Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is vulcanizing rubber
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing high-quality vulcanized rubber is a critical challenge for manufacturers across various industries. As businesses strive to enhance product durability and performance, understanding the complexities of vulcanization becomes essential. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of vulcanizing rubber, including its types, applications, and the essential factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
From automotive components to industrial seals, vulcanized rubber is integral to many products, offering superior strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam, will find valuable insights into the cost implications and quality benchmarks for vulcanized rubber. By examining the supplier vetting process and the nuances of sourcing, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Equipped with actionable information and expert advice, readers will navigate the complexities of the vulcanized rubber market with confidence, ensuring they select the right materials to meet their operational needs and drive business success. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product offerings and supply chain efficiency by diving into the essential knowledge this guide provides.
Оглавление
- Top 4 What Is Vulcanizing Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is vulcanizing rubber
- Understanding what is vulcanizing rubber Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is vulcanizing rubber
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is vulcanizing rubber’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is vulcanizing rubber
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is vulcanizing rubber
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is vulcanizing rubber’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is vulcanizing rubber Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is vulcanizing rubber With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is vulcanizing rubber
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is vulcanizing rubber Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is vulcanizing rubber
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is vulcanizing rubber
- Важный отказ от ответственности и условия использования
Understanding what is vulcanizing rubber Types and Variations
| Название типа | Ключевые отличительные особенности | Основные приложения B2B | Краткие плюсы и минусы для покупателей |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber Vulcanization | Derived from rubber tree latex; excellent elasticity and resilience | Tires, footwear, industrial seals | Плюсы: High elasticity, biodegradable. Конс: Prone to UV degradation, limited thermal resistance. |
| Synthetic Rubber Vulcanization | Made from petroleum by-products; versatile and customizable | Automotive parts, seals, hoses | Плюсы: High resistance to heat and chemicals, customizable properties. Конс: Environmental concerns, potential allergic reactions. |
| Heat-Cured Vulcanization | Uses heat and sulfur; results in strong, durable rubber | Gaskets, conveyor belts, hoses | Плюсы: Enhanced durability, good for high-stress applications. Конс: More complex processing, requires precise temperature control. |
| Cold Vulcanization | Utilizes chemical agents without heat; easier to apply | Repairing tires, small components | Плюсы: Quick application, no need for heating equipment. Конс: Generally less durable than heat-cured options, limited applications. |
| Accelerated Vulcanization | Involves accelerators for faster curing; improves efficiency | Automotive tires, industrial products | Плюсы: Reduced processing time, improved mechanical properties. Конс: More expensive additives, potential for uneven curing if not managed properly. |
What are the characteristics of Natural Rubber Vulcanization for B2B buyers?
Natural rubber vulcanization is derived from the latex of rubber trees, providing exceptional elasticity and resilience. It is widely used in products such as tires and footwear due to its superior stretchability and comfort. However, B2B buyers should consider its susceptibility to UV degradation and limited thermal resistance, which may affect its longevity in certain applications. This type of rubber is also biodegradable, aligning with environmentally conscious purchasing decisions.
How does Synthetic Rubber Vulcanization meet diverse industrial needs?
Synthetic rubber vulcanization is produced from petroleum by-products, offering a wide range of customizable properties suitable for various applications, including automotive parts and seals. Its high resistance to heat and chemicals makes it ideal for demanding environments. However, buyers should be aware of potential environmental concerns associated with synthetic materials and the risk of allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Understanding the specific requirements of each application will help in selecting the right type of synthetic rubber.
What advantages does Heat-Cured Vulcanization provide for industrial applications?
Heat-cured vulcanization employs heat and sulfur to create a robust and durable rubber product, making it well-suited for high-stress applications such as gaskets and conveyor belts. The enhanced durability ensures longevity and reliability in demanding environments. However, the complexity of the processing and the need for precise temperature control can pose challenges for manufacturers. Buyers should weigh these factors against the performance benefits when considering heat-cured options.
What are the benefits and limitations of Cold Vulcanization in B2B settings?
Cold vulcanization utilizes chemical agents to cure rubber without heat, making it a convenient option for quick repairs and small components. It is particularly effective for tire repairs, as it allows for immediate application without specialized equipment. However, its durability is generally lower than heat-cured options, which limits its use in high-performance applications. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific needs of their projects to determine if cold vulcanization is a viable solution.
How does Accelerated Vulcanization enhance production efficiency?
Accelerated vulcanization incorporates accelerators that speed up the curing process, significantly improving production efficiency for items like automotive tires and industrial products. This method reduces processing time and enhances mechanical properties, making it attractive for high-volume manufacturing. However, the use of more expensive additives and the potential for uneven curing require careful management. Buyers should assess the cost-benefit ratio of using accelerated vulcanization in their production processes.
