditions that may affect rubber performance. Compliance with ASTM standards for rubber products is essential for ensuring quality and safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for STS Transfer
| Materiaal | Typical Use Case for STS Transfer | Belangrijkste voordeel | Belangrijkste nadeel/beperking | Relatieve kosten (laag/gemiddeld/hoog) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roestvrij staal | Hoses, fittings, and storage tanks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Hoog |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components and tanks | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Polyurethaan | Hoses and seals | Lightweight and flexible | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Rubber | Fenders and flexible hoses | Good shock absorption | Wear and tear in harsh conditions | Laag |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials best suited for STS operations, enabling informed decision-making that aligns with both operational needs and regulatory compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sts transfer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for STS Transfer Equipment?
The manufacturing process for equipment used in Ship to Ship (STS) transfer operations involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of cargo transfer. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for STS Transfer Equipment?
Material preparation is the first step, where high-grade materials such as marine-grade stainless steel and specialized polymers are sourced. These materials are selected for their resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand harsh marine environments. Quality suppliers typically provide certifications for these materials, ensuring they meet international standards.
After sourcing, the materials undergo inspection for defects and compliance with specified standards. This initial quality control (IQC) is crucial, as it lays the foundation for the entire manufacturing process. Suppliers should provide documentation proving the materials’ compliance with relevant regulations, such as those from the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the American Petroleum Institute (API).
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Manufacturing STS Transfer Equipment?
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into functional components. Techniques such as casting, forging, and machining are commonly employed. For instance, marine hoses used in STS operations may be extruded or molded to specific dimensions, ensuring they can handle high pressures and flow rates.
During this stage, manufacturers often utilize computer numerical control (CNC) machines for precision. This technology ensures that components are manufactured to exact specifications, reducing the risk of malfunctions during operations. Regular inspections during this phase (In-Process Quality Control, or IPQC) help catch any deviations early, saving time and resources.
How is the Assembly Process Conducted for STS Transfer Equipment?
The assembly process is where individual components come together to form the complete system. This stage often involves skilled labor, as proper assembly is crucial for ensuring the integrity and safety of the equipment. Assemblers must follow detailed work instructions and checklists to ensure each step is performed correctly.
Quality checkpoints during assembly are vital. For instance, after assembling each component, a visual inspection may be conducted to check for alignment and secure fittings. Furthermore, manufacturers should maintain a record of assembly procedures and any discrepancies for transparency and traceability.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in STS Transfer Equipment Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and appearance of the equipment. Techniques such as painting, coating, or galvanizing are commonly used to protect against corrosion and wear. Specialized coatings may be applied to components that will be exposed to harsh marine environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Before the final product is shipped, a Final Quality Control (FQC) check is performed. This comprehensive inspection assesses the entire assembly against specifications and regulatory requirements. Documentation of these inspections is essential for B2B buyers, providing assurance that the products meet international safety and quality standards.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
What International Standards and Certifications Are Relevant for STS Transfer Equipment?
B2B buyers should be aware of various international standards that govern the manufacturing and quality assurance of STS transfer equipment. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized standards, focusing on quality management systems and ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
Industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area or API standards for oil and gas equipment, are also critical. These certifications demonstrate that products comply with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these standards is vital. This knowledge helps in selecting suppliers who adhere to recognized quality assurance protocols, ensuring the reliability of the equipment.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality control in the manufacturing process of STS transfer equipment involves several checkpoints to ensure compliance with international standards. These include:
Illustrative image related to sts transfer
- Inkomende kwaliteitscontrole (IQC): Verification of raw materials against specifications and standards.
- Kwaliteitscontrole tijdens het proces (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product to ensure it meets all quality and regulatory standards.
Each of these checkpoints should be documented, providing a clear audit trail for buyers. Buyers should request these quality records from suppliers to verify adherence to quality protocols.
Hoe kunnen B2B-inkopers de kwaliteitscontrole van leveranciers controleren?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. One effective method is conducting audits, where buyers can assess the manufacturing facilities, review quality control processes, and ensure compliance with international standards.
