Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sts operation
In today’s complex global market, sourcing reliable ship-to-ship (STS) operations presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As the demand for efficient cargo transfer increases, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of STS operations becomes essential. This guide aims to equip decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the diverse landscape of STS operations, encompassing various types, applications, regulatory requirements, and cost considerations.
From oil tankers to gas carriers, the ability to conduct STS operations efficiently can significantly impact logistics and bottom lines. However, potential risks, including environmental concerns and compliance with international regulations, necessitate careful planning and execution. This comprehensive resource not only outlines the operational requirements and best practices but also emphasizes the importance of vetting suppliers and service providers to ensure safety and efficiency in these high-stakes operations.
By leveraging the insights and actionable strategies presented in this guide, international B2B buyers will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions. The content is tailored to meet the specific needs of stakeholders in diverse markets, including those in Saudi Arabia and Germany, enabling them to optimize their STS operations while mitigating risks and enhancing profitability.
Оглавление
- Top 4 Sts Operation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sts operation
- Understanding sts operation Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of sts operation
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sts operation’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for sts operation
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sts operation
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sts operation’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sts operation Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sts operation With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sts operation
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sts operation Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sts operation
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sts operation
- Важный отказ от ответственности и условия использования
Understanding sts operation Types and Variations
| Название типа | Ключевые отличительные особенности | Основные приложения B2B | Краткие плюсы и минусы для покупателей |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional STS | Transfers cargo between two vessels at anchor or underway. | Oil and gas transportation, bulk cargo transfer. | Pros: Cost-effective, reduced port fees. Cons: High risk of spills and environmental hazards. |
| Ship-to-Ship Bunkering | Focuses on transferring fuel oil from one vessel to another. | Fuel supply for vessels, especially in remote areas. | Pros: Minimizes downtime, flexible scheduling. Cons: Regulatory complexities, potential for fuel quality issues. |
| STS with Cargo Lifting | Involves cranes or lifting equipment for cargo transfer. | Heavy cargo handling, specialized logistics. | Pros: Suitable for non-liquid cargo, enhanced safety. Cons: Higher operational costs, requires specialized equipment. |
| Emergency STS | Conducted in urgent situations, often with limited planning. | Crisis response, spill recovery efforts. | Pros: Quick response to emergencies. Cons: Increased risk, potential for insufficient safety measures. |
| STS for LNG | Specialized for Liquefied Natural Gas transfers. | LNG shipping and distribution. | Pros: High efficiency, tailored for specific cargo. Cons: Requires specialized vessels and equipment. |
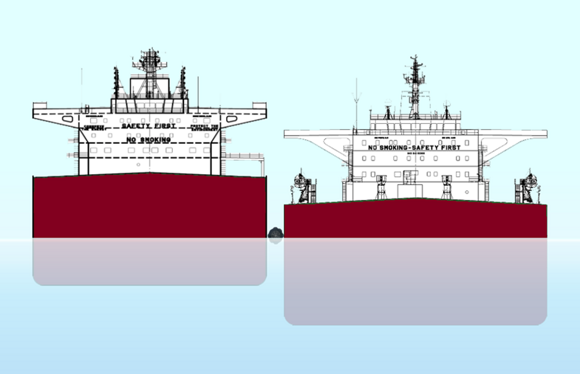
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Conventional STS Operations?
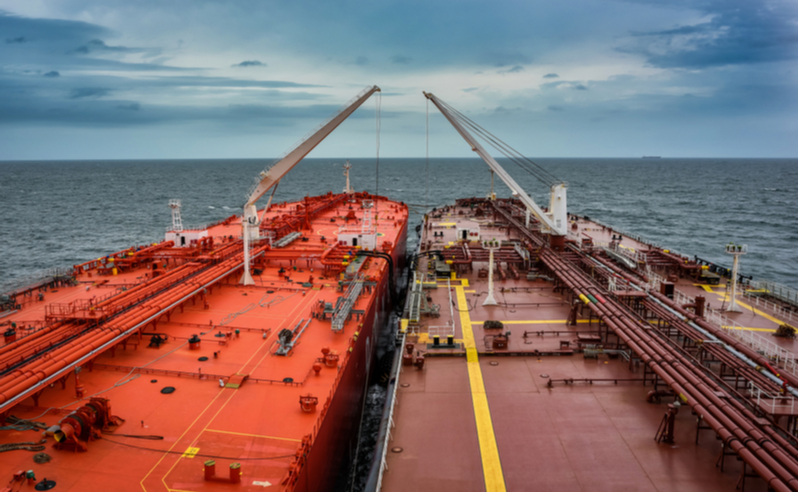
Conventional STS operations involve the transfer of liquid cargo between two vessels that are either anchored or underway. This method is predominantly used for oil and gas transportation, allowing large carriers to offload their cargo without entering port facilities. Buyers should consider the operational efficiency and cost savings associated with reduced port fees, but they must also be aware of the environmental risks and regulatory compliance that come with such operations.