Key Industrial Applications of what is vulcanizing rubber
| Промышленность/сектор | Specific Application of what is vulcanizing rubber | Ценность/выгода для бизнеса | Ключевые соображения по поиску источников для данного приложения |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Tire manufacturing | Enhanced durability and performance under stress | Ensure compliance with regional safety standards and certifications. |
| Строительство | Seals and gaskets for machinery | Improved resistance to environmental factors | Sourcing from reliable suppliers with quality assurance processes. |
| Consumer Goods | Footwear production | Increased comfort and longevity of products | Consider customization options for specific design needs. |
| Electronics | Keypads and buttons | Greater tactile response and durability | Verify compatibility with electronic components and materials. |
| Industrial Equipment | Vibration dampeners and mounts | Reduced wear on machinery, leading to lower maintenance costs | Look for suppliers with experience in heavy-duty applications. |
How is Vulcanizing Rubber Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, vulcanizing rubber is primarily utilized in tire manufacturing. The vulcanization process enhances the rubber’s strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, allowing tires to withstand high pressure and harsh driving conditions. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to source tires that meet local climate and road conditions. Additionally, compliance with safety standards and certifications is essential to ensure product reliability and performance.
What Role Does Vulcanizing Rubber Play in Construction?
In construction, vulcanized rubber is essential for producing seals and gaskets used in various machinery and equipment. These components must resist environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and chemical exposure. Businesses benefit from the enhanced durability and reliability of vulcanized rubber, which reduces the risk of leaks and machinery downtime. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with robust quality assurance processes to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of these products.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
How is Vulcanizing Rubber Beneficial in Consumer Goods?
Vulcanized rubber is widely used in the production of footwear, providing increased comfort, flexibility, and durability. The vulcanization process allows for a better fit and longer-lasting products, which are crucial for consumer satisfaction and brand loyalty. For B2B buyers in the consumer goods sector, customization options are vital to meet specific design and functional requirements. Sourcing from suppliers that offer innovative designs and materials can help businesses differentiate their products in a competitive market.
Why is Vulcanizing Rubber Important for Electronics?
In the electronics industry, vulcanized rubber is commonly used for keypads and buttons, where tactile response and durability are critical. The enhanced properties of vulcanized rubber ensure that electronic devices can withstand frequent use without degradation. International buyers should verify the compatibility of vulcanized rubber components with other electronic materials to prevent performance issues. Additionally, sourcing from experienced suppliers can help ensure that the products meet required specifications and performance standards.
What Benefits Does Vulcanizing Rubber Provide in Industrial Equipment?
Vulcanized rubber is crucial for creating vibration dampeners and mounts in industrial equipment, significantly reducing wear and tear on machinery. This application leads to lower maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency. For businesses in sectors such as manufacturing, sourcing high-quality vulcanized rubber components is essential for long-term reliability. Buyers should look for suppliers that specialize in heavy-duty applications and can provide evidence of performance under rigorous conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is vulcanizing rubber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Vulcanized Rubber Products
Проблема: B2B buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality vulcanized rubber products that meet their specific needs. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions with limited access to advanced manufacturing capabilities, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers frequently encounter inconsistent product quality, leading to increased costs and delays in production schedules. The fear of sourcing inferior materials that could compromise product integrity is a significant concern.
Решение: To overcome this sourcing challenge, buyers should prioritize establishing relationships with certified manufacturers known for their quality control processes. It’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, including reviewing certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Buyers can also leverage platforms that connect them with vetted suppliers and request samples before committing to larger orders. Additionally, engaging in direct communication with suppliers can help clarify material specifications, production capabilities, and lead times. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks associated with quality but also fosters long-term partnerships that can adapt to future needs.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
Scenario 2: Understanding the Technical Aspects of Vulcanized Rubber
Проблема: Many B2B buyers lack a deep understanding of the technical properties of vulcanized rubber, which can lead to misapplication in their products. For instance, different formulations of vulcanized rubber vary in elasticity, heat resistance, and durability, making it challenging for buyers to select the appropriate type for their applications. This knowledge gap can result in product failures, increased warranty claims, and customer dissatisfaction.
Решение: To bridge this knowledge gap, buyers should invest time in educational resources and training programs that focus on the properties and applications of vulcanized rubber. Engaging with industry experts or attending workshops can provide valuable insights into the specific performance characteristics of various rubber formulations. Moreover, buyers should collaborate closely with their suppliers to receive tailored recommendations based on their unique product requirements. Utilizing technical datasheets and requesting detailed explanations of the vulcanization process can also empower buyers to make informed decisions. This foundational knowledge will enable them to select the right materials that enhance product performance and longevity.
