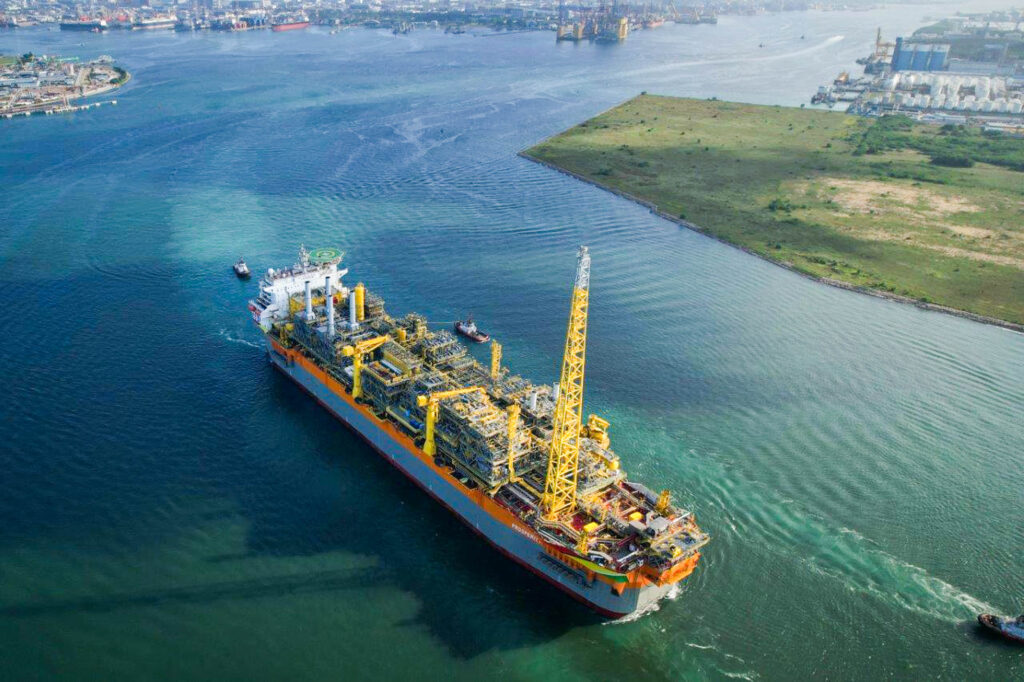
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fpso operation
In an era where the quest for oil and gas resources is increasingly challenging, understanding the intricacies of Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operations is crucial for international B2B buyers. The complexities of sourcing the right FPSO solutions can overwhelm decision-makers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where emerging markets are rapidly evolving. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of FPSO operations, covering essential topics such as types of FPSOs, their various applications, supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements.
By empowering buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide ensures that stakeholders can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and environmental commitments. Whether you are exploring new-build FPSOs for deepwater extraction or considering conversion options for existing vessels, this resource provides clarity on navigating the global FPSO market. The guide is tailored to address the unique challenges faced by buyers from diverse regions, offering strategic solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. With this knowledge at your fingertips, you can confidently approach FPSO operations and leverage them to meet your energy production goals in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Índice
- Top 3 Fpso Operation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fpso operation
- Understanding fpso operation Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of fpso operation
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fpso operation’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for fpso operation
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fpso operation
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fpso operation’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fpso operation Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fpso operation With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fpso operation
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fpso operation Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fpso operation
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fpso operation
- Aviso importante e termos de utilização
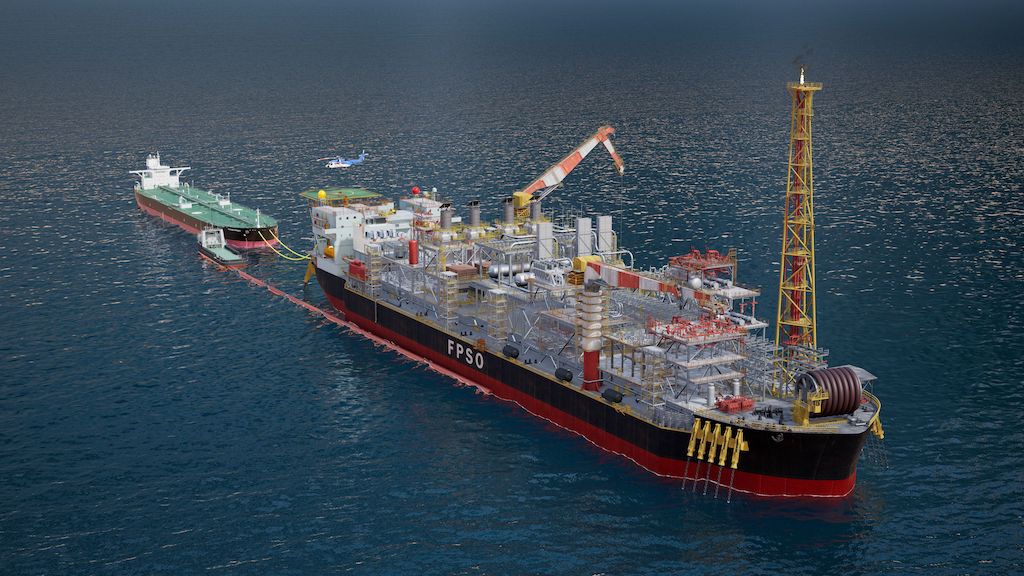
Understanding fpso operation Types and Variations
| Tipo Nome | Principais caraterísticas distintivas | Aplicações B2B primárias | Breves prós e contras para os compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| New-Build FPSO | Custom-designed units, high production capacity (up to 250,000 bpd) | Large-scale oil fields, deepwater exploration | Prós: Tailored solutions, advanced technology. Contras: Higher initial investment. |
| Large Conversion FPSO | Converted from Very Large Crude Carriers (VLCCs), moderate capacity (up to 150,000 bpd) | Mid-size oil fields, existing infrastructure | Prós: Cost-effective, quicker deployment. Contras: Limited customization compared to new builds. |
| Small Conversion FPSO | Smaller vessels, often converted from smaller tankers, lower capacity | Marginal fields, remote locations | Prós: Lower capital expenditure, flexible. Contras: Limited storage and processing capabilities. |
| FPSO with Turret Mooring | Integrated turret for 360° rotation, suited for harsh environments | Deepwater oil extraction, dynamic positioning | Prós: Enhanced stability, improved operational efficiency. Contras: Complex maintenance requirements. |
| FPSO with Emission Solutions | Focus on reducing environmental impact, near-zero emissions technology | Eco-conscious projects, regulatory compliance | Prós: Aligns with sustainability goals, potential cost savings. Contras: May require higher upfront costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of New-Build FPSOs?
New-build FPSOs are custom-designed units capable of handling high production volumes, often exceeding 250,000 barrels per day (bpd). They are constructed from the ground up, allowing for the integration of the latest technologies and operational efficiencies. These units are ideal for large-scale oil fields in deepwater locations, where traditional fixed platforms are impractical. Buyers should consider the initial investment, which is generally higher, but may be offset by long-term operational savings and efficiency gains.
How Do Large Conversion FPSOs Compare?
Large conversion FPSOs are typically repurposed from existing Very Large Crude Carriers (VLCCs) and offer moderate production capacities of up to 150,000 bpd. This type of FPSO is particularly advantageous for mid-sized oil fields or where existing infrastructure can be leveraged. The conversion process is generally quicker than building a new FPSO, making it a cost-effective solution. However, buyers should note that customization options are somewhat limited compared to new builds, which may affect long-term adaptability.
What Are the Advantages of Small Conversion FPSOs?
