Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to vulcanize rubber
In the ever-evolving landscape of the global rubber industry, understanding how to vulcanize rubber effectively is essential for B2B buyers aiming to enhance product durability and performance. Sourcing high-quality vulcanized rubber components can be particularly challenging for businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse applications and varying quality standards exist. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by exploring the intricacies of the vulcanization process, including types of vulcanization methods, their applications across different industries, and critical factors for supplier vetting.
From automotive to construction, the demand for robust rubber products continues to rise, making it imperative for international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. This guide empowers you with essential insights into the vulcanization process, helping you identify reputable suppliers and evaluate costs effectively. We delve into the specific attributes of vulcanized rubber, such as its resistance to wear and environmental conditions, ensuring you understand the advantages it brings to your operations.
By providing a thorough understanding of vulcanization and actionable strategies for sourcing, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the global rubber market confidently. Whether you’re based in Germany, Vietnam, or anywhere in between, the insights shared here will enable you to enhance your procurement strategy and ensure the success of your business in a competitive environment.
Índice
- Top 4 How To Vulcanize Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to vulcanize rubber
- Understanding how to vulcanize rubber Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to vulcanize rubber
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to vulcanize rubber’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to vulcanize rubber
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to vulcanize rubber
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to vulcanize rubber’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to vulcanize rubber Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to vulcanize rubber With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to vulcanize rubber
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to vulcanize rubber Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to vulcanize rubber
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to vulcanize rubber
- Aviso importante e termos de utilização
Understanding how to vulcanize rubber Types and Variations
| Tipo Nome | Principais caraterísticas distintivas | Aplicações B2B primárias | Breves prós e contras para os compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Vulcanization | Involves heating rubber with sulfur under pressure; higher temperatures (up to 150°C). | Manufacturing tires, industrial seals | Pros: Superior strength and durability; efficient for large-scale production. Cons: Higher initial setup costs; requires specialized equipment. |
| Free Vulcanization | Uses steam or hot air for vulcanization; lower pressure settings. | Smaller batches, custom rubber products | Pros: More flexible for custom applications; lower equipment costs. Cons: Longer curing times; may not achieve the same strength as pressure vulcanization. |
| Accelerated Vulcanization | Incorporates chemical accelerators to speed up the curing process. | High-volume production of rubber components | Pros: Reduced production time; allows for rapid scaling. Cons: Risk of scorching if not carefully controlled; potential for reduced material properties. |
| Sulfur vs. Alternative Agents | Uses sulfur as a primary agent; alternatives like selenium and tellurium can be applied. | Specialty applications requiring specific properties | Pros: Sulfur is cost-effective and widely available; enhances rubber’s properties. Cons: Alternatives may be more expensive; specific applications may limit agent choice. |
| Cold Vulcanization | Utilizes chemical agents at room temperature; no heat required. | Repairing rubber products, maintenance tasks | Pros: Easy to apply; suitable for on-site repairs. Cons: Generally weaker bonds; not suitable for high-performance applications. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Pressure Vulcanization?
Pressure vulcanization is distinguished by its use of high temperatures and pressure to cure rubber with sulfur. This method is optimal for manufacturing applications requiring robust materials, such as tires and industrial seals. The process enhances the strength and durability of rubber, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it requires specialized equipment, which can increase initial investment costs for manufacturers.
How Does Free Vulcanization Differ from Other Methods?
Free vulcanization employs steam or hot air to cure rubber, making it a more adaptable option for smaller batches or custom products. This method is less capital-intensive, allowing businesses to enter the rubber market without significant upfront costs. However, the curing time is longer compared to pressure methods, which may delay production schedules for urgent orders.
What are the Benefits of Accelerated Vulcanization?
Accelerated vulcanization involves the addition of chemical accelerators to speed up the curing process, allowing for high-volume production of rubber components. This method is particularly advantageous for businesses looking to scale up operations quickly. While it can significantly reduce production time, manufacturers must carefully control the process to avoid scorching and potential loss of material properties.
Why Choose Sulfur Over Alternative Vulcanization Agents?
Sulfur remains the primary agent in the vulcanization process due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to enhance rubber properties. While alternatives like selenium and tellurium can be used for specific applications, they are typically more expensive and may not be necessary for general use. Buyers should assess their specific needs and budget when selecting vulcanization agents.
When is Cold Vulcanization the Right Choice?
Cold vulcanization is a practical option for on-site repairs and maintenance tasks, utilizing chemical agents at room temperature. This method is easy to apply and does not require specialized equipment, making it accessible for businesses looking to perform quick repairs. However, it generally results in weaker bonds, limiting its use in high-performance applications.