Scenario 3: Navigating Cost Implications of Vulcanized Rubber
Проблема: B2B buyers often face pressure to minimize costs while maintaining quality when procuring vulcanized rubber. The misconception that lower prices equate to better deals can lead to selecting inferior products that ultimately increase total operational costs due to failures, replacements, and warranty claims. Buyers in cost-sensitive industries, such as automotive or construction, may find themselves at a crossroads when balancing cost with quality.
Решение: To effectively navigate these cost implications, buyers should adopt a value-based procurement strategy rather than a purely price-focused approach. This involves conducting a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis that considers not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term performance, maintenance, and replacement costs associated with vulcanized rubber products. Buyers should seek out suppliers that offer transparent pricing structures and value-added services, such as customization or engineering support. Establishing long-term contracts with reliable suppliers can also yield cost benefits while ensuring access to high-quality materials. By focusing on the overall value rather than just upfront costs, buyers can secure durable, high-performance vulcanized rubber products that ultimately contribute to their bottom line.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is vulcanizing rubber
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Vulcanizing Rubber?
When selecting materials for vulcanizing rubber, it is essential to consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze three common materials used in the vulcanization process: natural rubber, synthetic rubber (specifically styrene-butadiene rubber), and silicone rubber. Each material has unique properties that can significantly influence product performance and application.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
What Are the Key Properties of Natural Rubber in Vulcanization?
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of rubber trees, boasts excellent elasticity and tensile strength. It performs well under a wide range of temperatures, typically rated from -50°C to 80°C. However, it is less resistant to ozone, UV light, and certain chemicals, which can limit its applications in harsh environments.
Pros: Natural rubber is cost-effective and offers superior elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility, such as tires and seals.
Cons: Its susceptibility to environmental factors can lead to premature degradation, necessitating protective additives or coatings.
Влияние на применение: Natural rubber is best suited for applications where flexibility is paramount, but it may not be suitable for environments with high ozone or UV exposure.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where climatic conditions can vary significantly.
How Does Synthetic Rubber (SBR) Compare in Vulcanization?
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a widely used synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros: SBR is more resistant to heat and aging compared to natural rubber, offering better performance in demanding environments. It is also less expensive than some other synthetic options.
Cons: While SBR has good mechanical properties, it may not provide the same level of elasticity as natural rubber, which can be a drawback in certain applications.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
Влияние на применение: SBR is commonly used in tire manufacturing and industrial applications where durability and wear resistance are critical.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should verify that SBR products meet regional compliance standards, as the material can vary in formulation and performance.
What Advantages Does Silicone Rubber Offer in Vulcanization?
Silicone rubber is renowned for its exceptional temperature resistance, withstanding extremes of -60°C to 250°C. It is also highly resistant to UV light, ozone, and various chemicals, making it ideal for specialized applications.
Pros: The versatility of silicone rubber allows for use in a wide range of applications, including automotive and medical devices. Its stability under extreme conditions makes it a preferred choice for high-performance applications.
Cons: Silicone rubber can be more expensive than natural or synthetic alternatives, which may be a consideration for cost-sensitive projects.
Влияние на применение: Silicone rubber is particularly suited for applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical resistance, such as gaskets and seals in automotive and aerospace industries.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Compliance with international standards (e.g., FDA for food applications) is crucial, especially for buyers in regions with strict regulatory environments like Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Vulcanizing Rubber
| Материал | Typical Use Case for what is vulcanizing rubber | Ключевое преимущество | Основные недостатки/ограничения | Относительная стоимость (низкая/средняя/высокая) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Tires, seals, flexible components | Excellent elasticity and tensile strength | Susceptible to ozone and UV degradation | Низкий |
| Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Industrial tires, conveyor belts | Good abrasion resistance and durability | Less elastic than natural rubber | Средний |
| Silicone Rubber | Gaskets, seals in automotive and medical fields | High temperature and chemical resistance | Higher cost compared to other rubbers | Высокий |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in vulcanizing rubber. Understanding these factors is crucial for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is vulcanizing rubber
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Vulcanizing Rubber?
The manufacturing process of vulcanized rubber involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary performance standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to procure high-quality rubber products.
Material Preparation: How Is Rubber Prepared for Vulcanization?
The initial stage involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. Rubber, whether natural or synthetic, is combined with sulfur and other additives to enhance its properties. The preparation typically includes:
-
Mixing: The rubber is mixed with sulfur, accelerators, fillers, and other additives in a controlled environment. This step is crucial as it determines the final characteristics of the vulcanized rubber.
-
Mastication: This process breaks down the rubber’s molecular structure, making it easier to mix with other materials. It also enhances the rubber’s processability.
-
Контроль качества: Initial checks (IQC – Incoming Quality Control) are conducted to ensure that all materials meet specified standards before proceeding to the next stage.