Small conversion FPSOs are often transformed from smaller tankers and are designed for lower production capacities, making them suitable for marginal fields or remote locations. They offer a lower capital expenditure compared to larger units, making them an attractive option for operators with budget constraints. While these FPSOs provide flexibility and quicker deployment, buyers should be aware of their limited storage and processing capabilities, which may necessitate more frequent offloading.
Why Choose FPSOs with Turret Mooring?
FPSOs equipped with turret mooring systems allow for unrestricted 360° rotation, enabling them to maintain stability in harsh marine environments. This feature is particularly beneficial for deepwater extraction, where dynamic positioning is crucial. While the enhanced operational efficiency is a significant advantage, buyers must also consider the complexities involved in maintenance and the potential for increased operational costs.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
How Do FPSOs with Emission Solutions Benefit Buyers?
FPSOs that focus on emission solutions are designed to minimize environmental impact and achieve near-zero emissions. These units are increasingly relevant in eco-conscious projects or regions with stringent regulatory compliance. While the initial costs may be higher due to advanced technology, buyers can benefit from long-term savings and improved public perception, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Key Industrial Applications of fpso operation
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of FPSO Operation | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Principais considerações de fornecimento para esta aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Offshore Oil Production in Deepwater Fields | Increased access to hard-to-reach oil reserves | Reliability of technology, local regulatory compliance |
| Energias renováveis | Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Integration | Reduced carbon footprint and enhanced sustainability | Expertise in CCS technologies, integration capabilities |
| Maritime Logistics | Efficient Oil Offloading Operations | Streamlined logistics and reduced operational costs | Safety protocols, equipment compatibility |
| Environmental Services | Water Treatment and Management | Compliance with environmental regulations | Technology for water treatment, environmental certifications |
| Engineering and Design | Custom FPSO Design and Engineering Solutions | Tailored solutions for specific operational needs | Proven track record, flexibility in design modifications |
How is FPSO Operation Used in Oil and Gas Production?
FPSO operations are crucial for offshore oil production, particularly in deepwater fields where traditional platforms are impractical. These floating units allow for the extraction, processing, and storage of oil directly at sea, thereby reducing the need for extensive infrastructure on land. By utilizing FPSOs, companies can tap into previously inaccessible reserves, significantly enhancing their production capabilities. Buyers should prioritize sourcing reliable FPSO technology that complies with local regulations and ensures operational efficiency, especially in regions like Africa and South America where regulatory landscapes may vary.
What Role Does FPSO Operation Play in Renewable Energy Solutions?
FPSOs are increasingly being integrated into renewable energy initiatives, particularly in carbon capture and storage (CCS) operations. By capturing CO2 emissions from oil production and storing them subsea, FPSOs contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint of oil extraction activities. This innovative application aligns with global sustainability goals, making it attractive for companies aiming to enhance their environmental credentials. Buyers in the renewable energy sector should focus on suppliers with expertise in CCS technologies and proven integration capabilities to ensure effective and compliant operations.
How Can FPSO Operations Improve Maritime Logistics?
FPSOs enhance maritime logistics by streamlining oil offloading operations. These vessels are equipped with advanced offloading systems that allow for efficient transfer of oil to shuttle tankers, minimizing downtime and operational costs. This is particularly beneficial in regions with challenging maritime conditions, as FPSOs can be positioned closer to production sites. Businesses should consider the safety protocols and equipment compatibility of FPSOs when sourcing these solutions, as efficient logistics can significantly impact overall profitability.
What Environmental Services Can FPSOs Provide?
FPSOs also play a vital role in environmental management, particularly in the treatment and management of produced water. The ability to process and treat water on board helps companies meet stringent environmental regulations and reduce the risk of ecological damage. This capability is essential for international buyers operating in diverse regulatory environments, as compliance is critical for sustaining operations. When sourcing FPSO solutions for environmental services, companies should prioritize technology that ensures effective water treatment and comes with necessary environmental certifications.
How Do Engineering and Design Services Enhance FPSO Operations?
Custom FPSO design and engineering solutions allow operators to tailor these floating units to specific operational requirements. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for companies working in unique environmental conditions or with specific production goals. By engaging with experienced engineering firms, businesses can achieve optimized designs that enhance efficiency and safety. Buyers should seek providers with a proven track record in FPSO modifications to ensure that their specific needs are met while maintaining high standards of operational integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fpso operation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Harsh Environmental Conditions in FPSO Operations
O problema: B2B buyers often face challenges related to operating FPSOs in harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme weather, rough seas, or deep-water environments. These conditions can lead to operational disruptions, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety risks for personnel. Companies need to ensure that their FPSOs are not only operational but also resilient to environmental stressors that can threaten production efficiency and worker safety.
A solução: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize the procurement of FPSOs equipped with advanced mooring systems and robust hull designs that enhance stability and flexibility. Investing in FPSOs that feature adaptive turret systems allows for 360° rotation, which helps the vessel adjust to changing environmental conditions. Additionally, incorporating real-time monitoring technology can provide critical data on weather patterns and sea states, enabling proactive operational adjustments. Buyers should engage with experienced suppliers who offer integrated solutions, including emergency response plans and maintenance services tailored to the specific operational environment, thereby ensuring minimal downtime and enhanced safety protocols for offshore crews.
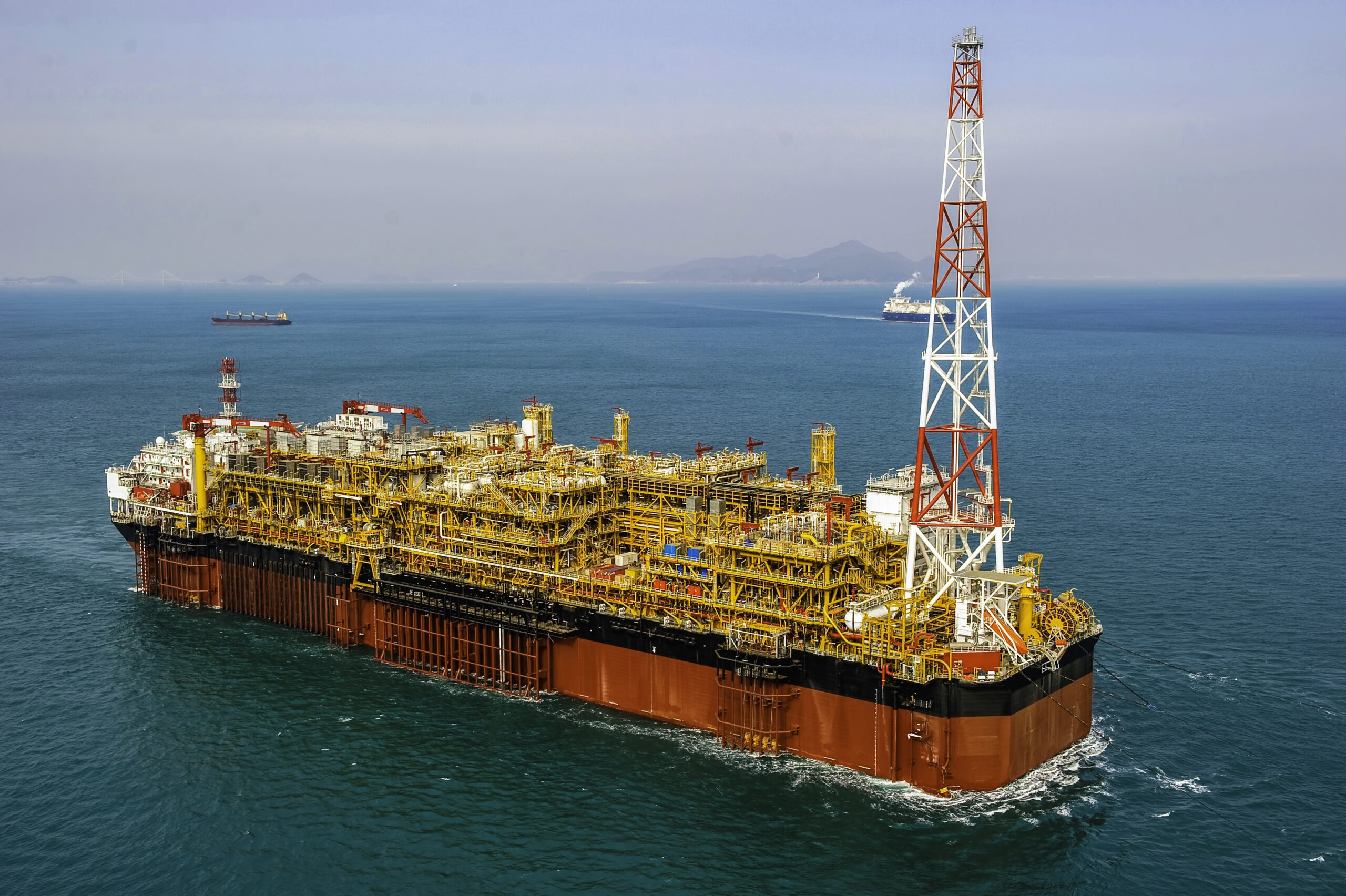

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Scenario 2: Managing Operational Costs and Efficiency in FPSO Projects
O problema: Many buyers encounter difficulties in managing the operational costs associated with FPSO projects, particularly concerning maintenance, energy consumption, and logistics. The complexity of FPSO operations often leads to unexpected expenses, which can strain budgets and affect project viability, especially in competitive markets like Africa and South America.