How Does Ship-to-Ship Bunkering Differ from Other STS Types?
Ship-to-Ship bunkering focuses specifically on the transfer of fuel oil between vessels. This is crucial for supplying fuel to ships that may not have access to traditional refueling infrastructure, especially in remote areas. Buyers benefit from minimized vessel downtime and flexible scheduling; however, they must navigate the regulatory landscape and ensure fuel quality to avoid operational disruptions.
What Are the Advantages of STS with Cargo Lifting?
STS with cargo lifting incorporates cranes or specialized lifting equipment to facilitate the transfer of non-liquid cargo. This method is particularly useful for heavy and oversized items that require careful handling. B2B buyers should weigh the enhanced safety and suitability for diverse cargo types against the increased operational costs and the need for specialized equipment, which may not be readily available.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
When Is Emergency STS Operation Necessary?
Emergency STS operations are conducted under urgent circumstances, often with limited planning. They are essential for crisis response scenarios, such as oil spill recovery or urgent cargo delivery. While this method allows for a quick response, buyers should be mindful of the heightened risks involved and the potential for inadequate safety measures, which can lead to further complications.
Why Is STS for LNG Important in the Shipping Industry?
STS operations specifically designed for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) are tailored to meet the unique requirements of LNG transfers. This method is highly efficient and suitable for the shipping and distribution of LNG, which is increasingly in demand due to its lower environmental impact compared to other fossil fuels. Buyers must consider the specialized vessels and equipment required for LNG STS operations, which can affect overall logistics and costs.
Key Industrial Applications of sts operation
| Промышленность/сектор | Specific Application of sts operation | Ценность/выгода для бизнеса | Ключевые соображения по поиску источников для данного приложения |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Transfer of crude oil between tankers | Reduces port fees and minimizes turnaround time | Compliance with MARPOL regulations, trained personnel |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Transfer of liquid chemicals | Enhances logistics efficiency and reduces transport costs | Proper equipment and safety measures, emergency response |
| Maritime Logistics | Bunkering operations for ships | Streamlines fuel supply and reduces downtime for vessels | Quality of bunker fuel, environmental regulations compliance |
| Возобновляемая энергия | Transfer of biofuels between vessels | Supports sustainable practices and reduces carbon footprint | Certification of biofuels, adherence to environmental guidelines |
| Shipping and Freight | Loading and unloading cargo at sea | Increases flexibility in logistics and reduces congestion at ports | Coordination with port authorities, vessel compatibility |
How is ‘sts operation’ utilized in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, ship-to-ship (STS) operations are crucial for transferring crude oil between large tankers, particularly in regions where port access is restricted due to draught limitations. This method allows for significant cost savings by eliminating port berthing fees and reducing the time spent at port, which can be critical in high-demand markets. International buyers must ensure compliance with MARPOL regulations and invest in adequately trained personnel to manage the complexities of the operation, including environmental safety measures.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
What role does ‘sts operation’ play in Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturers often utilize STS operations for the efficient transfer of liquid chemicals between vessels. This process enhances logistics efficiency by allowing transfers to occur at sea, thereby reducing transport costs and minimizing delays associated with port congestion. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who provide the necessary safety equipment and have established emergency response protocols, as the handling of chemicals involves inherent risks.
How does ‘sts operation’ enhance Maritime Logistics?
In maritime logistics, STS operations are employed for bunkering, where fuel is transferred from one vessel to another. This process is essential for maintaining the operational efficiency of ships, as it minimizes downtime and ensures vessels remain fueled during long voyages. B2B buyers should consider the quality of bunker fuel sourced and ensure compliance with local and international environmental regulations to avoid potential penalties and operational disruptions.
What benefits does ‘sts operation’ bring to the Renewable Energy Sector?
The renewable energy sector increasingly relies on STS operations for the transfer of biofuels between vessels. This method supports sustainable practices by facilitating the transportation of eco-friendly fuels without the need for extensive port infrastructure. Buyers must verify the certification of biofuels and ensure adherence to environmental guidelines to align with global sustainability goals, making this an attractive option for companies committed to reducing their carbon footprint.
How does ‘sts operation’ impact Shipping and Freight?