Key Industrial Applications of how to vulcanize rubber
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of how to vulcanize rubber | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Principais considerações de fornecimento para esta aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automóvel | Production of tires and rubber seals | Enhanced durability, improved safety, and performance | Quality of raw materials, compliance with safety standards |
| Construção | Rubber flooring and mats | Increased safety, slip resistance, and surface protection | Customization options, resistance to harsh conditions |
| Aeroespacial | Seals and gaskets for aircraft | Reliability in extreme conditions, reduced maintenance | Certification for aerospace applications, material specs |
| Petróleo e gás | Hoses and seals for drilling equipment | Resistance to chemicals and abrasion, extended lifespan | Compatibility with specific chemicals, temperature ratings |
| Bens de consumo | Rubberized grips for tools and appliances | Improved ergonomics and user safety | Design flexibility, adherence to consumer safety standards |
How is Rubber Vulcanization Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, vulcanization is critical for producing tires and rubber seals. This process enhances the durability and safety of tires, providing better traction and performance under various driving conditions. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality vulcanized rubber ensures compliance with local safety standards and regulations. Additionally, suppliers must provide materials that can withstand diverse environmental conditions, from extreme heat to heavy rainfall.
What Role Does Vulcanization Play in Construction Applications?
Rubber flooring and mats are widely utilized in construction for their slip-resistant properties and durability. Vulcanization strengthens the rubber, making it suitable for high-traffic areas and environments where safety is paramount. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider sourcing options that allow for customization in thickness and design to meet specific project requirements. The ability to withstand harsh weather conditions is also a crucial factor, ensuring longevity and minimal maintenance costs.
How is Vulcanization Beneficial in the Aerospace Sector?
In aerospace applications, vulcanization is essential for creating seals and gaskets that must perform reliably under extreme conditions. The vulcanized rubber can endure high temperatures and pressures, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacements. International buyers in this sector, especially from Europe, require suppliers that adhere to strict certification processes and material specifications to ensure safety and reliability in flight operations.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
Why is Vulcanization Important for Oil & Gas Applications?
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on vulcanized rubber for hoses and seals used in drilling equipment. The vulcanization process imparts resistance to chemicals and abrasion, which is vital in harsh operational environments. Buyers must source materials that not only meet industry standards but also exhibit compatibility with specific chemicals and temperature ratings. This ensures that the equipment operates efficiently while minimizing the risk of leaks or failures.
How Does Vulcanization Enhance Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods sector, rubberized grips for tools and appliances benefit significantly from vulcanization. This process improves the ergonomics of products, enhancing user safety and comfort during use. For B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, sourcing vulcanized rubber that meets consumer safety standards is essential. Suppliers should offer design flexibility to cater to various product specifications, ensuring that the final products are both functional and appealing to consumers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to vulcanize rubber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Control in Rubber Vulcanization
O problema: B2B buyers often face difficulties ensuring the quality of vulcanized rubber products, which can vary significantly based on the sourcing of raw materials and the vulcanization process itself. Inconsistent quality can lead to increased production costs, waste, and customer dissatisfaction, particularly for companies that rely on rubber components for high-stakes applications such as automotive or aerospace industries. This challenge is compounded in regions with less stringent regulatory oversight, leading to potential issues with material performance and compliance with industry standards.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
A solução: To address quality control challenges, B2B buyers should establish robust supplier relationships that prioritize transparency and quality assurance. It is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including audits of their manufacturing processes and certifications. Implementing a detailed specification sheet for vulcanization parameters—such as temperature, pressure, and curing time—can help standardize production and ensure consistency. Furthermore, investing in quality testing equipment and processes, such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance tests, can help verify that the final products meet the required specifications before they are delivered to end-users. By prioritizing quality at every stage of the supply chain, companies can reduce the risks associated with subpar materials.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Vulcanization Process for Different Applications
O problema: Many B2B buyers struggle with understanding the nuances of the vulcanization process and how it impacts the performance of rubber products in specific applications. This knowledge gap can lead to improper material selection, resulting in product failures or inefficiencies that could have been avoided. For instance, using a standard vulcanization method for applications requiring high-temperature resistance can lead to premature degradation of rubber products.
A solução: Buyers should invest in training sessions or workshops focused on the rubber vulcanization process tailored to their specific applications. Collaborating with chemical engineers or rubber technologists can provide insights into the best practices for vulcanization tailored to specific performance criteria. It is beneficial to create a material selection guide that outlines the different types of rubber compounds and their ideal vulcanization methods, including the use of accelerators and activators. Additionally, engaging in pilot testing of vulcanized products in the intended application environment can help identify potential issues early in the development process, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs in the Vulcanization Process
O problema: Cost management is a persistent issue for B2B buyers involved in rubber vulcanization, especially in competitive markets where margins are tight. The costs associated with raw materials, energy consumption during the vulcanization process, and labor can quickly add up, affecting the overall profitability of rubber products. Buyers may also find themselves at the mercy of fluctuating prices for sulfur and other vulcanization agents, complicating budgeting and financial planning.