Additionally, requesting quality reports and certifications can provide insights into a supplier’s commitment to quality. Third-party inspections can also be beneficial, offering an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s operations and quality assurance practices.
It is essential for buyers to engage in open communication with suppliers about their quality control practices. Understanding any nuances, especially in international contexts, can help mitigate risks associated with product quality and compliance.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various certification and quality control nuances when sourcing STS transfer equipment. Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that affect the certification process. For instance, products intended for the European market must comply with CE marking regulations, while those in the Middle East may require adherence to local standards.
Buyers should also consider the language barrier when reviewing documentation and certifications. Ensuring that all quality assurance documents are available in a language that is understandable to the buyer can prevent miscommunication and compliance issues.
Furthermore, cultural differences may influence the interpretation of quality standards and practices. Buyers should conduct thorough research and possibly engage local experts to better understand the quality landscape in their target regions.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for STS transfer equipment is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient operations in their maritime activities.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sts transfer’
To streamline your procurement process for ship-to-ship (STS) transfer services, this practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist. Each step is designed to help you navigate the complexities of STS operations and ensure you partner with reliable service providers.
Stap 1: Je technische specificaties definiëren
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for your STS transfer needs. This includes understanding the types of cargo to be transferred (e.g., crude oil, liquefied gas), the size of vessels involved, and any environmental considerations. Having these details upfront helps potential suppliers tailor their proposals to meet your operational requirements.
Stap 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that any supplier you consider adheres to international regulations and guidelines, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL). Compliance is essential to avoid legal liabilities and ensure safe operations. Request documentation that verifies their adherence to these standards.
Stap 3: Potentiële leveranciers evalueren
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Look for company profiles, case studies, and references from other clients in similar industries or regions. This will give you insights into their reliability and performance history. Additionally, assess their experience with STS operations, particularly in your target geographical areas.
Stap 4: Verify Equipment and Technology
Inspect the equipment and technology used by potential suppliers for STS operations. Key equipment includes fenders, hoses, and pumping systems. Make sure these assets are well-maintained and meet the operational standards required for safe and efficient transfers. Inquire about their maintenance protocols to ensure reliability during operations.
Stap 5: Assess Risk Management Practices
Understanding a supplier’s risk management protocols is vital for the safety of your cargo and crew. Inquire about their contingency plans for emergencies, such as equipment malfunctions or adverse weather conditions. A robust risk management strategy should include regular training for crew members and detailed operational plans to mitigate potential hazards.
Stap 6: Review Insurance Coverage
Confirm that the supplier has adequate insurance coverage for STS operations. This should include liability coverage for cargo loss or damage, environmental pollution, and any accidents that may occur during the transfer. Reviewing their insurance policies protects your investment and provides peace of mind during the operation.
Stap 7: Onderhandelen over voorwaarden en condities
Finally, negotiate the terms and conditions of the STS transfer agreement. Pay attention to pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that the contract includes clear clauses regarding liability, insurance, and compliance with safety standards. A well-defined agreement minimizes misunderstandings and sets clear expectations for both parties.
By following this checklist, you can systematically approach the procurement of STS transfer services, ensuring that you choose a supplier capable of meeting your needs while adhering to the highest safety and regulatory standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sts transfer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in STS Transfer Operations?
Understanding the cost structure involved in Ship to Ship (STS) transfer operations is crucial for international buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materialen: This encompasses the marine hoses, fenders, and other equipment required for safe cargo transfer. The quality and specifications of these materials can significantly influence pricing.
-
Arbeid: Skilled personnel are essential for executing STS operations. Costs can vary based on the crew’s experience and the complexity of the transfer. Additionally, safety training and compliance with international regulations add to labor costs.
-
Productie Overhead: This includes expenses related to the maintenance and operation of transfer equipment, such as cranes and pumps. Regular inspections and certifications are necessary to ensure operational safety and compliance, impacting overall costs.