How Is Rubber Formed During the Vulcanization Process?
Once the material is prepared, the next step is forming the rubber into the desired shape. This stage includes:
-
Формовка: The mixed rubber is placed in molds to create specific shapes. The molding process can vary from compression molding to injection molding, depending on the complexity of the desired product.
-
Heating: The molded rubber is then subjected to heat in a vulcanizing press. This step is crucial, as it activates the sulfur and accelerators, allowing them to form cross-links between the rubber molecules.
-
Cooling: After heating, the rubber is cooled to set its shape. Proper cooling is essential to avoid warping or deformities in the final product.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Vulcanized Rubber Production?
The finishing stage refines the product to meet aesthetic and functional standards. Key processes include:
-
Trimming and Deflashing: Excess rubber from the molding process is trimmed away to achieve a clean finish.
-
Surface Treatment: Depending on the application, the surface may be treated to enhance properties like adhesion or abrasion resistance.
-
Окончательный контроль качества (ОКК): A final inspection ensures that the product meets all specifications before it is packaged and shipped.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is critical in the production of vulcanized rubber, especially for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. Several international standards guide the quality processes:

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
-
ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Buyers should look for suppliers certified under ISO 9001.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: Depending on the application, other certifications may be relevant. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, while API certifications are important for rubber products used in the oil and gas industry.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Vulcanized Rubber Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process involves several quality control checkpoints to ensure product integrity:
-
Входящий контроль качества (IQC): This involves checking raw materials for conformity to specifications before they enter the production process.
-
Внутрипроцессный контроль качества (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify any deviations from set standards early, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
-
Окончательный контроль качества (ОКК): Before shipping, products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all quality standards and specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Vulcanized Rubber?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that vulcanized rubber products meet performance standards:
-
Tensile Strength Testing: This measures the rubber’s ability to withstand pulling forces, ensuring it can handle the intended load.
-
Elongation at Break Testing: This evaluates the rubber’s elasticity, confirming that it can stretch without breaking.
-
Hardness Testing: Often performed using a durometer, this test measures the rubber’s resistance to indentation, which correlates to its durability.
-
Abrasion Resistance Testing: This assesses how well the rubber can withstand wear and tear, an essential factor for many applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring supplier quality is paramount. Here are several strategies:
-
Аудиты поставщиков: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This helps verify compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers assess their quality assurance practices and performance metrics.
-
Проверки третьих сторон: Engaging independent inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances when dealing with international suppliers:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes toward quality can help buyers communicate expectations clearly and effectively.
-
Соответствие нормативным требованиям: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties.
-
Logistical Considerations: Importing products may introduce additional quality risks. Ensuring that products are handled properly during transport is crucial for maintaining quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in vulcanizing rubber, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is vulcanizing rubber’
In the realm of industrial materials, vulcanized rubber stands out for its enhanced strength and elasticity, making it a preferred choice across various sectors. This guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a practical checklist for sourcing vulcanized rubber, ensuring informed decisions that align with technical requirements and market demands.
Шаг 1: Определите технические характеристики
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for sourcing the right type of vulcanized rubber. Consider factors such as the intended application, required durability, and environmental conditions. This will guide your supplier discussions and ensure you procure a product that meets your operational needs.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
- Key Attributes to Specify:
- Hardness (measured in Shore A)
- Temperature resistance range
- Chemical resistance properties
Шаг 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to verify their credentials and industry standing. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 or ASTM. This step reduces the risk of quality issues and ensures that you are partnering with reputable manufacturers.
- Verification Checklist:
- Review quality management certifications
- Check for industry-specific compliance (e.g., automotive, medical)
Шаг 3: Оцените потенциальных поставщиков
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; conducting thorough due diligence can reveal insights into their reliability and product quality.
- Considerations for Evaluation:
- Years in business and experience in vulcanized rubber manufacturing
- Client testimonials and case studies that reflect their capabilities
Шаг 4: Запрос образцов для тестирования
Obtaining samples before placing a bulk order is vital. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality of the vulcanized rubber against your specifications. This step can also help identify any discrepancies in performance or characteristics.
- Testing Parameters to Consider:
- Tensile strength and elongation at break
- Abrasion resistance and compression set
Шаг 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, negotiate pricing and payment terms. Ensure that the pricing reflects the quality of the material and aligns with your budget constraints. Discuss terms such as delivery schedules, minimum order quantities, and warranty provisions.
- Important Negotiation Points:
- Bulk order discounts
- Payment terms (e.g., net 30, net 60)
Шаг 6: Review Logistics and Shipping Options
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of vulcanized rubber. Discuss shipping options with your supplier to ensure they can meet your delivery requirements. Consider factors like lead times, shipping costs, and customs clearance, especially for international transactions.