A solução: To effectively manage costs, buyers should consider adopting a holistic approach to their vulcanization operations. This includes negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers for raw materials to lock in favorable pricing and reduce the impact of market fluctuations. Exploring alternative vulcanization agents, such as new chemical accelerators that may offer cost benefits or efficiency gains, can also be advantageous. Implementing energy-efficient technologies in the vulcanization process, such as advanced heating systems or insulation methods, can further reduce operational costs. Lastly, regular reviews of production processes to identify waste and inefficiencies can lead to significant cost savings, allowing companies to remain competitive without compromising product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to vulcanize rubber
When selecting materials for the vulcanization of rubber, it is essential to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the vulcanization process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Sulfur in Rubber Vulcanization?
Sulfur is the primary agent used in the vulcanization of rubber. It enhances the cross-linking of polymer chains, significantly improving the material’s strength and elasticity.
- Key Properties: Sulfur provides excellent heat resistance and enhances the tensile strength of rubber. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C during the vulcanization process.
- Pros & Cons: The main advantage of sulfur is its ability to create durable and resilient rubber products. However, it requires precise control during the vulcanization process to avoid scorching, which can ruin the material.
- Impacto na aplicação: Sulfur-vulcanized rubber is compatible with various media, making it suitable for automotive, industrial, and consumer applications.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East may prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to these standards.
How Does Carbon Black Affect Rubber Vulcanization?
Carbon Black is often added as a reinforcing filler during the vulcanization process, enhancing the mechanical properties of rubber.
- Key Properties: Carbon black improves tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and UV stability. It also contributes to the thermal conductivity of rubber.
- Pros & Cons: The addition of carbon black results in a more durable product, but it can increase production costs. The manufacturing process may also become more complex due to the need for precise mixing.
- Impacto na aplicação: Carbon black-reinforced rubber is ideal for tires and industrial applications where durability and wear resistance are critical.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers should be aware of the environmental regulations regarding carbon black usage, particularly in Europe, where there are stringent restrictions on emissions.
What Role Do Accelerators Play in the Vulcanization Process?
Accelerators are chemical agents that speed up the vulcanization process, allowing for shorter curing times and improved efficiency.
- Key Properties: Accelerators can significantly reduce the time required for vulcanization, making the process more efficient. They can also enhance the overall quality of the final product.
- Pros & Cons: While accelerators improve production efficiency, they can also introduce variability in the final product’s properties if not carefully managed.
- Impacto na aplicação: The use of accelerators is particularly beneficial in high-volume production settings where time and consistency are critical.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: Compliance with local regulations regarding chemical additives is essential. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide certifications for the accelerators used.
How Do Fillers Influence the Vulcanization of Rubber?
Fillers such as calcium carbonate or silica are used to modify the properties of rubber during vulcanization.
- Key Properties: Fillers can improve the cost-effectiveness of rubber products by reducing the amount of expensive rubber needed. They also affect the density and thermal stability of the final product.
- Pros & Cons: While fillers can lower costs, they may also compromise certain mechanical properties, such as elasticity and tensile strength.
- Impacto na aplicação: Fillers are commonly used in applications where cost is a significant factor, such as in the production of lower-grade rubber products.
- Considerações para compradores internacionais: Buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between cost and performance, especially in regions where quality standards are high.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rubber Vulcanization
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to vulcanize rubber | Vantagem chave | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfur | General rubber products | Enhances strength and elasticity | Requires precise control to avoid scorching | Médio |
| Carbon Black | Tires, industrial components | Improves durability and abrasion resistance | Increases production costs | Médio |
| Accelerators | High-volume production | Reduces curing time | Can introduce variability in properties | Médio |
| Fillers | Cost-sensitive rubber products | Lowers material costs | May compromise mechanical properties | Baixa |
This guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their rubber vulcanization processes. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to vulcanize rubber
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Vulcanizing Rubber?
The manufacturing process for vulcanizing rubber involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. The primary phases include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Rubber Vulcanization?
The first step in the vulcanization process is the careful preparation of raw materials. Typically, natural or synthetic rubber is selected based on the desired properties of the final product. Additives such as sulfur, accelerators, fillers, and other agents are then mixed into the rubber to enhance its strength, durability, and other characteristics.
This mixing is often done in a two-roll mill or an internal mixer, where the rubber is combined with the additives at controlled temperatures. The quality of these materials is crucial, as impurities can compromise the vulcanization process and the integrity of the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Rubber Vulcanization?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. The rubber compound is shaped using various techniques, including:
- Moldagem: Rubber is placed into molds to create specific shapes. This method is suitable for producing complex geometries and is commonly used for parts like seals and gaskets.
- Extrusão: In this process, the rubber is forced through a die to create continuous shapes, such as hoses or profiles. Extrusion is efficient for producing long parts with uniform cross-sections.
- Calendering: This technique involves passing the rubber compound through a series of rollers to create sheets of a specified thickness. Calendered sheets are often used for flooring or matting applications.
Each forming technique has its own set of requirements and can influence the properties of the vulcanized rubber.
How Is the Assembly of Vulcanized Rubber Products Managed?