A solução: To improve cost management, buyers should consider adopting modular FPSO designs that facilitate efficient upgrades and maintenance. Modularization allows companies to replace or upgrade specific components without the need for extensive dry-docking, thus minimizing operational downtime. Furthermore, buyers can enhance efficiency by leveraging digital solutions for asset management and predictive maintenance. By utilizing data analytics, companies can forecast maintenance needs and optimize resource allocation, reducing operational costs. Collaborating with FPSO providers that offer flexible contracting models—such as leasing options or performance-based contracts—can also help align costs with production outcomes, ensuring financial viability in fluctuating market conditions.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Environmental Regulations in FPSO Operations
O problema: Navigating the complex landscape of environmental regulations poses a significant challenge for FPSO operators. Buyers must ensure that their operations comply with local and international environmental standards to avoid penalties, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. This is particularly crucial in regions with stringent regulations, such as Europe, where environmental sustainability is a top priority.
A solução: To address compliance issues effectively, buyers should engage FPSO operators who prioritize environmental management in their design and operational processes. Selecting FPSOs that incorporate advanced technologies for emissions reduction and waste management can significantly enhance compliance. For instance, the adoption of closed-loop systems for produced water treatment and flaring reduction technologies can minimize environmental impact. Buyers should also consider implementing comprehensive environmental management systems (EMS) that monitor compliance metrics in real time, allowing for timely adjustments and reporting. Regular training for personnel on environmental best practices and compliance requirements further ensures that all team members are aligned with sustainability goals. Partnering with legal experts in environmental regulations can provide additional assurance that operations are within legal parameters, thereby safeguarding the company’s reputation and operational integrity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fpso operation
What Are the Key Materials for FPSO Operations?
In the context of Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operations, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and safety of the installation. Here, we analyze four common materials used in FPSO operations: carbon steel, stainless steel, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and titanium. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact operational performance.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in FPSO Applications?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and ability to withstand high pressures. It has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and is relatively easy to weld.
Pros & Cons: The durability of carbon steel makes it a popular choice for structural components. However, its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in marine environments, can lead to significant maintenance costs. While it is cost-effective, the need for protective coatings can complicate manufacturing and increase overall expenditure.
Impacto na aplicação: Carbon steel is suitable for structural frameworks and storage tanks but requires careful consideration of corrosion resistance, particularly when in contact with seawater.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A36 or equivalent. The availability of protective coatings that meet environmental regulations is also crucial.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in FPSO Operations?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its chromium content, making it suitable for harsh marine environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,500°F (815°C) and has good mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and reduced maintenance needs, making it ideal for components exposed to seawater. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be challenging to fabricate due to its hardness.
Impacto na aplicação: Stainless steel is commonly used in piping systems and valves where corrosion resistance is paramount. Its compatibility with various media, including crude oil and natural gas, enhances its utility in FPSO operations.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM A312 for pipes and ASTM A240 for sheets. Cost considerations may vary significantly based on local availability and import tariffs.
How Does High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Contribute to FPSO Operations?
Key Properties: HDPE is lightweight, with excellent chemical resistance and a temperature range of -40°F to 180°F (-40°C to 82°C). It is also UV resistant, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of HDPE is its low weight, which simplifies installation and reduces transportation costs. However, it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications and can deform under extreme heat.
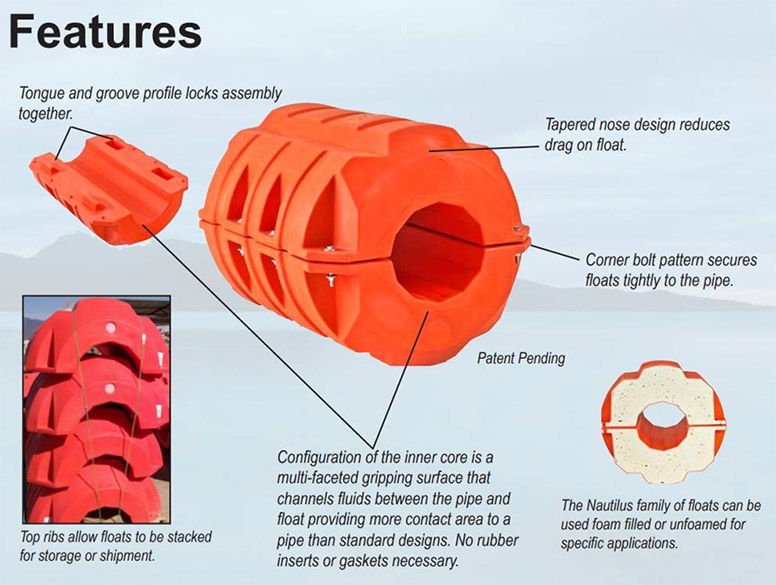
Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Impacto na aplicação: HDPE is often used for piping systems and storage tanks, especially for transporting chemicals and water. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but care must be taken to ensure it meets pressure requirements.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Compliance with standards like ASTM D3350 is essential. Buyers should also consider the material’s performance in local climates, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
What Advantages Does Titanium Offer for FPSO Operations?
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1,600°F (871°C).
Pros & Cons: The durability and lightweight nature of titanium make it ideal for critical applications where corrosion is a concern. However, it is significantly more expensive than other materials and can be difficult to machine.
Impacto na aplicação: Titanium is often used in high-stress components such as pressure vessels and heat exchangers due to its robustness. Its compatibility with aggressive media makes it a preferred choice in challenging environments.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B348 for titanium bars and rods. The high cost may necessitate a thorough cost-benefit analysis to justify its use in specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for FPSO Operations
| Material | Typical Use Case for fpsо operation | Vantagem chave | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural frameworks, storage tanks | Cost-effective, high strength | Suscetível à corrosão | Baixa |
| Aço inoxidável | Piping systems, valves | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, challenging to fabricate | Elevado |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Piping systems, storage tanks | Lightweight, chemical resistance | Not suitable for high-pressure | Médio |
| Titanium | Pressure vessels, heat exchangers | Exceptional strength and durability | Very high cost, difficult to machine | Elevado |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the various materials used in FPSO operations, highlighting their properties, advantages, and considerations for international buyers. Understanding these factors can aid in making informed decisions that align with operational needs and regulatory requirements.