- Logistics Considerations:
- Shipping methods (air, sea, land)
- Potential for delays and how to mitigate them
Шаг 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
After procurement, set up a quality control process to monitor the performance of the vulcanized rubber. Regular checks can help identify any deviations from specifications and ensure ongoing quality assurance. This is particularly important for long-term contracts or repeat orders.
- Quality Control Measures:
- Regular inspections and testing of incoming materials
- Feedback loops with suppliers to address any quality issues promptly
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing vulcanized rubber, ensuring that they select the right suppliers and materials for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is vulcanizing rubber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Vulcanizing Rubber Sourcing?
When sourcing vulcanized rubber, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary components include:
-
Материалы: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor, including natural or synthetic rubber and sulfur. The choice of rubber type (natural vs. synthetic) directly impacts pricing, with synthetic rubber generally being more cost-effective but varying in quality and performance.
-
Труд: Labor costs encompass the wages for skilled workers involved in the vulcanization process. This includes workers responsible for mixing, molding, and quality assurance. Labor costs can vary by region; for instance, countries with lower wage standards may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Производственные накладные расходы: This includes utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, making it vital to partner with suppliers who prioritize operational efficiency.
-
Инструментальная оснастка: Custom molds and tooling necessary for producing specific rubber products can incur substantial costs. Buyers should consider the longevity and adaptability of tooling when negotiating prices.
-
Контроль качества (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures the final product meets specified standards. While this may add to upfront costs, it reduces the risk of defects and returns, ultimately saving money in the long run.
-
Логистика: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on distance, mode of transportation, and packaging requirements. Incoterms also play a crucial role in defining responsibilities and costs associated with shipping.
-
Маржа: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can aid in negotiating better pricing.
What Influences Pricing in Vulcanized Rubber Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing, making it crucial for buyers to understand their impact:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often result in lower per-unit costs. Establishing long-term contracts may also yield better pricing.
-
Технические характеристики и персонализация: Customized products or specific material requirements can increase costs. Buyers should balance their needs with budget constraints and explore options for standard products that meet their requirements.
-
Материалы: The choice of materials, including the quality of rubber and additives, can significantly affect pricing. Opting for higher-quality materials may increase costs but can enhance the product’s performance and lifespan.
-
Quality Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge a premium. However, these certifications can provide assurance of product reliability and compliance with international standards.
-
Факторы поставщика: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but offer greater assurance of quality and service.
-
Инкотермс: Understanding the implications of Incoterms on shipping and delivery responsibilities can prevent unexpected costs. Different terms can shift financial burdens between buyers and suppliers.
How Can Buyers Negotiate and Optimize Costs in Vulcanized Rubber Sourcing?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Понимание общей стоимости владения (TCO): Beyond initial pricing, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. This broader perspective can guide purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Market Insights: Stay informed about market trends, including raw material prices and regional economic factors. This knowledge can strengthen negotiation positions.
-
Стройте отношения с поставщиками: Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and service. Suppliers may be more willing to negotiate favorable terms with trusted clients.
-
Explore Global Sourcing Options: International suppliers may offer competitive pricing due to lower labor costs. However, consider logistics and potential tariffs when evaluating total costs.
-
Будьте внимательны к нюансам ценообразования: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local demand, supply chains, and economic conditions. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these nuances can enhance negotiation outcomes.
Отказ от ответственности
The prices and costs discussed in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific supplier agreements, market conditions, and regional factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is vulcanizing rubber With Other Solutions
In the realm of rubber production, vulcanization is a well-established method that enhances the physical properties of rubber, making it stronger, more elastic, and better suited for a wide range of applications. However, several alternative methods and materials exist that can achieve similar outcomes. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
| Сравнительный аспект | What Is Vulcanizing Rubber | Alternative 1: Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Alternative 2: Silicone Rubber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Производительность | High strength and elasticity; excellent abrasion resistance | Good flexibility and durability; lower heat resistance | High temperature resistance; good chemical stability |
| Стоимость | Moderate to high cost; varies based on sulfur and additives used | Generally lower cost; can be more cost-effective for certain applications | Higher initial cost; longer lifespan can offset initial investment |
| Простота реализации | Requires specific equipment and processes (heat and sulfur) | Easier to mold and process; can be injection molded | Requires specialized molding techniques; can be complex |
| Техническое обслуживание | Low maintenance; durable under various conditions | Low maintenance; retains properties over time | Moderate maintenance; can degrade in extreme conditions |
| Лучший пример использования | Heavy-duty applications like tires, gaskets, and footwear | Soft-touch applications, seals, and automotive parts | High-performance applications, medical devices, and cookware |
What Are Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) and How Do They Compare?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are a class of materials that combine the characteristics of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics. They are flexible, durable, and can be easily molded into various shapes, making them an attractive alternative to vulcanized rubber. The main advantage of TPEs is their cost-effectiveness and ease of processing. They can be molded using standard plastic techniques, reducing production costs and time. However, TPEs may not perform as well under high-temperature conditions compared to vulcanized rubber, which can limit their use in certain heavy-duty applications.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
How Does Silicone Rubber Stack Up Against Vulcanized Rubber?