Once the rubber is formed, the assembly stage may begin, especially for products composed of multiple parts. This can include bonding rubber to other materials, such as metals or textiles, which often requires additional adhesives or processes like heat treatment.
Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
Assembly operations must be conducted under strict quality control measures to ensure that joints and seams are secure and meet strength specifications. This is particularly important for products that will be subjected to high levels of stress or environmental exposure.
What Finishing Steps Are Involved in the Vulcanization Process?
The final stage is finishing, which can involve several processes to enhance the appearance and performance of the rubber products. This may include trimming excess material, surface treatments, or the application of protective coatings.
Finishing is also a critical point for ensuring the product meets aesthetic and functional requirements, such as color matching or surface texture.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Rubber Vulcanization?
Quality assurance in rubber vulcanization is vital for ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key quality control measures include adherence to relevant international standards, rigorous inspection checkpoints, and comprehensive testing methods.
Que normas internacionais devem os compradores B2B considerar?
For B2B buyers, understanding the applicable international standards is crucial. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards globally, providing a framework for consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications, should be considered.
These standards ensure that the products are manufactured to specific quality and safety requirements, which is especially important in regulated markets.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Rubber Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are essential at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Controlo de qualidade de entrada (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Ensuring that materials meet specifications helps prevent defects in the final product.
- Controlo de qualidade durante o processo (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process is critical. This may include checking temperature and pressure during vulcanization and ensuring that forming techniques are performed correctly.
- Controlo de qualidade final (FQC): Once the products are completed, they should undergo a thorough inspection to ensure they meet all specifications and standards. This may involve physical testing, visual inspections, and functional assessments.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Rubber Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods for vulcanized rubber products include:
- Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the force required to break a rubber sample, indicating its strength and elasticity.
- Hardness Testing: Determines the hardness of the rubber, which affects its performance in different applications.
- Compression Set Testing: Assesses the rubber’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed, which is vital for seals and gaskets.
Each of these testing methods provides valuable insights into the quality and performance of the final product.
Como podem os compradores B2B verificar o controlo de qualidade dos fornecedores?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is critical to ensuring consistent product quality. Here are several methods to assess supplier QC:
What Auditing Processes Should Be Considered?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to evaluate their quality management systems. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting production facilities, and assessing compliance with international standards.
Buyers should consider periodic audits, especially when entering new partnerships or when significant changes occur in the supplier’s processes.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
How Can Buyers Access Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers can provide further assurance of their quality control practices. Many suppliers will have third-party inspections conducted by accredited organizations, which can validate compliance with industry standards.
Buyers should ask for copies of these reports and verify their authenticity with the issuing organizations.
Quais são as nuances do controlo de qualidade para os compradores internacionais B2B?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances when it comes to quality control in different regions. For instance, regulations may vary significantly between Europe and Africa or South America, impacting product compliance and certifications.
Understanding these regional differences is essential for navigating the complexities of international trade and ensuring that products are suitable for their intended markets.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for vulcanizing rubber are complex but critical for delivering high-quality products. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure that they source reliable and compliant rubber products for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to vulcanize rubber’
To support B2B buyers in the procurement of rubber vulcanization services and materials, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure quality and reliability in the sourcing process. Vulcanization is critical for enhancing rubber’s properties, making it suitable for various applications. Following this checklist will help you make informed decisions and secure the best suppliers for your needs.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
Passo 1: Definir as suas especificações técnicas
Clearly outline your requirements for the rubber products you need, including dimensions, material type, and performance characteristics. This step is vital as it ensures that potential suppliers can meet your specific needs. Consider the following aspects:
– Material Composition: Specify whether you need natural rubber, synthetic rubber, or a blend.
– Performance Criteria: Define factors such as tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to chemicals or temperature.
Passo 2: Pesquisa de potenciais fornecedores
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in rubber vulcanization. This step is essential for finding reliable partners who can deliver quality products. Look for:
– Industry Experience: Favor suppliers who have extensive experience in your specific industry.
– Geographical Considerations: Evaluate suppliers based on their location to minimize shipping costs and lead times.
Passo 3: Avaliar as certificações dos fornecedores
Before moving forward, ensure that suppliers hold relevant industry certifications. Certifications can indicate compliance with international quality standards, which is crucial for maintaining product integrity. Key certifications to check include:
– ISO 9001: Ensures a quality management system is in place.
– ISO 14001: Indicates commitment to environmental management, important for sustainability.
Passo 4: Request Samples for Testing
Request product samples to evaluate the quality and suitability of the rubber materials. Testing samples allows you to assess the performance characteristics and compatibility with your applications. Focus on:
– Durability Testing: Check for abrasion resistance and tensile strength.
– Performance Under Conditions: Assess how the rubber performs under specific environmental conditions relevant to your application.
Passo 5: Review Production Capabilities
Investigate the production capabilities of potential suppliers to ensure they can handle your order volume and timeline. Understanding their capacity helps prevent future delays. Consider:
– Production Scale: Confirm if they can meet both small and large batch requirements.