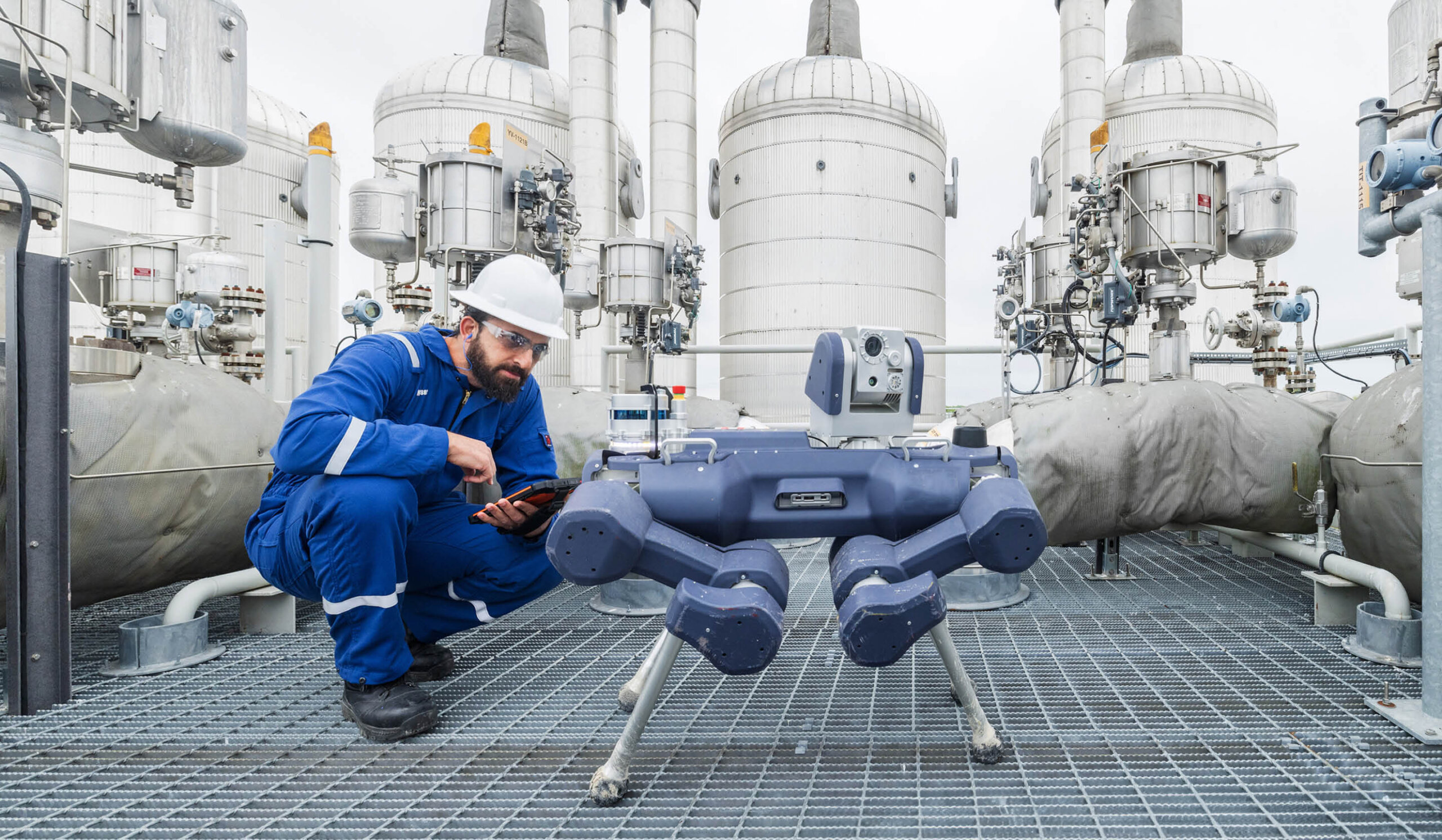
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fpso operation
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for FPSO Operations?
The manufacturing process of Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) units involves several key stages, each integral to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and operational requirements. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers more effectively.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in FPSO Construction?
The first stage in the manufacturing process focuses on selecting and preparing materials. FPSOs are primarily constructed from high-strength steel to withstand harsh marine environments. Additional materials may include specialized coatings for corrosion resistance and insulation materials for thermal management.
Materials undergo rigorous inspection and testing before being approved for use. This includes verifying compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 and specific industry certifications like API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications. Buyers should ensure their suppliers have robust material sourcing and quality control procedures in place to guarantee the integrity of materials used in FPSO construction.
2. What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in FPSO Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, the next step involves forming them into the desired shapes and structures. Common techniques include:
-
Welding: This is the predominant method used to join sections of the FPSO hull and topside modules. Advanced welding techniques, including automated and robotic welding, enhance precision and reduce human error.
-
Cutting: High-precision cutting methods, such as laser cutting and plasma cutting, are employed to shape steel plates and components accurately.
-
Bending and Rolling: Steel plates are bent and rolled to create curved sections of the hull, ensuring structural integrity and hydrodynamic efficiency.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming techniques used by suppliers, as advanced methods can significantly enhance the quality and durability of the FPSO.
3. How is Assembly Conducted for FPSOs?
Assembly is a critical phase where various components and systems are integrated into the FPSO. This involves:
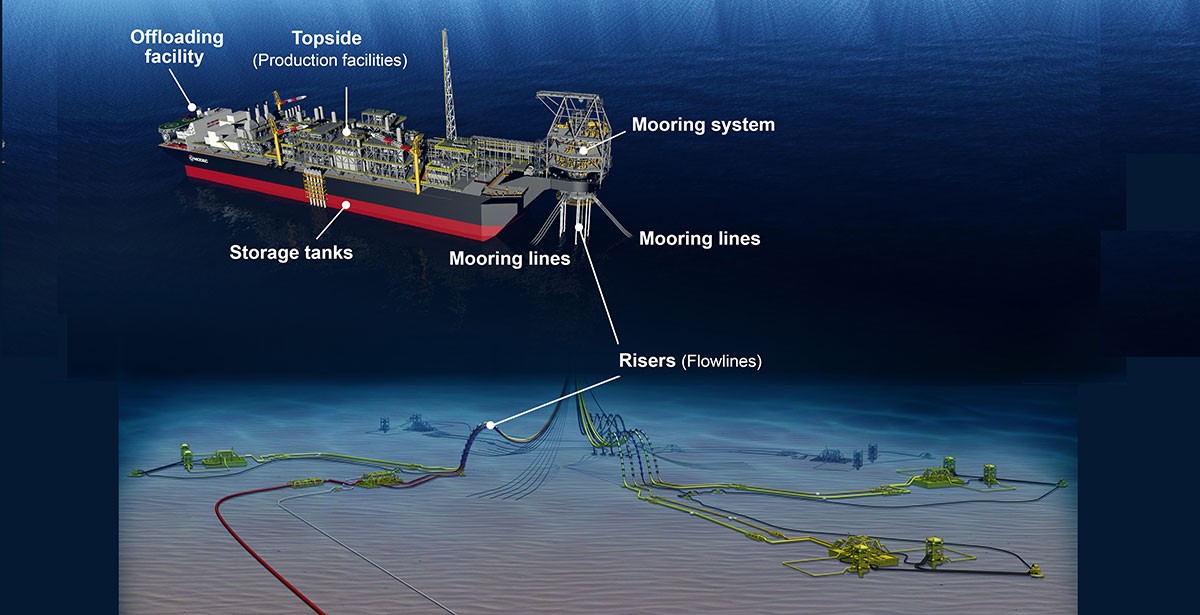
Illustrative image related to fpso operation
-
Module Assembly: The topside facilities, including processing units and living quarters, are often constructed as modular units. This modular approach allows for efficient assembly and flexibility in design.