In the shipping and freight industry, STS operations are utilized for loading and unloading cargo at sea, providing an alternative to traditional port operations. This flexibility helps alleviate congestion at ports and allows for quicker turnaround times, which is vital in maintaining supply chain efficiency. When sourcing services for STS operations, businesses should coordinate closely with port authorities and ensure vessel compatibility to facilitate smooth operations and avoid delays.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sts operation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance Challenges in STS Operations
Проблема: B2B buyers often face significant challenges in navigating the complex regulatory landscape surrounding Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations. Regulations such as MARPOL Annex I and the MEPC 59 guidelines can be overwhelming, particularly for companies operating in diverse international waters. Many buyers struggle to ensure that all necessary documentation, approvals, and compliance protocols are in place before initiating an STS operation. This can lead to costly delays, potential legal repercussions, and environmental penalties if not handled correctly.
Решение: To effectively manage regulatory compliance, buyers should establish a systematic approach to STS operations. First, consider investing in a dedicated compliance management software that tracks regulatory updates specific to the regions of operation, including requirements from local port authorities. Additionally, forming partnerships with local maritime law experts can provide invaluable insights into regional regulations. Buyers should also develop a comprehensive STS operation plan that aligns with international guidelines and is approved by relevant authorities. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated in response to changing regulations to ensure ongoing compliance and mitigate the risk of operational disruptions.
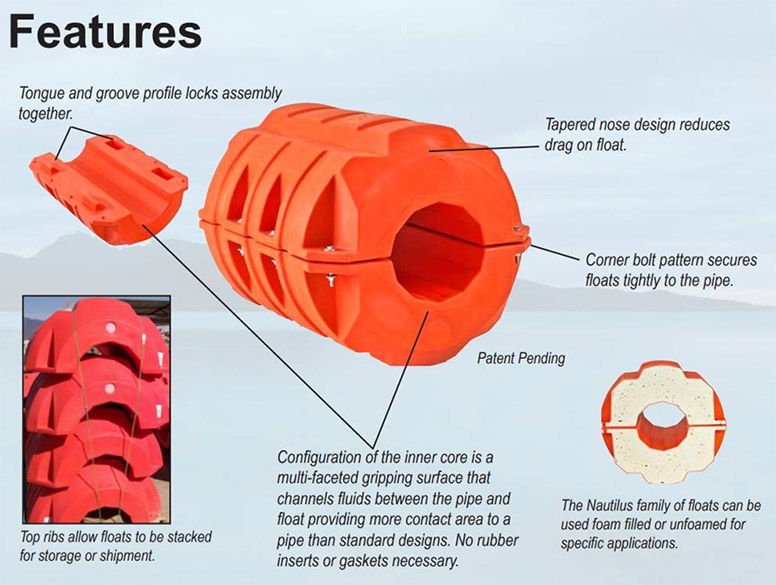
Illustrative image related to sts operation
Scenario 2: Mitigating Environmental and Safety Risks During STS Operations
Проблема: The inherent risks associated with STS operations, such as environmental pollution and safety hazards, are major concerns for B2B buyers. Oil and gas transfers in open waters increase the likelihood of spills and accidents, which can have catastrophic consequences. Buyers often struggle to implement adequate safety measures and protocols, leaving them vulnerable to environmental damage and financial liabilities.
Решение: To mitigate these risks, buyers must prioritize safety and environmental protection by investing in high-quality STS equipment and training. This includes ensuring that all vessels involved are equipped with the latest spill response tools and that the crew is well-trained in emergency response procedures. Conducting regular drills can reinforce safety protocols and prepare the crew for real-world scenarios. Furthermore, buyers should adopt comprehensive risk assessment strategies prior to each operation. This involves evaluating weather conditions, crew readiness, and vessel compatibility to enhance operational safety. Engaging third-party safety consultants can also provide an external review of safety practices, ensuring that all measures meet or exceed industry standards.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Communication Barriers in STS Operations
Проблема: Effective communication between vessels during STS operations is crucial but often poses challenges for B2B buyers. Language barriers, technical jargon, and miscommunication can lead to operational errors, which may result in accidents or delays. This is particularly concerning in multinational operations where crews may speak different languages or have varying levels of familiarity with STS procedures.
Решение: To address communication barriers, it is essential to establish clear communication protocols before commencing STS operations. Buyers should invest in robust communication technologies that facilitate real-time information exchange between vessels. Using standardized terminology in a common language can help reduce misunderstandings. Additionally, employing bilingual crew members or translators during operations can bridge language gaps. Regular training sessions focusing on communication skills and operational procedures can further enhance crew interactions. Developing a shared digital platform for both vessels to access operational guidelines and updates in real time can streamline communication and ensure that all parties are aligned throughout the transfer process.