– Technology and Equipment: Evaluate the technology used for vulcanization to ensure it meets modern standards.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
Passo 6: Negociar condições e preços
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and terms of service. This step is crucial to achieving a favorable deal that aligns with your budget and expectations. Pay attention to:
– Descontos por volume: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders.
– Payment Terms: Discuss payment schedules and any upfront costs.
Passo 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, establish clear communication channels with your chosen supplier. Effective communication is key to ensuring that your specifications are met and to resolve any issues that may arise during production. Make sure to:
– Designate Points of Contact: Assign specific individuals from both sides to handle inquiries and updates.
– Set Regular Check-Ins: Schedule periodic meetings to review progress and address any concerns.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process for vulcanized rubber, ensuring they select the best suppliers to meet their needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to vulcanize rubber Sourcing
When considering the cost structure for sourcing vulcanized rubber, it is essential to break down the various components that contribute to the overall pricing. Understanding these components will enable B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, particularly in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Quais são os principais componentes de custo no fornecimento de borracha vulcanizada?
-
Materiais: The primary material in vulcanization is rubber, typically natural or synthetic. Additional materials like sulfur, accelerators, fillers (e.g., carbon black), and protective agents also play a critical role. The quality and origin of these materials can significantly impact costs, with premium-grade materials leading to higher expenses.
-
Trabalho: Labor costs encompass the wages for skilled technicians who oversee the vulcanization process, along with any additional workforce needed for handling and quality control. Regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may see increased overall pricing compared to regions with more competitive labor markets.
-
Despesas gerais de fabrico: This includes costs associated with factory operation, such as utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of machinery. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, thereby affecting the final price of vulcanized products.
-
Ferramentas: Custom molds and equipment necessary for producing specific rubber products can incur substantial initial costs. These costs are often amortized over large production runs, making them more manageable per unit for larger orders.
-
Controlo de qualidade (CQ): Ensuring that the vulcanized rubber meets industry standards and customer specifications requires rigorous quality control procedures. The costs associated with testing and certification can vary based on the complexity of the product and the required certifications.
-
Logística: Transportation and warehousing costs can add significant overhead, especially for international shipments. These costs vary based on distance, shipping method, and the chosen Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers during shipping.
-
Margem: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing structure, which can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence pricing in the vulcanized rubber market:
-
Volume e quantidade mínima de encomenda (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs, making it financially advantageous for buyers to negotiate for bulk purchasing.
-
Especificações e personalização: Custom formulations or specific product characteristics may lead to higher prices due to the additional resources required for production.
-
Qualidade e certificações: Products that come with industry certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and compliance.
-
Factores do fornecedor: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more than newer entrants.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects pricing and logistics costs. For instance, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) might be more expensive upfront but could offer better risk management for buyers.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices based on volume. Establish long-term relationships with suppliers to foster better pricing arrangements.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with logistics, maintenance, and potential quality issues.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that could impact overall costs when sourcing from different regions.
-
Seek Transparency in Pricing: Request detailed breakdowns of costs from suppliers to understand where your money is going. This transparency can help identify areas for cost reduction.
-
Evaluate Supplier Capabilities: Assess suppliers based on their ability to meet specific requirements, timelines, and quality standards, which can lead to better long-term value.
Conclusão
Sourcing vulcanized rubber requires a comprehensive understanding of the various cost components and pricing influencers. By leveraging insights into these elements, international B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance cost efficiency and product quality. It is crucial to approach the market with a holistic view, ensuring that all factors are considered to achieve the best possible outcomes for your sourcing needs.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to vulcanize rubber With Other Solutions
In the realm of rubber manufacturing, vulcanization is a well-established method that enhances the properties of rubber, making it suitable for various applications. However, there are alternative methods that can also achieve similar results. Understanding these alternatives allows businesses to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application needs.
| Aspeto de comparação | How To Vulcanize Rubber | Alternative 1: Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Alternative 2: Chemical Crosslinking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Excellent durability, heat resistance, and tensile strength | Good elasticity and flexibility, but lower heat resistance | High strength and chemical resistance, but can be brittle |
| Custo | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for sulfur and heating | Generally lower production costs; less complex | Higher costs due to chemicals and processes involved |
| Facilidade de implementação | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor | Easier to process and mold; can be done with standard equipment | Requires precise control of chemical reactions |
| Manutenção | Low maintenance; equipment needs regular checks | Low maintenance; equipment is often standard | Moderate maintenance; requires monitoring chemical processes |
| Melhor caso de utilização | Ideal for high-performance applications like tires, gaskets | Suitable for consumer products, toys, and flexible components | Best for industrial applications requiring chemical resistance |
What Are Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) and Their Advantages?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are a blend of rubber and plastic, offering a combination of the best properties of both materials. They can be processed like plastics, allowing for easier manufacturing and shaping. TPEs provide good flexibility and elasticity, making them suitable for various consumer products like seals, gaskets, and toys. However, they typically do not withstand high temperatures as well as vulcanized rubber, which may limit their use in demanding environments.