-
Integration of Systems: Key systems, such as mooring systems, power generation, and processing equipment, are integrated during this stage. This requires close coordination among various teams to ensure all systems function seamlessly together.
-
Quality Control Checks: Throughout the assembly process, multiple quality control checkpoints (IQC – Incoming Quality Control, IPQC – In-Process Quality Control) are established to monitor compliance with design specifications and operational standards.
B2B buyers should assess the assembly protocols of potential suppliers to ensure they adhere to best practices, thereby minimizing risks associated with operational failures.
4. What Finishing Processes Are Involved in FPSO Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the FPSO’s durability and performance. This stage includes:
-
Coating and Painting: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of the FPSO. This process is crucial, especially for units operating in harsh marine environments.
-
Final Inspections: Comprehensive inspections are conducted to identify any defects or areas needing improvement before the FPSO is delivered. Final Quality Control (FQC) checks include pressure testing of systems, structural integrity assessments, and performance evaluations.
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers use internationally recognized finishing standards, which can significantly impact the operational efficiency and safety of the FPSO.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should FPSO Manufacturers Follow?
Quality assurance is pivotal in FPSO manufacturing, ensuring that the units are safe, reliable, and compliant with international standards. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that organizations must follow to ensure consistent quality in products and services.
-
CE Marking: This certification indicates that the FPSO complies with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Specific to the oil and gas industry, these standards ensure that products and services meet rigorous performance and safety benchmarks.
How Are QC Checkpoints Structured in FPSO Manufacturing?
The QC process in FPSO manufacturing is structured around several checkpoints to ensure quality at every stage:

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
-
Controlo de qualidade de entrada (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide certification for materials to verify compliance with relevant standards.
-
Controlo de qualidade durante o processo (IPQC): Quality checks are performed during the manufacturing and assembly stages. This includes monitoring welding quality, system integrations, and adherence to design specifications.
-
Controlo de qualidade final (FQC): Before delivery, the FPSO undergoes extensive testing, including pressure tests and system performance evaluations. Only after passing these tests is the FPSO deemed ready for operation.
B2B buyers should request detailed QC reports from suppliers to ensure that these checkpoints are effectively implemented.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in FPSO Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and safety of FPSOs:
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, and magnetic particle testing are used to identify internal and surface flaws without damaging the material.
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This method tests the integrity of pressure vessels and pipelines by filling them with water and applying pressure to identify leaks or weaknesses.
-
Teste de desempenho: Systems are tested under operational conditions to ensure they function as intended and meet performance specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier QC Processes?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
-
Auditorias a fornecedores: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with industry standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed QA reports can help buyers assess the effectiveness of a supplier’s QC processes and their adherence to international standards.
-
Inspecções por terceiros: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality management practices and product integrity.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific QC nuances:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context can aid in communication and expectations regarding quality standards.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must be aware of local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms, affecting the certification and acceptance of FPSOs in specific markets.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Coordinating quality control across international supply chains can be challenging. Buyers should establish clear communication channels and contingency plans to mitigate risks related to quality and delivery.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for FPSO operations, ensuring they meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
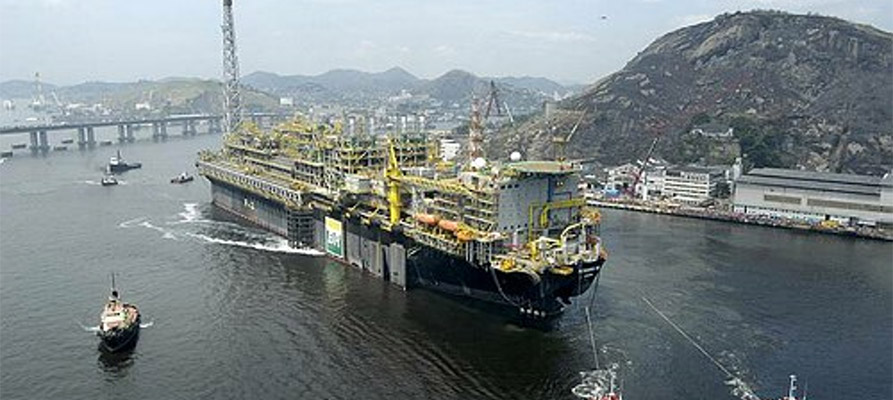
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fpso operation’
Introdução
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operations. As FPSOs play a critical role in offshore oil and gas extraction, understanding the key steps in the sourcing process can significantly impact project success. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right FPSO solutions tailored to your operational needs.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Passo 1: Definir as suas especificações técnicas
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential for aligning your FPSO requirements with potential suppliers. This step should include defining the production capacity, processing capabilities, and storage needs specific to your project.
– Considerations:
– What is the expected volume of oil and gas to be processed?
– What environmental conditions will the FPSO operate in, and what mooring system is required?
Passo 2: Conduct Market Research for Suppliers
A thorough market analysis is crucial for identifying reputable FPSO suppliers. Research industry leaders and emerging players in the FPSO market, focusing on their project portfolios and geographical presence.
– Key Actions:
– Review case studies to understand their operational successes and challenges.
– Attend industry conferences or webinars to network and gather insights.
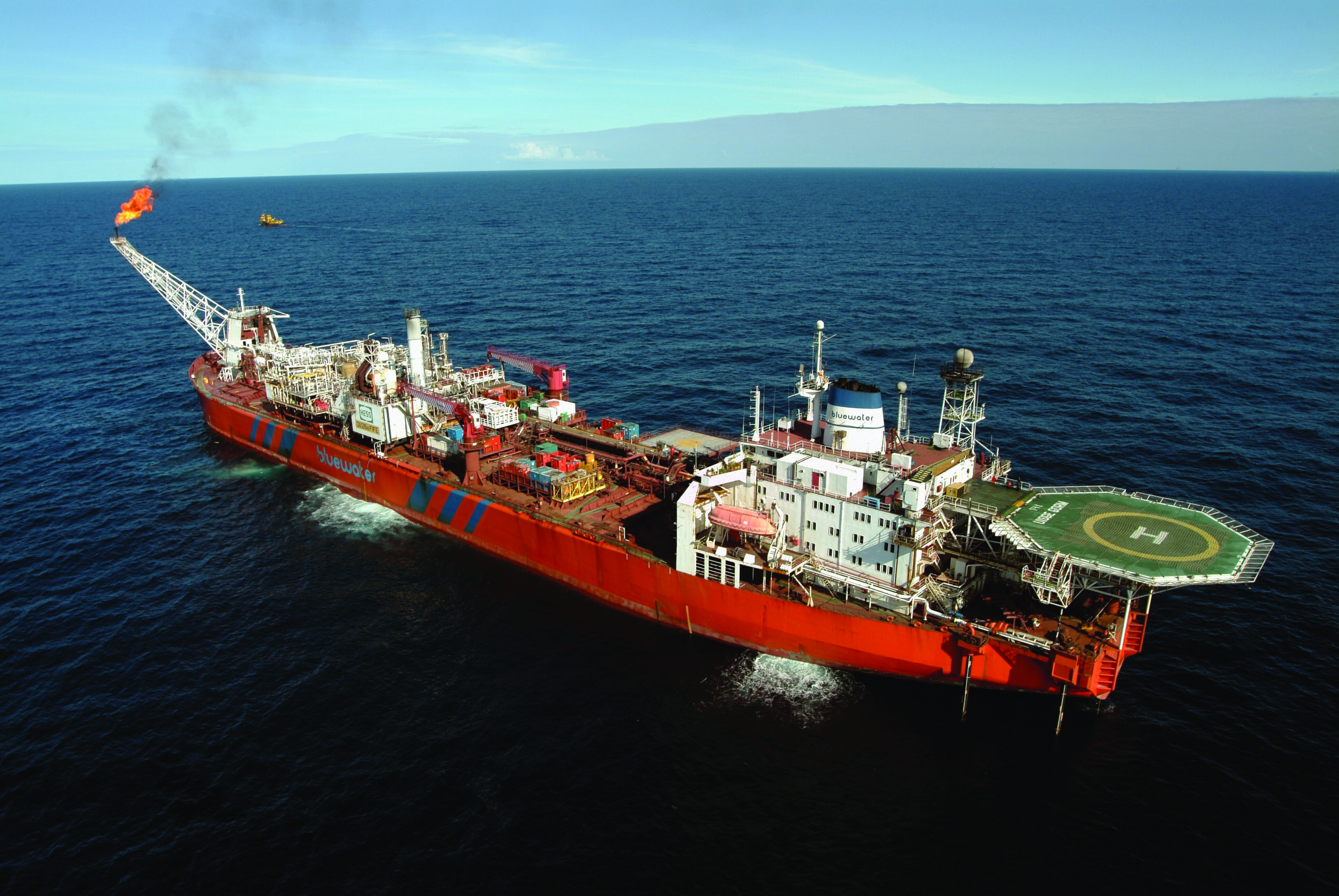
Passo 3: Avaliar potenciais fornecedores
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of potential suppliers. This involves requesting detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients in similar markets.