-
Gereedschap: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized operations, particularly when dealing with different cargo types or sizes. The need for tailored solutions can increase upfront costs.
-
Kwaliteitscontrole (QC): Adhering to international safety and environmental standards requires stringent QC measures. This involves regular audits, documentation, and the potential for additional testing, all of which contribute to the overall cost.
-
Logistiek: Transporting vessels to and from the STS location incurs costs, including fuel, port fees, and insurance. These logistics expenses can vary widely depending on the distance and conditions of the operation.
-
Marge: Suppliers typically include a margin in their pricing to cover risks and ensure profitability. Buyers should be aware that margins can vary based on the supplier’s reputation and service quality.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect STS Transfer Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of STS transfer operations:
-
Volume/MOQ (minimum bestelhoeveelheid): Larger volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs, making it advantageous for buyers who can commit to higher quantities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges during the procurement process.
-
Materialen: The choice of materials impacts both cost and quality. High-quality materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to savings in the long run through reduced maintenance and enhanced safety.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with ISO certifications or other industry standards may charge a premium. However, these certifications often translate to higher reliability and lower risk during operations.
-
Factoren van leveranciers: The supplier’s location, reputation, and service capabilities can affect pricing. Suppliers with extensive experience in STS operations may command higher prices but offer better service and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade is essential. Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in STS Transfer?
To achieve cost-efficiency in STS transfer sourcing, consider the following strategies:
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understanding market rates and the competitive landscape can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not only the initial costs but also the long-term expenses associated with maintenance, compliance, and potential delays. A lower upfront price may not always be the best value.
-
Build Strong Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a solid rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing, preferential treatment, and improved service.
-
Be Clear About Requirements: Clearly define your needs to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs or delays.
-
Onderhandelen over voorwaarden: Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and any penalties for delays. Flexible terms can provide significant savings and operational efficiencies.
-
Consider Local Regulations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional regulations that may influence costs, such as tariffs or import duties.
Conclusion: Understanding STS Transfer Pricing is Essential for B2B Buyers
Navigating the complexities of STS transfer pricing requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and influencers. By leveraging negotiation strategies and maintaining a focus on total cost of ownership, international buyers can optimize their procurement processes and ensure successful STS operations. Always consult with experienced suppliers and industry experts to make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with STS transfers.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, specific operational requirements, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct due diligence before finalizing contracts.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
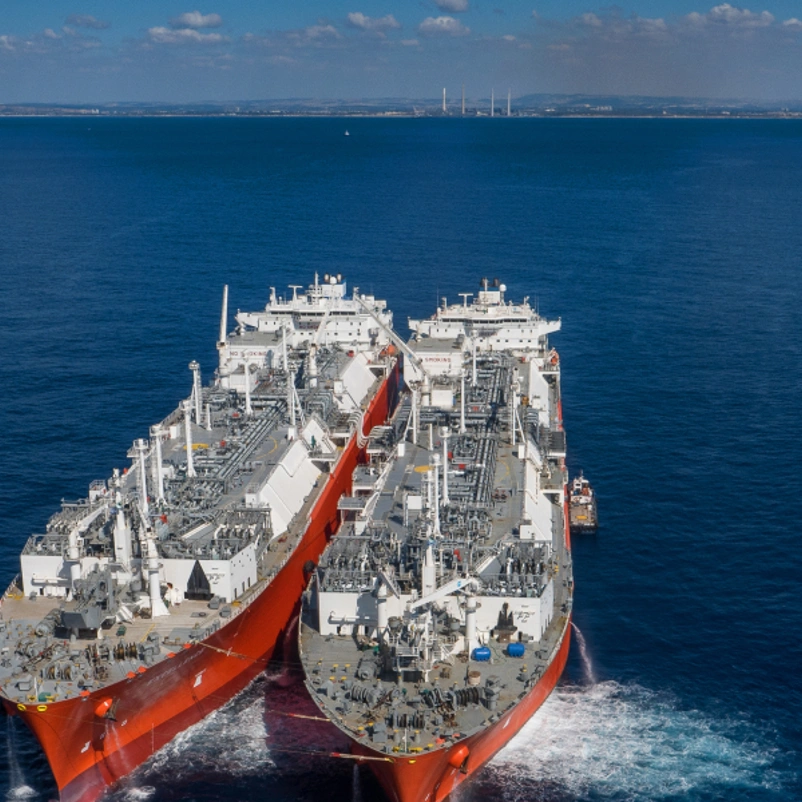
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sts transfer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to STS Transfer in Maritime Operations
As international trade continues to evolve, businesses are presented with various methods for transporting bulk cargo across maritime routes. Ship to Ship (STS) transfer, commonly utilized for transferring oil and liquefied gas, is just one of several options available to companies. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of alternative solutions is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their operations and mitigate risks. Below is a comparative analysis of STS transfer against two viable alternatives: Shore-to-Ship (S2S) transfer and Floating Storage and Offloading Units (FSO).