Silicone rubber is another alternative that offers unique benefits, particularly in high-temperature environments and applications requiring chemical resistance. Its ability to maintain performance across a wide temperature range makes it ideal for specialized applications such as medical devices, cookware, and automotive seals. While silicone rubber typically comes with a higher initial cost, its longevity and resistance to degradation can make it a worthwhile investment in the long run. On the downside, silicone may require more intricate molding techniques compared to vulcanized rubber, which could complicate the manufacturing process.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Rubber Solution?
When selecting between vulcanized rubber and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific application requirements. Factors such as performance needs, budget constraints, and manufacturing capabilities should all play a significant role in the decision-making process. For heavy-duty applications requiring high strength and elasticity, vulcanized rubber remains the preferred choice. However, for applications that prioritize cost efficiency and ease of processing, TPEs may be more suitable. In contrast, silicone rubber is ideal for specialized environments where temperature and chemical resistance are critical. Ultimately, a thorough analysis of the project requirements will lead to the most effective solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is vulcanizing rubber
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Vulcanizing Rubber?
When dealing with vulcanized rubber, understanding its technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Класс материала
Material grade refers to the quality and type of rubber used in vulcanization, which can be either natural or synthetic. Each grade has distinct properties influencing performance characteristics such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the final product meets specific application requirements, which is vital for industries like automotive and manufacturing.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can withstand before failure. For vulcanized rubber, a high tensile strength indicates that the material can endure significant stress without breaking. This property is particularly important for applications such as tires and industrial seals, where reliability under pressure is critical.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
3. Elongation at Break
This property quantifies how much a rubber material can stretch before it breaks, expressed as a percentage of its original length. Vulcanized rubber typically exhibits higher elongation at break compared to non-vulcanized rubber, which translates to enhanced flexibility and resilience. This characteristic is essential for products that require bending or stretching, like hoses and gaskets.
4. Hardness (Shore A)
Hardness indicates the resistance of rubber to indentation, measured using the Shore A durometer scale. Vulcanized rubber can be formulated to achieve varying hardness levels, which is crucial for applications requiring specific performance characteristics. A harder rubber may be used for load-bearing applications, while softer rubber is better suited for cushioning or sealing.
5. Устойчивость к истиранию
Abrasion resistance refers to the ability of vulcanized rubber to withstand wear from friction and contact with other materials. This property is significant in applications such as conveyor belts and flooring, where frequent contact can lead to degradation. High abrasion resistance ensures longevity and reduces replacement costs, making it a key consideration for manufacturers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Vulcanizing Rubber?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers in sourcing high-quality vulcanized rubber components that meet specific industry standards.
2. MOQ (минимальное количество заказа)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies, as it can significantly impact inventory management and cost-effectiveness.
3. RFQ (запрос котировок)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of vulcanized rubber, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and lead times from different manufacturers, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Инкотермс (международные коммерческие термины)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions involving vulcanized rubber, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risk management during transport.

Illustrative image related to what is vulcanizing rubber
5. Время выполнения
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to the delivery of the product. For vulcanized rubber, understanding lead times is crucial for production planning and ensuring that supply chains remain uninterrupted.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing vulcanized rubber more effectively, ensuring they make choices that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is vulcanizing rubber Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Vulcanized Rubber Sector?
The vulcanized rubber market is experiencing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for durable and high-performance materials across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Global trends indicate a shift towards lightweight and resilient materials, with vulcanized rubber standing out due to its superior strength and elasticity compared to traditional rubber. Emerging technologies in manufacturing processes, such as automation and advanced polymer blending, are also enhancing production efficiency and product quality. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Sourcing trends highlight a growing preference for suppliers that offer customization options, enabling buyers to tailor materials to specific applications. Additionally, buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers with a strong track record in quality assurance and compliance with international standards. Countries like Nigeria and Vietnam are becoming significant players in the vulcanized rubber supply chain, leveraging their local resources and manufacturing capabilities to meet the rising global demand. As the market evolves, B2B buyers must stay attuned to these trends to identify opportunities and mitigate risks in their supply chains.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping the Sourcing of Vulcanized Rubber?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of vulcanized rubber. The environmental impact of rubber production, particularly regarding deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions, has raised awareness among B2B buyers about the importance of ethical supply chains. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
Certifications like ISO 14001 and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) are gaining traction among buyers seeking to ensure their suppliers meet stringent environmental standards. Additionally, the demand for ‘green’ vulcanized rubber, which utilizes eco-friendly additives and sustainable sourcing of raw materials, is on the rise. This shift not only helps mitigate environmental impact but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. B2B buyers must consider these factors when evaluating potential suppliers, as sustainability can influence brand reputation and market competitiveness.