By proactively addressing these pain points, B2B buyers can enhance the efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance of their STS operations, leading to smoother transactions and reduced operational risks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sts operation
What Materials Are Commonly Used in STS Operations?
In the context of ship-to-ship (STS) operations, material selection is critical for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with international regulations. The materials used in various components—such as hoses, couplings, and valves—must withstand the harsh marine environment while being compatible with the specific cargo being transferred. Below, we analyze four common materials used in STS operations, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
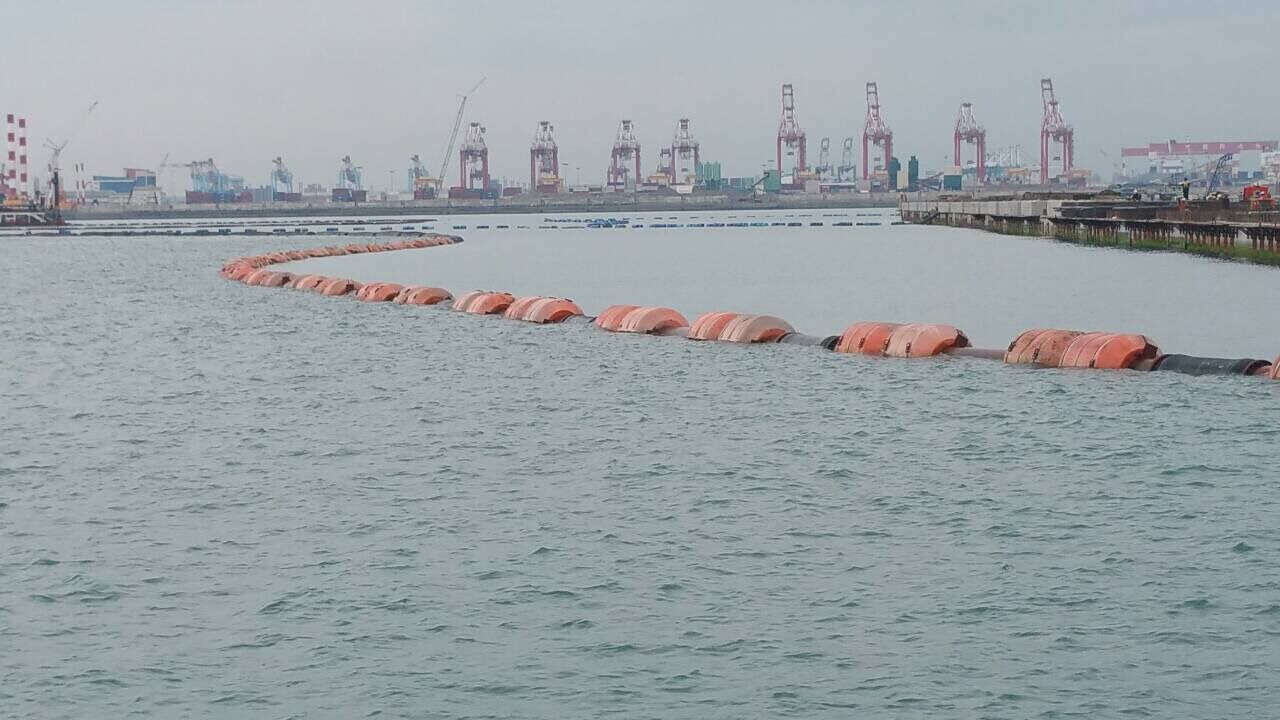
What Are the Key Properties of Rubber Hoses in STS Operations?
Rubber hoses are widely used for transferring liquid cargo, particularly in oil and gas applications. Key properties include high flexibility, temperature ratings up to 100°C (212°F), and the ability to withstand pressures of around 10 bar (145 psi).
Плюсы: Rubber hoses are lightweight, easy to handle, and resistant to abrasion. They can be manufactured in various lengths and diameters, making them versatile for different STS setups.
Конс: However, they can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone, leading to a shorter lifespan compared to other materials. Additionally, they may require regular inspections and maintenance.
Влияние на применение: Rubber hoses are compatible with a wide range of hydrocarbons, but care must be taken to ensure they are suitable for specific cargo types, especially those with high aromatic content.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local regulations and international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management.
How Do Stainless Steel Components Enhance STS Operations?
Stainless steel is often used for couplings, valves, and other fittings due to its excellent corrosion resistance and strength. Key properties include temperature ratings up to 500°C (932°F) and high-pressure ratings, making it suitable for various marine applications.
Плюсы: The durability of stainless steel components means they require less frequent replacement, reducing long-term costs. They are also less likely to contaminate the cargo, maintaining product integrity.