– What to Look For:
– Supplier experience in your region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
– Evidence of successful FPSO operations and maintenance over time.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Passo 4: Verificar as certificações e a conformidade
Ensuring that suppliers meet industry standards and regulatory requirements is critical for operational safety and environmental compliance. Confirm that the FPSO units and operations align with international safety standards and local regulations.
– Important Checks:
– Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management.
– Verify compliance with local regulatory bodies relevant to offshore operations.
Passo 5: Assess Technological Capabilities
Investigate the technological innovations that suppliers incorporate into their FPSO solutions. Advanced technology can enhance operational efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability.
– Focus Areas:
– Modular design capabilities that allow for easy upgrades and scalability.
– Innovations in emissions reduction technologies, such as those aimed at achieving near-zero emissions.
Passo 6: Review Contractual Terms and Flexibility
Examine the contractual terms offered by suppliers, including leasing versus purchasing options. Understanding the flexibility of these contracts is crucial for adapting to changing project needs or market conditions.
– Key Considerations:
– Are there options for maintenance and operational support included in the contract?
– What are the terms for early termination or extension?
Passo 7: Plan for Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Finally, ensure that your selected supplier offers robust support and maintenance services post-procurement. A strong support structure is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring operational continuity.
– What to Confirm:
– Availability of inspection, maintenance, and repair (IMR) services.
– Response times for emergency situations and regular maintenance schedules.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing FPSO operations, ensuring a successful partnership that meets both current and future operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fpso operation Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in FPSO Operations?
When analyzing the cost structure of Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operations, several key components come into play. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materiais: The costs associated with raw materials can vary significantly based on the specifications and customization required for each FPSO project. High-quality steel, specialized equipment for hydrocarbon processing, and mooring systems are among the primary materials used, often sourced from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Trabalho: Labor costs encompass both skilled and unskilled labor involved in the construction, operation, and maintenance of FPSOs. This includes engineers, technicians, and support staff. Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographical location, local labor laws, and availability of skilled workforce, particularly in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Despesas gerais de fabrico: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary based on the operational efficiency of the manufacturing facilities and their proximity to supply chains.
-
Ferramentas: The investment in tooling is essential for efficient production and maintenance of FPSOs. This can involve specialized machinery for construction and repair, which can be a significant upfront cost but is necessary for ensuring quality and speed.
-
Controlo de qualidade (CQ): Ensuring that the FPSOs meet stringent safety and environmental regulations requires a robust QC process. This involves testing materials, inspecting equipment, and ensuring compliance with international standards, which can add to the overall costs.
-
Logística: Transporting large components to remote offshore locations can incur substantial logistics costs. These costs can be affected by the choice of transportation methods, distance, and the complexity of the delivery process, especially in regions with limited infrastructure.
-
Margem: Suppliers typically build in a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and the specific requirements of the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Impact FPSO Sourcing Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in FPSO operations, which can significantly affect total project costs.
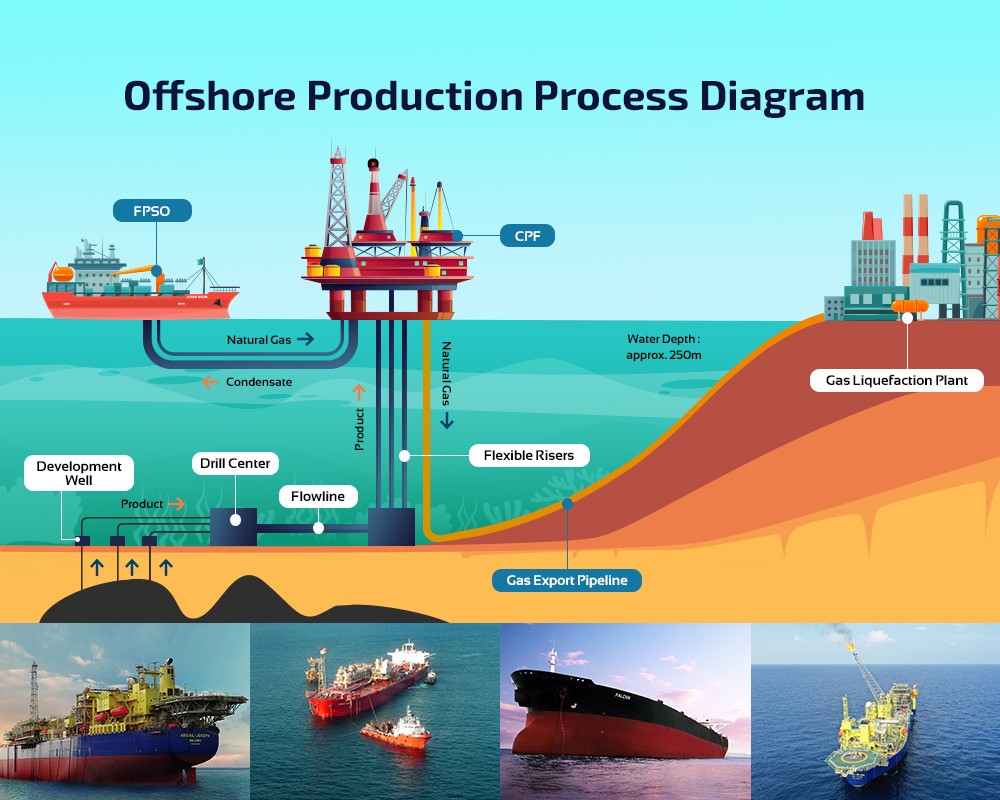
Illustrative image related to fpso operation
-
Volume/MOQ: The volume of materials ordered can lead to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to optimize costs, particularly when sourcing bulk materials.
-
Especificações e personalização: Custom-designed FPSOs may incur higher costs due to specialized materials and engineering requirements. Buyers need to weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Qualidade dos materiais e certificações: Higher-quality materials often come with a premium price tag. Additionally, certifications required for environmental and safety standards can add to costs but are essential for compliance.
-
Factores do fornecedor: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants may offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can impact the total landed cost of FPSOs. Buyers should be aware of the responsibilities and risks associated with different terms, as these can influence overall project costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in FPSO Operations?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of FPSO sourcing is crucial for achieving cost efficiency.