What Is the Historical Context of Vulcanized Rubber in the B2B Market?
The evolution of vulcanized rubber dates back to the mid-19th century, when Charles Goodyear patented the vulcanization process, revolutionizing the rubber industry. This process involved treating rubber with sulfur and heat, significantly enhancing its strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. Initially, vulcanized rubber found applications in products like tires and footwear, but its uses have expanded dramatically over the decades.
Today, vulcanized rubber is integral to various industries, from automotive to healthcare, due to its unmatched performance characteristics. As B2B buyers navigate the current market landscape, understanding the historical significance of vulcanized rubber can provide valuable context for its applications and the innovations that continue to shape its future. The ongoing development of synthetic alternatives and advancements in vulcanization techniques further highlight the importance of this material in modern manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is vulcanizing rubber
-
How does vulcanization improve rubber properties?
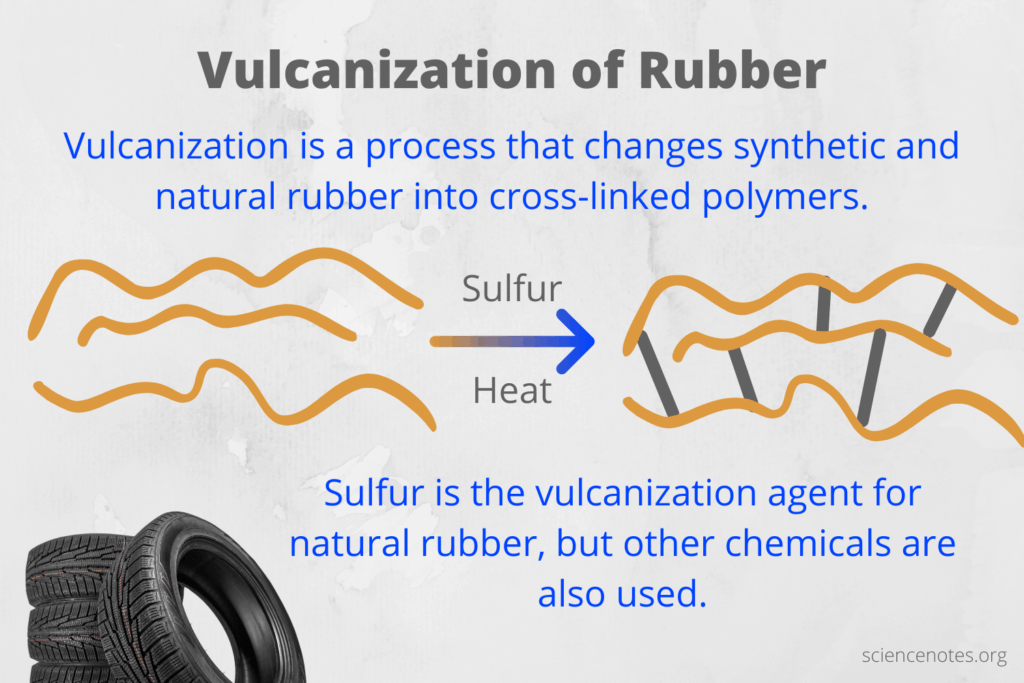
Vulcanization is a chemical process that enhances the properties of rubber by introducing sulfur and heat. This process creates cross-links between polymer chains, significantly increasing the rubber’s strength, elasticity, and durability. As a result, vulcanized rubber can withstand greater pressure and resist deformation, making it ideal for demanding applications in industries like automotive, construction, and manufacturing. -
What are the primary applications of vulcanized rubber in various industries?
Vulcanized rubber is widely used across multiple sectors due to its enhanced properties. Common applications include tires, seals, gaskets, hoses, footwear, and various automotive components. Additionally, it is utilized in electronics for keypads and insulators, as well as in construction for flooring and insulation materials, making it a versatile choice for B2B buyers. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing vulcanized rubber suppliers?
When sourcing suppliers for vulcanized rubber, consider their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and industry experience. Evaluate their certifications, such as ISO standards, to ensure compliance with international quality benchmarks. Additionally, inquire about their ability to provide custom formulations and the minimum order quantities (MOQs) they support to meet your production needs. -
How can I customize vulcanized rubber products for my specific needs?