Конс: The initial cost of stainless steel components can be high, and they may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate sourcing.
Влияние на применение: Stainless steel is compatible with most liquid cargoes, including corrosive substances, making it a reliable choice for diverse STS operations.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 or DIN 17440 is essential, especially for buyers in Europe and South America, where quality assurance is paramount.
What Role Does Composite Material Play in STS Operations?
Composite materials, particularly those reinforced with fibers, are increasingly used for hoses and other components in STS operations. Key properties include lightweight construction, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals.
Плюсы: Composite hoses can handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various cargo types. They are also resistant to corrosion and UV degradation.
Конс: The manufacturing complexity of composite materials can lead to higher costs. Additionally, they may not be as robust as metal alternatives in high-impact scenarios.
Влияние на применение: Composites are particularly effective for transferring aggressive chemicals and hydrocarbons, offering a safer alternative in sensitive environments.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet international standards like ISO 1307 for flexible hoses, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
How Does PVC Compare in STS Operations?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is often used for lighter-duty applications in STS operations, such as for smaller hoses or fittings. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 60°C (140°F) and moderate pressure capabilities.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
Плюсы: PVC is cost-effective, lightweight, and easy to manufacture. It also provides good chemical resistance for certain applications.
Конс: However, PVC may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications, limiting its use in more demanding STS operations.
Влияние на применение: While PVC can handle some hydrocarbons, it is not recommended for heavy oil or high-aromatic cargoes due to potential degradation.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Compliance with local regulations and standards such as ASTM D1784 is crucial, particularly for buyers in Europe, where environmental considerations are increasingly important.
Summary Table of Material Selection for STS Operations
| Материал | Typical Use Case for STS Operation | Ключевое преимущество | Основные недостатки/ограничения | Относительная стоимость (низкая/средняя/высокая) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Hoses | Liquid cargo transfer | Lightweight and flexible | UV degradation over time | Средний |
| Нержавеющая сталь | Couplings and valves | Отличная коррозионная стойкость | High initial cost | Высокий |
| Композит | Hoses for aggressive chemicals | Chemical and UV resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | От среднего до высокого |
| ПВХ | Lighter-duty hoses and fittings | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited temperature and pressure capabilities | Низкий |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials commonly used in STS operations, enabling informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and compliance with relevant regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sts operation
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for STS Operations?
The manufacturing process for equipment and systems used in Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the highest levels of efficiency, safety, and quality. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first stage of the manufacturing process involves selecting and preparing raw materials that meet stringent industry standards. Common materials used include high-strength steel and corrosion-resistant alloys, which are essential for the harsh marine environment.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
- Material Selection: Suppliers must ensure that materials comply with international standards such as ASTM, ISO, and API specifications. This can include verifying the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the materials.
- Pre-Processing: Raw materials undergo cutting, bending, and surface treatment to enhance their durability and resistance to environmental factors. Processes like shot blasting or galvanization may be employed to prepare the surface for further processing.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Equipment for STS Operations?
Forming processes are crucial for shaping the equipment used in STS operations, such as hoses, manifolds, and cargo transfer systems.
- Techniques: Common techniques include welding, forging, and machining. For example, specialized welding methods like TIG or MIG welding may be used to ensure strong, leak-proof joints.
- Equipment Manufacturing: The design and manufacturing of equipment must consider factors such as pressure ratings and compatibility with various types of cargo, including oil and gas.
3. Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into Final Products?
Once individual components are manufactured, they must be assembled into complete systems. This stage requires precision and attention to detail to ensure that all parts function together seamlessly.
- Assembly Process: Automated assembly lines may be utilized for efficiency, while skilled technicians carry out quality checks during assembly.
- Integration Testing: After assembly, systems undergo integration testing to confirm that all components work together effectively. This may involve simulating operational conditions to ensure reliability.
4. Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied to Ensure Quality and Compliance?
The finishing stage involves applying coatings, labels, and final inspections to ensure that the equipment meets quality and regulatory standards.
- Surface Treatment: Coatings may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and reduce maintenance needs. This could include painting or applying specialized marine-grade coatings.
- Final Inspections: Comprehensive inspections are conducted to verify compliance with specifications and regulations, including checks for dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing process for STS operations. B2B buyers must be vigilant in assessing suppliers’ QA measures to ensure product reliability and safety.
International Standards: Which Certifications Should Suppliers Hold?
Suppliers should adhere to recognized international standards to demonstrate their commitment to quality. Key certifications include:
- ISO 9001: This standard specifies requirements for a quality management system and is applicable across various industries, including maritime.