How Does Chemical Crosslinking Compare to Vulcanization?
Chemical crosslinking involves using specific chemicals to create bonds between rubber molecules, enhancing strength and durability. This method can produce rubber with excellent chemical and heat resistance, making it suitable for industrial applications. However, the process can be complex and often requires precise control over chemical reactions, which can increase the production time and costs. Additionally, the final product may be more brittle than vulcanized rubber, potentially limiting its applications.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
Conclusion: Which Rubber Processing Method Is Right for Your Business?
Choosing the right rubber processing method depends on your specific needs, including application, budget, and production capabilities. Vulcanization remains the gold standard for high-performance applications, but alternatives like TPE and chemical crosslinking may offer advantages in cost and ease of use for less demanding products. B2B buyers should evaluate their requirements carefully, considering factors such as durability, flexibility, and thermal resistance, to select the most appropriate solution for their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to vulcanize rubber
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Rubber Vulcanization?
Understanding the technical properties of rubber vulcanization is crucial for businesses looking to procure or manufacture high-quality rubber products. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Grau do material
Material grade refers to the quality and composition of the rubber used in the vulcanization process. Different grades of rubber (such as natural rubber, SBR, or EPDM) have distinct properties, including elasticity, temperature resistance, and durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the final product meets specific application requirements, thereby reducing the risk of product failure.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of stress that a rubber material can withstand while being stretched. It is an essential property for applications that involve stretching or heavy loads. In B2B transactions, understanding tensile strength helps buyers determine the suitability of rubber products for their intended use, especially in industries like automotive and construction.
3. Hardness (Shore A)
Hardness, often measured on the Shore A scale, indicates the material’s resistance to indentation. Different applications require different hardness levels; softer rubbers offer better flexibility, while harder rubbers provide more durability. B2B buyers must consider hardness to ensure that the rubber components perform optimally in their specific environments.
4. Elongation at Break
This property measures how much a rubber sample can stretch before it breaks. High elongation at break indicates better flexibility and resilience. For businesses, knowing this property is vital when designing products that must endure dynamic stresses, such as seals or gaskets.
5. Compression Set
Compression set is the measure of a material’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed. A low compression set indicates a material’s capability to maintain its performance over time, which is particularly crucial in sealing applications. Understanding compression set allows B2B buyers to assess the longevity and reliability of rubber products.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Rubber Vulcanization?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the rubber vulcanization sector. Here are some common terms:

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
1. OEM (Fabricante de Equipamento Original)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in another company’s products. In the rubber industry, OEMs play a critical role in ensuring that components meet stringent specifications. B2B buyers often engage with OEMs to source customized rubber parts that fit specific applications.
2. MOQ (Quantidade mínima de encomenda)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects budgeting and inventory management. Smaller companies may struggle to meet MOQs, while larger firms can leverage bulk orders for cost savings.
3. RFQ (Pedido de Cotação)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. In the rubber industry, an RFQ typically outlines the specifications for vulcanized rubber products, allowing suppliers to provide tailored pricing. This process is vital for B2B buyers to ensure competitive pricing and quality assurance.
4. Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother cross-border transactions.
5. Curing Agent
A curing agent is a chemical compound added to rubber during the vulcanization process to facilitate crosslinking. This term is critical for B2B buyers who need to understand how different curing agents can affect the properties of the final rubber product, influencing factors like durability and heat resistance.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing vulcanized rubber products, ultimately leading to enhanced product performance and customer satisfaction.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to vulcanize rubber Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends in Rubber Vulcanization?
The global rubber vulcanization market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods. Emerging economies in Africa and South America are expanding their industrial bases, leading to greater consumption of vulcanized rubber products. In Europe, particularly in countries like Germany and Vietnam, innovations in manufacturing processes and materials are enhancing product quality and performance. Key trends include the adoption of advanced technologies such as automation and data analytics, which streamline the vulcanization process, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. Additionally, there is a growing preference for customized rubber solutions that cater to specific applications, enabling international B2B buyers to differentiate their offerings in competitive markets.
Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping sourcing strategies, allowing buyers to leverage real-time data for better decision-making. Blockchain technology is also emerging, facilitating transparency in supply chains and enhancing trust between suppliers and buyers. As environmental regulations tighten globally, companies are increasingly seeking sustainable sourcing options that align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Rubber Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the rubber vulcanization sector. The environmental impact of traditional rubber production and vulcanization processes is significant, often involving harmful chemicals and unsustainable practices that contribute to deforestation and pollution. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt environmentally friendly methods and materials, including natural rubber from certified sustainable sources.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials, such as those verified by the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), is gaining traction. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for responsible products. Furthermore, companies that invest in sustainable practices often benefit from reduced operational costs and increased efficiency, making them more competitive in the global marketplace. By focusing on ethical supply chains, buyers can ensure compliance with international standards while also contributing positively to the environment.