Customization of vulcanized rubber products typically involves specifying material properties, dimensions, and additional features such as color or additives. Engage with potential suppliers early in the process to discuss your requirements and explore their ability to accommodate unique specifications. Many suppliers offer samples or prototypes to help you assess the suitability of their products before committing to larger orders. -
What are common payment terms when purchasing vulcanized rubber internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary significantly based on supplier policies and buyer agreements. Common terms include letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring the supplier’s financial security. Always clarify any additional fees, such as shipping and customs duties, that may apply. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for vulcanized rubber products?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control procedures. This may include certifications, testing methods, and adherence to industry standards. Conducting factory visits or audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider implementing a third-party inspection service to verify product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing vulcanized rubber?
Logistics plays a crucial role in the timely delivery of vulcanized rubber products. Understand the shipping options available, including air and sea freight, and the associated costs. Be aware of customs regulations in your country, as well as any import duties or tariffs. Working with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and avoid potential delays. -
How do I handle potential disputes with my vulcanized rubber supplier?
When dealing with potential disputes, it is vital to have a clear contract that outlines the terms of the agreement, including delivery timelines, quality expectations, and dispute resolution procedures. Maintain open communication with your supplier to address issues as they arise. If disputes escalate, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods to avoid lengthy legal battles.
Top 4 What Is Vulcanizing Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Walker Rubber – Custom Rubber Extrusions
Домен: walker-rubber.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Введение: Rubber Extrusions, Custom Rubber Extrusions, Angle Extrusion, Rubber Boat Window Seals, Brick Grabs, Cab Tyres, Rubber Cable Protection, Coloured Extrusions, Container Door Seal Extrusion, Conveyor Side Skirting, Rubber Door Seals, EPDM Extrusions, Rubber Expansion Seals, Rubber Façade Seal Extrusions, Flame Retardant Extrusions, Food Grade Extrusions, Rubber Gate Seals, Rubber Glazing Seals, H Pr…
2. WARE – Boiler Rentals & Services
Домен: wareinc.com
Зарегистрирован: 2000 (25 лет)
Введение: WARE is an industrial & commercial boiler rental and service company specializing in sales, service, valve repair, rentals, parts, turnkey solutions, and boiler training. Key offerings include: 1. Boiler Rentals – Serving a wide range of applications and industries. 2. Boiler Sales – New, used, and remanufactured boiler equipment with over 70 years of experience. 3. Aux Equipment – Industrial boil…
3. ScienceDirect – Vulcanization Process
Домен: sciencedirect.com
Зарегистрирован: 1997 (28 лет)
Введение: Vulcanization is a chemical process that enhances the elasticity and retractile force of rubbery or elastomeric materials by forming a crosslinked molecular network, reducing permanent deformation after the removal of applied forces. It typically involves the insertion of crosslinks between polymer chains using sulfur or other vulcanizing agents. The process is critical in the rubber industry, tra…
4. Merriam-Webster – Vulcanization Process
Домен: merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Введение: Vulcanization is the process of chemically treating natural or synthetic polymers, especially rubber, to enhance properties such as elasticity, strength, and stability. The process involves adding sulfur to rubber and heating the mixture under pressure to form sulfur cross-links between the polymer chains, which increases the material’s durability. The term was named by chemist Charles Goodyear in…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is vulcanizing rubber
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of vulcanized rubber is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance product quality and performance. The vulcanization process significantly improves the strength, elasticity, and durability of rubber, making it a preferred choice for diverse applications, from automotive components to industrial seals. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, buyers can ensure access to high-quality vulcanized rubber, which not only meets stringent performance standards but also aligns with sustainability goals.
As global markets continue to evolve, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable and innovative rubber solutions will only increase. B2B buyers are encouraged to forge partnerships with reputable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions and support sustainable practices.
In a landscape where quality and reliability are paramount, investing in vulcanized rubber represents a strategic advantage. Take proactive steps today to secure your supply chain and elevate your product offerings. Engage with trusted suppliers and explore the latest advancements in vulcanization technology to stay ahead of the competition.
Важный отказ от ответственности и условия использования
⚠️ Важное заявление об отказе от ответственности
Информация, представленная в данном руководстве, включая сведения о производителях, технические характеристики и анализ рынка, предназначена исключительно для информационных и образовательных целей. Она не является профессиональной консультацией по закупкам, финансовой или юридической консультацией.
Несмотря на то, что мы приложили все усилия для обеспечения точности и своевременности информации, мы не несем ответственности за любые ошибки, упущения или устаревшую информацию. Условия рынка, сведения о компании и технические стандарты могут быть изменены.
Покупатели B2B должны проводить независимую и тщательную юридическую экспертизу. перед принятием решения о покупке. Это включает в себя прямые контакты с поставщиками, проверку сертификатов, запрос образцов и обращение за профессиональной консультацией. Риск, связанный с использованием любой информации, содержащейся в данном руководстве, несет исключительно читатель.