-
Negociação: Engage in thorough negotiations with suppliers. Understanding market trends and having a clear idea of your project needs can empower buyers to secure better terms and prices.
-
Custo total de propriedade (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just initial costs. This includes maintenance, operational expenses, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality materials may reduce long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations and economic conditions in the supplier’s region, which can impact pricing. Building relationships with multiple suppliers can also provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations and compliance requirements, as these can influence costs and project timelines.
-
Market Research: Conduct comprehensive market research to understand pricing trends and supplier capabilities. This knowledge can help in making informed decisions and optimizing sourcing strategies.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices associated with FPSO operations can vary significantly based on multiple factors, including market conditions, project specifications, and supplier negotiations. Therefore, it is essential for buyers to conduct their own research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fpso operation With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for FPSO Operations
In the offshore oil and gas industry, Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) units are pivotal for extracting hydrocarbons from deepwater fields. However, various alternative solutions can also facilitate oil and gas production. This analysis will compare FPSO operations with two viable alternatives: fixed platforms and semi-submersible platforms. Each option has its unique advantages and drawbacks, making it essential for B2B buyers to evaluate which solution aligns best with their operational needs and financial constraints.
Comparison Table of FPSO Operations and Alternatives
| Aspeto de comparação | FPSO Operation | Fixed Platform | Semi-Submersible Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | High mobility; suitable for deepwater and remote locations | Best for shallow waters; limited mobility | Good performance in varying sea conditions |
| Custo | Higher upfront capital but lower operational costs in the long term | Lower initial investment; high maintenance | Moderate cost; flexible design may increase expenses |
| Facilidade de implementação | Complex installation; requires specialized vessels for assembly | Easier to install; less complex design | Moderate complexity; requires specific mooring technology |
| Manutenção | Requires regular inspections and maintenance; can be costly | Generally lower maintenance, but less flexible | Moderate maintenance needs; sensitive to environmental factors |
| Melhor caso de utilização | Ideal for deepwater fields and remote areas | Best for established shallow fields | Suitable for mid-water locations and harsh environments |
Análise pormenorizada das alternativas
1. Fixed Platforms
Fixed platforms are traditional structures anchored to the seabed, primarily used in shallow waters. They are generally less expensive to install than FPSOs and require less ongoing maintenance. However, their immobility can be a significant drawback, as they cannot be repositioned to access new reserves. This limits their operational flexibility, making them less suitable for exploratory drilling in uncertain regions.
2. Semi-Submersible Platforms
Semi-submersible platforms are floating structures that maintain stability through buoyancy. They are capable of operating in deeper waters than fixed platforms and are designed to withstand harsher marine conditions. While they offer better stability and flexibility than fixed platforms, they also require advanced mooring systems and can incur higher operational costs. Their adaptability makes them a good choice for regions with variable weather patterns or seismic activity.
Conclusão: Escolher a solução certa para as suas necessidades
When considering FPSO operations versus alternative solutions like fixed platforms and semi-submersible platforms, B2B buyers must weigh performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. Each option presents distinct advantages and challenges, depending on the operational context. Buyers should assess their specific project requirements, including water depth, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, to make an informed decision that optimally supports their oil and gas extraction goals. By thoroughly analyzing these alternatives, companies can position themselves to maximize efficiency and profitability in their offshore operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fpso operation
What Are the Key Technical Properties Critical for FPSO Operations?
In the world of Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operations, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring effective performance, safety, and compliance with industry standards. Here are several essential specifications that buyers should consider:
-
Grau do material
FPSOs are typically constructed from high-strength steel to withstand harsh marine environments. The material grade often falls under standards like API 2H or ASTM A36, which define the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance needed for longevity and safety. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring structural integrity and minimizing maintenance costs over the FPSO’s operational lifespan. -
Production Capacity
The oil production capacity of an FPSO can range significantly, often between 50,000 to 250,000 barrels per day (bpd). This metric influences operational efficiency and profitability. Buyers must assess production capacity in relation to their resource estimates and market demand to ensure that the FPSO can meet their specific operational needs without incurring unnecessary costs. -
Mooring System Specifications
FPSOs utilize various mooring systems, such as turret mooring or spread mooring, tailored to specific environmental conditions and water depths. The choice of mooring system affects the FPSO’s stability and maneuverability. Understanding the specifications of these systems is essential for selecting an FPSO that can operate effectively in the intended location, especially in regions with severe weather conditions. -
Offloading Rate
The offloading rate refers to the maximum volume of oil that can be transferred from the FPSO to shuttle tankers within a given timeframe, typically measured in barrels per hour (bph). A higher offloading rate can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Buyers should evaluate this metric to optimize logistics and ensure timely delivery to refineries. -
Safety and Environmental Compliance Standards
FPSOs must adhere to strict safety and environmental regulations, including international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Compliance with these standards is not only a legal requirement but also enhances the operational credibility of the FPSO in the eyes of stakeholders, investors, and regulatory bodies.
What Are Common Trade Terms in FPSO Operations?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in FPSO operations. Here are some common trade terms that buyers should familiarize themselves with:
-
OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original)
This term refers to companies that produce the original equipment used in FPSOs, such as pumps, compressors, and processing units. Engaging with reputable OEMs ensures that buyers receive high-quality components that meet industry standards, which is critical for operational efficiency and safety. -
MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. In FPSO operations, understanding MOQ can help buyers manage inventory costs effectively and ensure they are not overcommitting to purchases that exceed their operational needs. -
RFQ (Pedido de Cotação)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing information for specific products or services. In the FPSO sector, submitting RFQs can help buyers compare costs and terms from different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making and budget management. -
Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
These are predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for FPSO buyers to understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations, which can significantly affect the overall project budget. -
CAPEX (Capital Expenditure)
CAPEX refers to the funds used by a company to acquire or upgrade physical assets such as FPSOs. Understanding CAPEX is essential for buyers to plan their investments strategically, ensuring that they allocate sufficient resources for both initial acquisition and long-term operational costs. -
OPEX (Operational Expenditure)
OPEX encompasses the ongoing costs for running an FPSO, including maintenance, labor, and utilities. By analyzing OPEX, buyers can better forecast their operational budgets and identify areas for cost optimization, which is critical for maintaining profitability in fluctuating market conditions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their FPSO operations while ensuring compliance and maximizing efficiency.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fpso operation Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the FPSO Operation Sector?
The FPSO operation sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by several global factors. Firstly, the ongoing energy transition is pushing companies to seek innovative solutions that balance profitability with sustainability. With oil and gas demand projected to remain robust in regions like Africa and South America, FPSOs offer a flexible and cost-effective means of extraction, particularly in deepwater environments where traditional platforms are not viable. The increasing complexity of offshore operations necessitates advanced technology, leading to a surge in digital solutions such as remote monitoring systems and predictive maintenance tools. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Moreover, there is a growing trend toward modularization and standardization in FPSO design. Companies like SBM Offshore are leveraging their Fast4Ward® program to streamline project execution, reduce costs, and shorten construction timelines by engaging vendors early in the supply chain. This approach not only enhances project delivery but also allows for a more agile response to market demands. Additionally, the rise of hybrid energy solutions, incorporating renewable sources alongside traditional oil and gas, is gaining traction, especially in regions pursuing a greener energy footprint.
International buyers from emerging markets such as Nigeria and Vietnam should also be aware of geopolitical factors influencing sourcing decisions. The stability of supply chains is critical, particularly in regions prone to political and economic fluctuations. Thus, securing partnerships with reliable suppliers that have a proven track record in navigating these complexities is essential for successful FPSO operations.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the FPSO Operation Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of FPSO operations, significantly influencing sourcing strategies and supplier relationships. The environmental impact of offshore oil and gas extraction is under scrutiny, compelling companies to adopt practices that minimize ecological footprints. This includes investing in technologies that reduce emissions and waste, as well as implementing strategies for responsible water management and habitat preservation.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance as stakeholders demand transparency in supply chains. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices and can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to local regulations are becoming prerequisites for suppliers in the FPSO sector.