| Vergelijkingsaspect | STS Transfer | Shore-to-Ship (S2S) Transfer | Floating Storage and Offloading (FSO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prestaties | High efficiency for large cargo volumes, but weather-dependent. | Reliable for consistent delivery; affected by port congestion. | Excellent for continuous operation; ideal for remote locations. |
| Kosten | Cost-effective for large vessels, but can incur extra costs due to delays. | Generally lower costs but varies with port fees. | High initial investment, but lower operational costs over time. |
| Gemak van implementatie | Requires skilled crew and regulatory compliance; complex logistics. | Relatively straightforward; fewer logistical challenges. | Requires specific site conditions; more complex setup. |
| Onderhoud | Regular checks and adherence to safety protocols needed. | Minimal maintenance; primarily involves shore facilities. | Requires ongoing maintenance of storage and offloading equipment. |
| Beste gebruikscasus | Ideal for large tankers unable to enter ports. | Best for smaller vessels needing quick access to cargo. | Suitable for offshore oil fields or areas with limited port access. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Shore-to-Ship (S2S) Transfer?
Shore-to-Ship (S2S) transfer is a method where cargo is directly transported from shore facilities to vessels at port. This approach offers a streamlined process for smaller vessels, allowing for efficient loading and unloading. One of the primary advantages of S2S transfer is its reliability, as it is less susceptible to the challenges faced at sea, such as adverse weather. However, S2S transfer can be hampered by port congestion and high docking fees, which may lead to delays and increased operational costs.
How Does Floating Storage and Offloading (FSO) Work, and What Are Its Limitations?
Floating Storage and Offloading Units (FSO) are specialized vessels designed to store and process hydrocarbons offshore. They can continuously offload cargo, making them ideal for remote locations where traditional port access is limited. The primary advantage of FSOs is their ability to operate independently of port facilities, reducing the need for costly onshore infrastructure. However, the initial setup costs can be significant, and they require specialized equipment and maintenance, which could be a drawback for companies with limited budgets.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the appropriate cargo transfer method depends on several factors, including the type of cargo, operational budget, and logistical capabilities. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs, such as the volume of cargo to be transferred, the geographical challenges of their routes, and the regulatory requirements of their operations. By carefully considering these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency while minimizing risks and costs. Ultimately, aligning the chosen method with their strategic goals will ensure optimal performance in their maritime operations.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
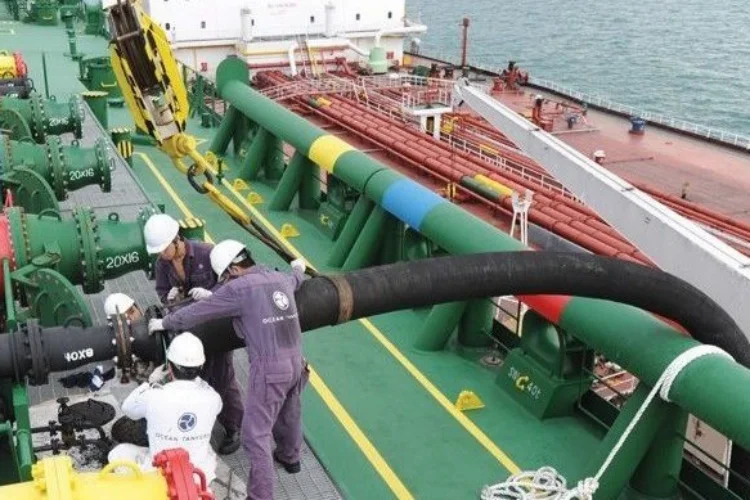
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sts transfer
What Are the Key Technical Properties Important for STS Transfer?