What Is the Historical Context of Rubber Vulcanization in B2B Sourcing?
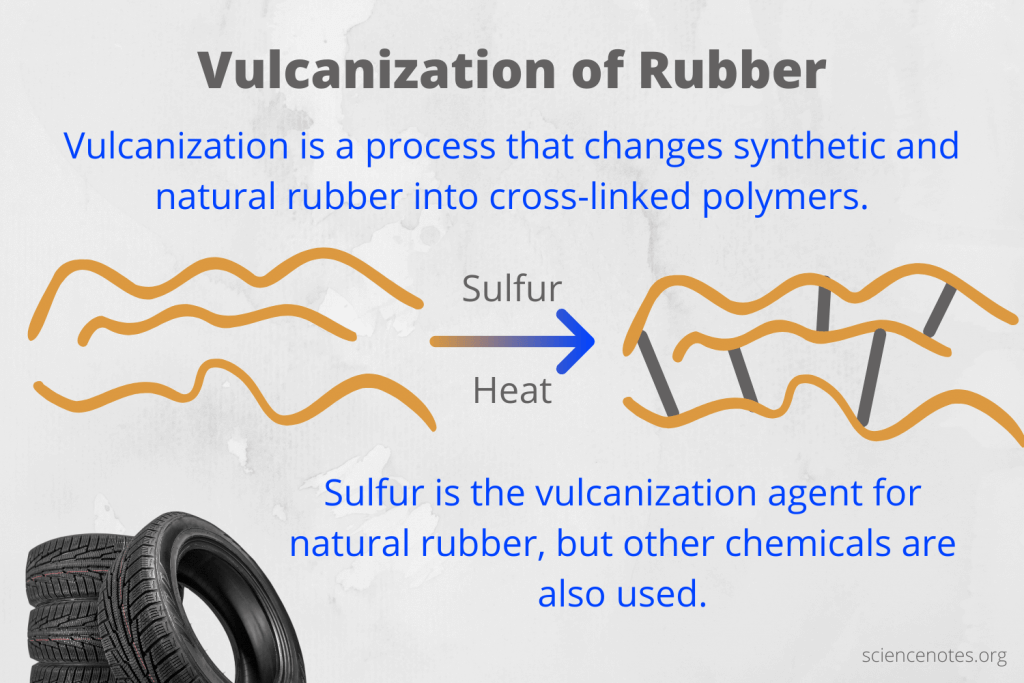
The process of rubber vulcanization was discovered in 1839 by Charles Goodyear, marking a pivotal moment in the development of rubber products. Initially, vulcanization involved heating rubber with sulfur to create cross-links within the polymer, enhancing its strength and durability. This innovation transformed rubber from a commodity into a versatile material used in countless applications, from tires to industrial components.
Historically, the vulcanization process has evolved significantly, with advancements in technology leading to improved efficiency and quality. Today, B2B buyers benefit from a wide range of vulcanized rubber products, tailored to meet specific industrial needs. The evolution of vulcanization techniques, coupled with the growing emphasis on sustainability, continues to shape the landscape of the rubber industry, presenting new opportunities for international buyers. As the market adapts to changing consumer demands and regulatory pressures, understanding this historical context is essential for making informed sourcing decisions in the rubber sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to vulcanize rubber
-
How do I determine the right vulcanization process for my rubber products?
Choosing the appropriate vulcanization process depends on the desired properties of the final product. Pressure vulcanization is ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability, as it uses heat and pressure to create strong crosslinks. Free vulcanization, on the other hand, is suitable for less demanding applications where flexibility and lower costs are priorities. Assess your product specifications, environmental conditions, and performance requirements to make an informed choice. Consulting with suppliers or experts in rubber manufacturing can also provide valuable insights tailored to your specific needs. -
What materials are typically used in the vulcanization process?
The primary material used in vulcanization is sulfur, which creates crosslinks between rubber polymer chains, enhancing strength and durability. Other materials may include accelerators to speed up the curing process, fillers like carbon black to improve tensile strength, and protective agents to prevent aging. Depending on the application, you might also consider using pigments for color or softeners for increased flexibility. Collaborating with your supplier to select the right combination of materials is crucial for achieving the desired properties in your rubber products. -
How can I ensure quality control in the vulcanization process?
To maintain high-quality standards, implement a comprehensive quality assurance (QA) program that includes regular monitoring of raw materials, processing conditions, and final product inspections. Utilize standardized testing methods to assess properties like tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. Working closely with your suppliers to establish clear QA protocols and expectations will help ensure that the vulcanization process meets international standards and your specific requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for vulcanized rubber products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific type of rubber products required. Generally, manufacturers may set MOQs to cover production costs and ensure efficiency. For custom products or specialized formulations, MOQs may be higher. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vulcanized rubber products internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can range from upfront payments to net 30 or 60 days, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common practices include letters of credit or escrow services to secure transactions. It’s essential to clarify payment terms early in negotiations and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement. Consider factors like currency exchange rates and transaction fees that may impact overall costs. -
How do I vet potential suppliers of vulcanized rubber?