- Стандарты API: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards specifically for equipment used in the oil and gas sectors, ensuring safety and reliability.
Industry-Specific Certifications: What Additional Certifications Are Relevant?
In addition to general quality standards, suppliers should also have industry-specific certifications:
- Маркировка CE: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, essential for buyers in Europe.
- MARPOL Compliance: For equipment involved in STS operations, adherence to MARPOL regulations is crucial for preventing marine pollution.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in STS Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic processes to ensure that products meet specified standards at various stages of manufacturing.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): How Are Raw Materials Assessed?
IQC is the first checkpoint in the QC process, focusing on the quality of incoming materials.
- Material Inspection: Suppliers should conduct thorough inspections of raw materials upon arrival, including checks for certifications and material properties.
- Documentation Verification: Verification of suppliers’ material test reports and compliance certificates is essential to ensure the reliability of the materials used.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): How Is Quality Monitored During Production?
During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are necessary to identify and rectify issues early.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
- Process Monitoring: Techniques like statistical process control (SPC) may be employed to monitor production parameters continuously.
- Routine Checks: Regular inspections at various stages of production can help catch defects before they escalate.
Final Quality Control (FQC): What Final Checks Are Conducted Before Shipping?
FQC is the last line of defense to ensure that the final product meets all quality and compliance requirements.
- Final Inspections: Comprehensive testing, including pressure tests and functionality checks, should be conducted before equipment is shipped.
- Documentation: Suppliers must provide detailed documentation, including test results and compliance certificates, to B2B buyers.
Как покупатели B2B могут проверять контроль качества поставщиков?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify that their suppliers adhere to quality control standards effectively.
Audits: What Should Be Included in Supplier Audits?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
- Audit Scope: Audits should encompass all aspects of the manufacturing process, including material sourcing, production methods, and quality control practices.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up audits can ensure that suppliers maintain compliance over time.
Reports and Documentation: What Key Documents Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request specific documentation to verify supplier quality control measures.
- Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports that outline testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
- Compliance Certificates: Obtaining copies of relevant certifications and compliance documents can help ensure that suppliers meet industry standards.
Third-Party Inspections: How Can Independent Inspections Enhance Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance the reliability of quality assurance.
- Independent Verification: Third-party inspectors can provide unbiased assessments of the manufacturing process and product quality.
- Global Reach: For international buyers, third-party services often have local expertise and can navigate regional compliance requirements effectively.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Essential for STS Operations?
In the highly regulated field of STS operations, quality assurance is not just a regulatory requirement but a crucial factor for operational success. By understanding the manufacturing processes and implementing rigorous quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure that they partner with suppliers capable of delivering reliable, safe, and compliant equipment for their STS operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sts operation’
Введение
Navigating the complexities of ship-to-ship (STS) operations requires careful planning and strategic sourcing. This checklist is designed for B2B buyers aiming to procure STS services efficiently while ensuring compliance with international regulations and safety standards. By following these steps, you can mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency during cargo transfers.
Шаг 1: Identify Your Cargo Specifications
Understanding the type of cargo you intend to transfer is paramount. This includes knowing the specific properties, such as its classification (e.g., oil, gas, chemicals), and any associated hazards. Proper identification allows for the selection of appropriate STS equipment and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
- Соображения:
- Obtain Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for your cargo.
- Verify the United Nations (UN) number for hazardous materials.
Шаг 2: Select Qualified STS Service Providers
Choosing the right service provider is critical to a successful STS operation. Look for companies with a proven track record in handling similar cargo types and operational environments.
- Что искать:
- Check for certifications and compliance with international standards (e.g., IMO, MARPOL).
- Request references from previous clients to assess reliability and performance.
Шаг 3: Evaluate Equipment and Technology
Ensure that the STS equipment provided by your chosen supplier is up to standard and well-maintained. Equipment failures can lead to costly delays and safety hazards.
- Key Equipment:
- Hose systems, fenders, and mooring lines must be inspected for wear and functionality.
- Verify that the equipment is suitable for the specific cargo and operational conditions.
Шаг 4: Conduct Risk Assessments
Prior to the operation, perform a comprehensive risk assessment. This step is crucial for identifying potential hazards and developing mitigation strategies.
- Focus Areas:
- Assess environmental impacts and emergency response procedures.
- Ensure that all crew members are briefed on risks associated with the cargo.
Шаг 5: Establish Communication Protocols
Effective communication between vessels is essential during STS operations. Set up clear communication channels and protocols to ensure seamless coordination.
- Соображения:
- Use reliable communication tools (e.g., VHF radios) and establish a chain of command.