When engaging in Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer operations, several technical specifications are critical to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. Here are some essential properties:
1. Material Grade of Hoses
The hoses used in STS operations must meet specific material grades, often made from high-grade rubber or composite materials. This ensures they can withstand the corrosive nature of crude oil and liquefied gases. The importance of material grade lies in its role in preventing leaks and ruptures, which could lead to environmental disasters and financial losses.
2. Pressure Tolerance
Pressure tolerance is a crucial specification for the hoses and pumps utilized in STS transfers. Typically, these systems must handle pressures ranging from 10 to 20 bar, depending on the type of cargo. High-pressure tolerance is vital for ensuring safe cargo transfer without risking equipment failure or spills.
3. Temperatuurbestendigheid
The ability of equipment to withstand varying temperatures is essential, especially when dealing with liquefied gases that may require cryogenic conditions. Equipment must be rated for specific temperature ranges to prevent material degradation, which could compromise the integrity of the cargo transfer.
4. Flow Rate Capacity
Flow rate capacity indicates how quickly cargo can be transferred between vessels. This is often measured in cubic meters per hour (m³/h) and can significantly impact operational efficiency. Understanding flow rate is essential for planning operations, as it affects turnaround time and associated costs.
5. Draught Requirements
Draught refers to the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the ship’s hull. It is crucial for determining whether a vessel can safely approach a port or transfer location. Knowledge of draught requirements helps in selecting appropriate vessels for STS operations, ensuring compliance with local regulations and preventing grounding incidents.
6. Safety Standards Compliance
Compliance with international safety standards, such as those set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), is paramount. This encompasses equipment certification, crew training, and operational protocols. Adhering to safety standards minimizes risks associated with STS operations, protecting both personnel and the environment.
What Common Trade Terms Should Buyers Understand in STS Transfer?
Understanding the specific jargon used in STS transfer operations can greatly enhance communication and negotiation between B2B buyers and service providers. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of STS, buyers may deal with OEMs for specialized hoses or pumps that meet industry standards. Familiarity with OEMs can help ensure that the equipment used is reliable and compliant.
2. MOQ (minimale bestelhoeveelheid)
MOQ defines the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or understocking crucial equipment for STS operations.
3. RFQ (Offerteaanvraag)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. In STS operations, issuing RFQs can help buyers compare prices and terms from different suppliers, enabling informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
4. Incoterms (internationale handelsvoorwaarden)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms used to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. They define who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs during the transfer of goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions in STS to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth operations.
5. Lightering
This term refers to the process of transferring cargo from a larger vessel to a smaller one. Lightering is a common practice in STS operations, especially when draught restrictions at ports require cargo to be offloaded to smaller vessels for docking.
6. Bunkeren
Bunkering involves the supply of fuel to ships. In the context of STS, it often occurs during cargo transfer operations, allowing vessels to refuel at sea rather than waiting for port access. This practice can save time and reduce operational costs, making it an essential aspect of STS logistics.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of STS operations more effectively, leading to safer and more efficient cargo transfers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sts transfer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the STS Transfer Sector?
The Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer sector is witnessing significant growth driven by global demand for energy resources, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key market drivers include the increasing need for efficient logistics solutions for oil and gas transportation due to port congestion and draught restrictions. The rise of floating storage units and the need for lightering operations to facilitate larger vessels navigating shallow ports are also influencing market dynamics.