To effectively vet suppliers, conduct thorough research that includes checking industry certifications, customer reviews, and case studies of previous work. Request samples of their products to evaluate quality firsthand. Engage in direct communication to assess their responsiveness and expertise. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible, as this can provide insights into their production capabilities and adherence to quality standards. -
Que considerações logísticas devo ter em conta ao importar borracha vulcanizada?
When importing vulcanized rubber, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling rubber products to ensure efficient transportation and compliance with international trade laws. It’s crucial to account for lead times and establish clear communication with your suppliers regarding shipping schedules to avoid delays in delivery. -
How can I customize vulcanized rubber products to fit my specific needs?
Customization of vulcanized rubber products is often possible through adjustments in formulation, dimensions, and surface treatments. Discuss your specific requirements with suppliers, including any desired properties like hardness, color, or special additives. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions, but be prepared to share detailed specifications and potentially meet minimum order quantities for customized products. Engaging in early-stage discussions can lead to successful collaboration and product development.
Top 4 How To Vulcanize Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Slingshot Forum – Homemade Vulcanized Rubber
Domínio: theslingshotforum.com
Registada: 2012 (13 anos)
Introdução: Homemade vulcanized rubber made from latex milk, sulphur, zinc oxide, and Fairy dishwasher soap (non-ionic tenside). The soap aids in mixing, zinc accelerates the process, and sulphur creates cross-links between polymer molecules. The vulcanization process takes 30 minutes in a standard kitchen oven. The resulting rubber is stretchy (up to 6:1 before tearing), dry, and snaps back well. Issues enco…
2. RubberCal – Corrugated Wide Rib Rubber Runner Mats
Domínio: rubbercal.com
Registada: 1999 (26 anos)
Introdução: Rubber vulcanization process involves heating natural sheet rubber with sulfur to strengthen its molecular structure. This process reduces elasticity but enhances strength, abrasion resistance, and durability. Key product: “Corrugated Wide Rib” Rubber Runner Mats, available in custom lengths up to 50ft, suitable for commercial and industrial floors, featuring textured underside for improved tracti…
3. WARE – Boiler Rental & Service Solutions
Domínio: wareinc.com
Registada: 2000 (25 anos)
Introdução: WARE is an industrial & commercial boiler rental and service company specializing in sales, service, valve repair, rentals, parts, turnkey solutions, and boiler training. They offer a wide range of boiler rentals for various applications and industries, new, used, and remanufactured boiler equipment, industrial boiler room auxiliary equipment like deaerators and heat exchangers, combustion equipme…
4. ScienceDirect – Vulcanization Process
Domínio: sciencedirect.com
Registada: 1997 (28 anos)
Introdução: Vulcanization is a chemical process that enhances the elasticity and retractile force of rubbery or elastomeric materials by forming a crosslinked molecular network. This process reduces permanent deformation after the removal of applied forces and typically involves the insertion of crosslinks between polymer chains using sulfur or other vulcanizing agents. Key aspects include:
1. Improved mecha…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to vulcanize rubber
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing in Rubber Vulcanization?
In summary, strategic sourcing in rubber vulcanization unlocks significant advantages for B2B buyers. By collaborating with reliable suppliers, companies can ensure access to high-quality raw materials and advanced vulcanization techniques that enhance the durability and performance of rubber products. Understanding the critical elements of vulcanization—such as the role of sulfur and the processes of pressure and free vulcanization—empowers buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs.

Illustrative image related to how to vulcanize rubber
How Can International Buyers Leverage Vulcanization Expertise?
For businesses operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to source vulcanized rubber effectively can be a game-changer. This process not only strengthens rubber but also broadens its application scope, enabling manufacturers to meet evolving consumer demands. By fostering relationships with experts in rubber vulcanization, companies can stay ahead of industry trends and technological advancements.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in the Rubber Industry?
As the rubber industry continues to evolve, B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace strategic sourcing as a pathway to innovation and competitiveness. Engaging with suppliers who are committed to quality and sustainability will be essential. Take the next step—explore partnerships that enhance your rubber product offerings, ensuring you remain a leader in your market.
Aviso importante e termos de utilização
⚠️ Declaração de exoneração de responsabilidade importante
As informações fornecidas neste guia, incluindo o conteúdo relativo a fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análises de mercado, destinam-se apenas a fins informativos e educativos. Não constitui aconselhamento profissional em matéria de aquisições, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos feito todos os esforços para garantir a exatidão e a atualidade das informações, não somos responsáveis por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desactualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e as normas técnicas estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem efetuar a sua própria diligência prévia independente e exaustiva antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isto inclui contactar diretamente os fornecedores, verificar as certificações, pedir amostras e procurar aconselhamento profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é suportado exclusivamente pelo leitor.