- Conduct joint drills to familiarize crews with communication procedures.
Шаг 6: Obtain Necessary Approvals and Permits
Before proceeding with the STS operation, secure all required approvals from relevant port authorities. This step is vital for legal compliance and to avoid potential fines or operational delays.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
- Required Documentation:
- Submit an STS operation plan to the relevant authority at least 48 hours prior to commencement.
- Ensure that your plan includes details such as vessel names, cargo type, and operation timeline.
Шаг 7: Implement Safety and Spill Response Measures
Prioritize safety by ensuring that all necessary firefighting and oil spill response equipment is on board and operational. This not only protects the crew and vessels but also minimizes environmental risks.
- Checklist:
- Verify that the crew is trained in emergency procedures.
- Conduct regular drills to prepare for potential incidents.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing of STS operations while ensuring compliance, safety, and efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sts operation Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in STS Operations?
When evaluating the cost structure of ship-to-ship (STS) operations, several essential components must be considered. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Материалы: This includes the equipment necessary for STS operations such as hoses, pumps, and safety gear. The cost of these materials can vary significantly based on their quality and the certifications required for operation.
-
Труд: Skilled labor is crucial for successful STS operations. The costs associated with training and employing qualified personnel can be substantial, particularly for crew members who need to understand the complexities of handling hazardous materials.
-
Производственные накладные расходы: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with the operation, including utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient overhead management can help reduce overall costs.
-
Инструментальная оснастка: Specialized equipment for STS operations must be maintained and occasionally replaced. Investment in high-quality tooling can mitigate risks associated with equipment failure during operations.
-
Контроль качества: Ensuring compliance with international standards and regulations (like MARPOL and SOPEP) requires rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with these processes are vital to maintaining safety and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Логистика: This includes the transportation of materials and equipment to and from the operational site. Logistics costs can fluctuate based on geographic location, distance, and the availability of local resources.
-
Маржа: Finally, businesses must factor in profit margins when pricing STS services. Competitive pricing strategies should balance profitability with market demands.
What Influences Pricing for STS Operations?
Several factors influence the pricing of STS operations, including volume, specifications, material quality, supplier reliability, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk operations often lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate volume discounts where possible to enhance cost-efficiency.
-
Технические характеристики и персонализация: Custom requirements may increase costs due to the need for specialized equipment or training. Clear communication of specifications can help manage expectations and costs.
-
Материалы: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Higher-quality materials that meet stringent international standards may incur higher upfront costs but can reduce long-term risks and liabilities.
-
Качество и сертификация: Suppliers with recognized certifications may charge a premium. However, this often translates to higher reliability and compliance with safety standards, potentially reducing total costs in the long run.
-
Факторы поставщика: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can also affect pricing. Establishing a relationship with a trusted supplier can lead to better terms and lower costs over time.
-
Инкотермс: Understanding and negotiating Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the overall cost structure.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for STS Operations?
For B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to significant cost savings.
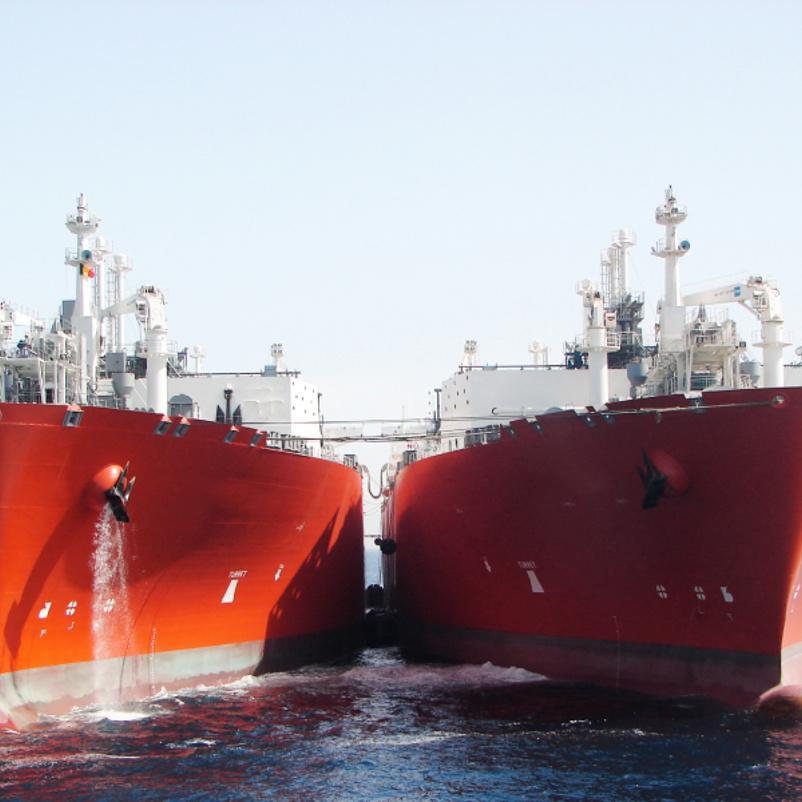

Illustrative image related to sts operation
-
Понимание общей стоимости владения (TCO): Buyers should look beyond initial pricing and consider the total cost of ownership, which includes ongoing maintenance, operational risks, and compliance costs.