Emerging B2B technology trends such as digitalization and automation are reshaping the STS transfer landscape. Remote monitoring systems and advanced analytics are being adopted to enhance safety and efficiency during operations. Furthermore, blockchain technology is gaining traction for ensuring transparency in cargo transfer and compliance with international regulations. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can integrate these technologies into their operations, offering a competitive edge in terms of speed and reliability.
Additionally, the STS sector is adapting to geopolitical changes, particularly in oil-producing regions. Trade agreements and international sanctions can impact sourcing strategies, necessitating that buyers remain agile and informed about global market conditions. Overall, international B2B buyers must prioritize partnerships with suppliers who can navigate these complexities while ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the STS Transfer Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical concern in the STS transfer sector, particularly given the environmental impact associated with oil and gas operations. The potential for spills and pollution during STS operations necessitates strict adherence to environmental regulations and best practices. International bodies, such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO), have established guidelines to mitigate risks, but the onus also lies on companies to implement robust sustainability initiatives.
Ethical sourcing is increasingly becoming a priority for B2B buyers, who are looking to partner with suppliers committed to minimizing their environmental footprint. This includes investing in ‘green’ certifications and materials that support eco-friendly operations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
Moreover, the industry is witnessing a shift toward adopting alternative energy sources, such as LNG (liquefied natural gas), which can significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional fuels. Buyers who prioritize sustainability in their sourcing strategies not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles but also position themselves favorably in a market that increasingly values environmental stewardship.
What Is the Evolution of STS Transfer in the B2B Context?
The STS transfer practice has evolved significantly since its inception, initially emerging as a necessary solution for transporting bulk cargo efficiently. Historically, lightering operations were primarily used to enable large vessels to navigate shallow ports, a practice that dates back centuries.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
In recent decades, technological advancements have revolutionized STS operations, with innovations in safety protocols, equipment, and real-time monitoring systems enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing risks. The increasing complexity of global supply chains has further driven the demand for STS services, as companies seek to optimize their logistics and reduce operational costs.
As the market continues to evolve, the focus on sustainability and compliance will likely shape the future of STS transfer, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed and adapt to these changes. Understanding the historical context of STS transfer provides valuable insights into current market dynamics and future trends, enabling buyers to make informed decisions in this critical sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sts transfer
-
How do I ensure the safety of my STS transfer operations?
To ensure the safety of STS transfer operations, it is crucial to adhere to international regulations set by bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL). Implementing a thorough STS Operation Plan that outlines procedures and responsibilities is essential. Regular training for crew members on equipment handling and emergency protocols can mitigate risks. Additionally, conducting pre-transfer safety checks and having an experienced person in overall advisory control (POAC) will enhance operational safety. -
What is the best vessel type for STS transfer operations?
The best vessel type for STS transfer operations typically includes specialized tankers designed for bulk cargo, such as crude oil or liquefied gas. These vessels, often referred to as mother and daughter vessels, should meet specific size and draught requirements based on the transfer location. Selecting vessels that are equipped with advanced cargo handling systems, including robust pumping and hose connection technologies, ensures efficient and safe operations. Additionally, vessels that comply with international safety and environmental regulations will enhance operational reliability. -
What should I consider when vetting STS service providers?
When vetting STS service providers, it’s important to assess their experience and track record in conducting safe and efficient operations. Request documentation that proves compliance with international safety standards and certifications. Evaluate their fleet capabilities, including the types of vessels available and their equipment specifications. Additionally, inquire about their crisis management protocols and training programs for crew members. Customer testimonials and references can also provide insights into their reliability and service quality. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for STS transfer services?
Typically, STS transfer services do not have a standardized minimum order quantity (MOQ) as it largely depends on the specifics of the operation, such as the cargo type and vessel capacities. However, some service providers may have operational thresholds based on the economic viability of the transfer. It’s advisable to discuss your particular needs with potential service providers to ascertain any operational limits or requirements that may apply to your STS transfers. -
What payment terms are common for international STS transfer contracts?