Moreover, the introduction of initiatives like emissionZERO® by SBM Offshore highlights the industry’s commitment to achieving near-zero emissions. This program not only addresses environmental concerns but also appeals to buyers who prioritize sustainability in their procurement processes. As a result, international B2B buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers that not only provide quality materials and services but also align with their sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of FPSOs and Their Evolution?
The FPSO concept has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1970s, originally designed to address the challenges of offshore oil extraction in remote and deepwater locations. Initially, FPSOs were primarily converted oil tankers, but advancements in engineering and technology have led to the development of purpose-built FPSOs capable of handling complex processing and storage tasks.
Over the decades, the FPSO sector has adapted to changing market dynamics, with an increasing focus on safety, efficiency, and environmental responsibility. The introduction of advanced mooring systems, improved processing technologies, and enhanced safety protocols has transformed FPSOs into sophisticated floating facilities that can operate effectively in harsh marine environments. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to both economic pressures and the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions, positioning FPSOs as a pivotal element in the future of offshore oil and gas production.
By understanding these trends and historical contexts, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments in the FPSO operation sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fpso operation
-
How do I evaluate potential FPSO suppliers for my project?
To effectively evaluate FPSO suppliers, consider their track record, technical expertise, and compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Review case studies of their previous projects, focusing on similar operational environments and production capacities. Engaging in direct discussions can provide insights into their operational capabilities and responsiveness. Additionally, verify their financial stability and assess their supply chain resilience, especially for projects in remote locations. Collaborating with suppliers who have a strong presence in your region can also ease logistics and enhance support. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting an FPSO model?
When selecting an FPSO model, assess the production capacity, which should align with your project’s expected output. Consider the environmental conditions of the operational site, such as water depth and weather patterns, as these will influence the design and mooring system. Evaluate the flexibility of the FPSO, including its ability to be repositioned for different fields. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s experience with customizations, as specific project requirements may necessitate modifications to the FPSO’s design or functionality. -
What are the common payment terms for FPSO contracts?
Payment terms for FPSO contracts vary by supplier but generally include an upfront deposit followed by milestone payments tied to project deliverables. It’s common to structure payments based on the completion of design phases, construction milestones, and successful commissioning. Ensure clarity on any performance guarantees or penalties associated with delays or non-compliance. For international transactions, consider currency fluctuations and payment methods that minimize risks, such as using letters of credit or escrow accounts. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in FPSO operations?
To ensure quality assurance in FPSO operations, select suppliers with robust quality management systems certified by recognized standards (like ISO 9001). Implement regular audits and inspections during the construction and operational phases. Establish clear KPIs for performance monitoring, including safety metrics and production efficiency. Collaborate closely with the supplier to facilitate open communication about any quality concerns that arise, ensuring they have a proactive approach to problem-solving. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for FPSO operations?
Logistics for FPSO operations involve careful planning of transportation for equipment and personnel to offshore sites. Evaluate the accessibility of the operational location, including the availability of ports and support vessels. Consider the time required for mobilization and demobilization of the FPSO, as well as the scheduling of shuttle tankers for oil offloading. Collaborate with experienced logistics partners who understand the complexities of offshore operations, including customs clearance and regulatory compliance. -
How does customization impact the cost of an FPSO?
Customization can significantly impact the cost of an FPSO. Tailoring design features, such as specific processing capacities or advanced safety systems, may lead to increased engineering and material costs. However, effective customization can enhance operational efficiency and reduce long-term operational expenses. It’s crucial to balance the immediate financial implications with the potential benefits of customized solutions that address unique project needs. Engage with suppliers early in the design phase to explore cost-effective customization options. -
What are the environmental considerations for FPSO operations?
Environmental considerations for FPSO operations include compliance with local and international regulations regarding emissions, waste disposal, and water discharge. Suppliers should implement advanced technologies to minimize environmental impacts, such as gas reinjection systems and waste treatment facilities. Assess the supplier’s commitment to sustainability initiatives, such as their participation in programs aimed at reducing carbon footprints. It’s also beneficial to review their incident history related to environmental breaches to gauge their operational responsibility. -
What are the typical lead times for FPSO delivery and commissioning?
Lead times for FPSO delivery and commissioning can vary widely based on factors such as the complexity of the project, the availability of materials, and the supplier’s workload. Typically, new builds can take anywhere from 18 to 36 months from contract signing to delivery, while conversions may require 12 to 24 months. To ensure timely delivery, establish clear project timelines and maintain regular communication with the supplier. Factor in potential delays due to regulatory approvals or logistical challenges, especially for projects in remote locations.
Top 3 Fpso Operation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Lmitac – FPSO Vessels
Domínio: lmitac.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introdução: Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) vessels are specialized ships designed for deepwater oil and gas exploration. They process oil and gas extracted from subsea wells, store the products, and offload them for transport. FPSOs can be dynamically positioned in deepwater and ultra-deepwater fields, remaining operational for several years. They store large quantities of oil and gas in th…
2. Investopedia – Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO)
Domínio: investopedia.com
Registada: 1999 (26 anos)
Introdução: Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) refers to a floating vessel located near an offshore oil field where oil is processed and stored until it can be transferred to a tanker for further transport and refining. FPSOs can vary in structure from converted supertankers to purpose-built vessels. The demand for FPSOs has increased due to declining onshore oil discoveries and advancements in…
3. DXPE – Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) Solutions
Domínio: dxpe.com
Registada: 1997 (28 anos)
Introdução: A Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) vessel is a large, ship-shaped unit used in offshore oil and gas production. It extracts, processes, stores, and transfers oil and gas directly at sea, without the need for fixed platforms or onshore infrastructure. FPSOs are widely used in deepwater environments for their flexibility and efficiency, contributing to over 30% of global crude oil p…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fpso operation
As the global energy landscape evolves, Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operations stand out as a pivotal solution for accessing offshore oil and gas reserves. The strategic sourcing of FPSO units not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces costs and environmental impacts. By investing in innovative technologies and flexible contracting models, international B2B buyers can harness the full potential of FPSOs to meet energy demands in challenging environments.
For markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the adaptability and mobility of FPSOs present unique opportunities for resource extraction in deepwater and remote locations. Engaging with experienced suppliers who prioritize advancements in safety, efficiency, and sustainability is essential. This ensures that your operations remain competitive and aligned with global sustainability targets.
Looking ahead, the future of FPSO operations will likely be shaped by technological advancements and a commitment to reducing emissions. Now is the time for stakeholders to act decisively. By forging partnerships with leading FPSO providers and embracing innovative practices, you can position your business at the forefront of the energy sector, ready to thrive in an increasingly dynamic and responsible market.
Aviso importante e termos de utilização
⚠️ Declaração de exoneração de responsabilidade importante
As informações fornecidas neste guia, incluindo o conteúdo relativo a fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análises de mercado, destinam-se apenas a fins informativos e educativos. Não constitui aconselhamento profissional em matéria de aquisições, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos feito todos os esforços para garantir a exatidão e a atualidade das informações, não somos responsáveis por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desactualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e as normas técnicas estão sujeitos a alterações.

Illustrative image related to fpso operation
Os compradores B2B devem efetuar a sua própria diligência prévia independente e exaustiva antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isto inclui contactar diretamente os fornecedores, verificar as certificações, pedir amostras e procurar aconselhamento profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é suportado exclusivamente pelo leitor.