Payment terms for international STS transfer contracts can vary significantly among service providers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments prior to the transfer, and remaining balances payable upon completion of the operation. It’s essential to negotiate clear terms that reflect the scope of services, potential risks, and the overall value of the operation. Establishing a secure payment method, such as letters of credit or escrow accounts, can further protect both parties in the transaction. -
How do I customize STS transfer services to fit my needs?
Customizing STS transfer services involves discussing your specific operational requirements with the service provider. Factors such as cargo type, transfer location, timing, and any unique safety or regulatory considerations should be addressed. Many providers are willing to tailor their services to accommodate special requests, such as specific equipment needs or enhanced safety protocols. Establishing open communication about your expectations will facilitate a more effective and tailored STS transfer operation. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for STS transfers?
Quality assurance measures for STS transfers should include regular inspections and maintenance of the vessels and equipment used during operations. Implementing a strict adherence to safety protocols and conducting pre-transfer risk assessments are critical. Additionally, maintaining a comprehensive record-keeping system for all transfers, including cargo documentation and incident reports, helps ensure accountability and compliance with international regulations. Periodic audits of operational practices and crew training will further enhance quality assurance. -
How can I manage logistics for STS transfer operations effectively?
Effective logistics management for STS transfer operations involves meticulous planning and coordination between all parties involved. This includes scheduling the transfer to align with weather conditions and vessel availability. It’s crucial to communicate with port authorities and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with local regulations. Utilizing digital platforms for real-time tracking and communication can enhance operational efficiency. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in maritime operations can also streamline the process and mitigate potential delays.
Top 5 Sts Transfer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Breakaway Couplings – Ship to Ship Transfer Solutions
Domein: losbreekkoppelingen.com
Geregistreerd: 2015 (10 jaar)
Inleiding: Ship to Ship (STS) transfer, also known as lightering, involves two storage tankers mooring side-by-side to transfer cargo, typically crude oil and liquefied gas, in open sea or at the outer port limit. Key procedures include lowering fenders, berthing the ships, connecting hoses, and commencing cargo transfer. Safety is paramount, with guidelines from the International Maritime Organization (IMO)…
2. Usebase – Ship-to-Ship Transfer Solutions
Domein: usebase.io
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Inleiding: Ship-to-Ship Transfer (STS) involves the transfer of cargo between two vessels while at sea or at the outer port limit (OPL). It is crucial for transferring crude oil, bulk cargo, or other petroleum products, optimizing port calls, bypassing port congestion, and handling challenging cargoes. Key situations for STS include transferring personnel or equipment, receiving shipments offshore from suppl…
3. Fendercare – Marine Transfer Solutions
Domein: fendercare.com
Geregistreerd: 1996 (29 jaar)
Inleiding: Ship-to-ship transfers, Biofuel STS transfers, LNG ship-to-ship transfers, global STS locations, STS superintendents, marine products including marine fenders, deck equipment, marine hoses, mooring equipment, quayside equipment. Fully equipped bases with hoses, fenders, and ancillary equipment. Over 100 experienced STS superintendents available 24/7. Technical marine assurance support. Support cra…
4. Britannia Pandi – STS Transfer Operations Guide
Domein: britanniapandi.com
Geregistreerd: 1999 (26 jaar)
Inleiding: Ship to ship (STS) transfer operations guidance includes the following key details: 1. Definition: STS transfer involves the transfer of cargo between two ships alongside each other, either stationary or underway. 2. Risks: Heightened risks are associated with STS operations, requiring skill and experience. 3. Protocols: Each ship follows its own protocols integrated into its Safety Management Sys…
5. Marine Insight – Ship to Ship Transfer
Domein: marine-inzicht.nl
Geregistreerd: 2010 (15 jaar)
Inleiding: This company, Marine Insight – Ship to Ship Transfer, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
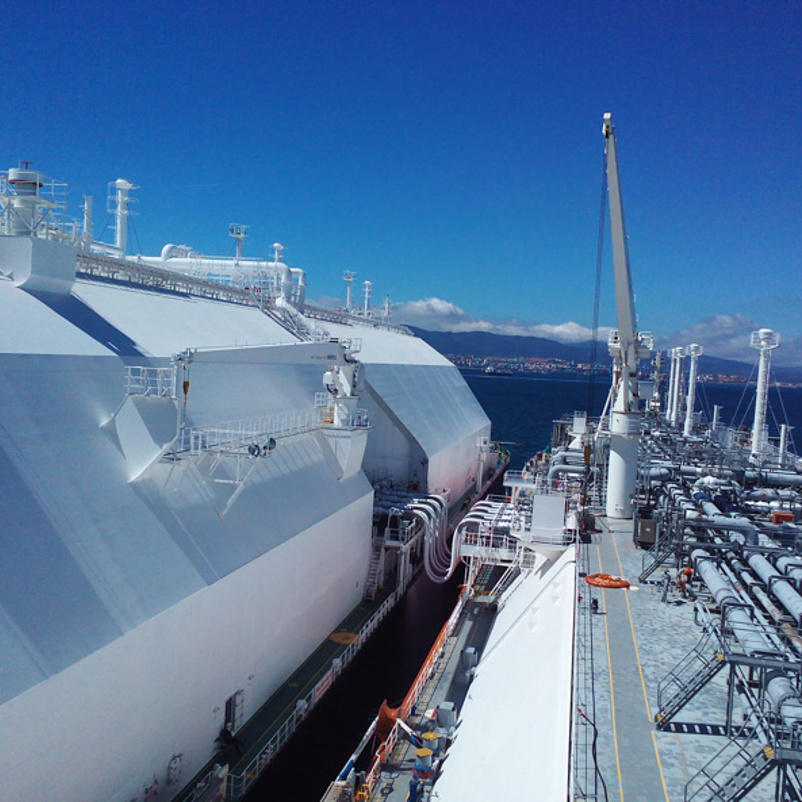
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sts transfer
In summary, the strategic sourcing of Ship to Ship (STS) transfer services is vital for optimizing the logistics of bulk cargo transportation, particularly in regions with varying port capabilities. By utilizing STS operations, businesses can efficiently manage draught restrictions, reduce costly port delays, and ensure timely deliveries of crude oil, liquefied gases, and other bulk commodities. For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of STS operations allows for better risk management and compliance with international regulations, ultimately enhancing supply chain resilience.

Illustrative image related to sts transfer
As the global demand for efficient and sustainable logistics continues to rise, investing in strategic sourcing for STS services will not only streamline operations but also foster partnerships with experienced providers who prioritize safety and environmental stewardship. Embracing these practices will position your business favorably in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Looking ahead, it is essential for businesses to remain proactive in seeking innovative solutions within the STS landscape. Engage with reputable service providers, stay informed about regulatory updates, and consider the implications of technological advancements in maritime operations. By doing so, you can secure a robust and future-ready supply chain that meets the evolving needs of your business.
Belangrijke disclaimer en gebruiksvoorwaarden
⚠️ Belangrijke disclaimer
De informatie in deze gids, inclusief inhoud over fabrikanten, technische specificaties en marktanalyses, is uitsluitend bedoeld voor informatieve en educatieve doeleinden. Het is geen professioneel aankoopadvies, financieel advies of juridisch advies.
Hoewel we al het mogelijke hebben gedaan om de nauwkeurigheid en actualiteit van de informatie te garanderen, zijn we niet verantwoordelijk voor eventuele fouten, weglatingen of verouderde informatie. Marktomstandigheden, bedrijfsgegevens en technische normen kunnen veranderen.
B2B-kopers moeten hun eigen onafhankelijke en grondige due diligence uitvoeren voordat je een aankoopbeslissing neemt. Dit houdt in dat u rechtstreeks contact moet opnemen met leveranciers, certificeringen moet controleren, monsters moet aanvragen en professioneel advies moet inwinnen. Het risico van het vertrouwen op informatie in deze gids wordt uitsluitend gedragen door de lezer.