-
Используйте маркетинговые исследования: Being informed about market trends and average pricing can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge allows for better discussions on price adjustments and value propositions.
-
Стройте долгосрочные отношения: Establishing a long-term partnership with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate when they see a commitment from buyers.
-
Focus on Efficiency: Buyers should seek out opportunities for cost efficiencies, such as optimizing logistics or consolidating orders, which can lead to reduced overall expenses.
-
Be Prepared for Pricing Nuances: Understanding the specific challenges and regulations in different regions can provide leverage in negotiations. For instance, buyers in Europe may face stricter compliance costs than those in other regions.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The information provided here is intended for guidance and is not indicative of specific pricing. Costs can vary significantly based on multiple factors, including location, market conditions, and specific operational requirements. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and engage with suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sts operation With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Ship-to-Ship Operations
As global trade continues to expand, efficient cargo transfer methods are critical for maritime operations. Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations, which involve the transfer of cargo between vessels, offer unique benefits but also come with challenges such as environmental risks and regulatory compliance. This section explores viable alternatives to STS operations, providing B2B buyers with insights into different methods that can achieve similar objectives while considering factors such as performance, cost, and implementation.
Comparison of STS Operations with Alternative Solutions
| Сравнительный аспект | STS Operation | Floating Storage and Regasification Unit (FSRU) | Terminal-to-Ship Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Производительность | High cargo transfer efficiency | High capacity for LNG; continuous operation | Moderate efficiency; limited by port capacity |
| Стоимость | Economical due to reduced port fees | High initial investment and operational costs | Moderate; dependent on port fees and logistics |
| Простота реализации | Requires extensive planning and training | Complex setup; requires specialized units | Relatively straightforward; dependent on infrastructure |
| Техническое обслуживание | High due to safety and environmental regulations | Moderate; requires maintenance of storage units | Variable; depends on terminal infrastructure |
| Лучший пример использования | Large volumes, remote locations | LNG transfer; consistent supply to terminals | Bulk cargo in high-traffic ports |
Подробный анализ альтернатив
Floating Storage and Regasification Unit (FSRU)
FSRUs are specialized vessels designed to store liquefied natural gas (LNG) and convert it back to gas for distribution. They can operate offshore or close to shore, allowing for flexible supply chain solutions. One of the main advantages of FSRUs is their ability to provide a continuous gas supply without the need for extensive land-based infrastructure. However, the initial investment is considerably high, and operational costs can also be significant, making them less appealing for short-term or intermittent needs.
Terminal-to-Ship Transfer
This method involves transferring cargo directly from a terminal to a vessel at a port. It is commonly used for bulk commodities and provides a straightforward approach to cargo handling. The ease of implementation is one of its strongest points, as established port infrastructures facilitate operations. However, the efficiency of this method can be limited by port congestion and capacity constraints. In addition, terminal-to-ship transfers may incur higher costs due to port fees and logistics associated with land-based operations.
Заключение: Выбор правильного решения для ваших нужд
When selecting the most suitable cargo transfer solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, including the type of cargo, volume, and geographic constraints. While STS operations offer high efficiency and cost savings, alternatives like FSRUs and terminal-to-ship transfers can provide unique advantages depending on the context. Evaluating the trade-offs between performance, cost, and ease of implementation will guide buyers in making informed decisions that align with their logistical strategies and compliance needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sts operation
What Are the Key Technical Properties for STS Operations?
Understanding the essential technical properties related to Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations is crucial for B2B buyers involved in the maritime and logistics sectors. Below are several critical specifications that play a pivotal role in ensuring safe and efficient STS operations.
-
Material Grade of Transfer Hoses
The material grade used for transfer hoses must be suitable for the type of cargo being transferred, especially when dealing with hazardous materials like oil or gas. Typically, these hoses are made from reinforced rubber or thermoplastic materials that can withstand high pressures and temperatures. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital to prevent leaks, which can lead to environmental hazards and financial liabilities. -
Tolerance Levels for Equipment
Equipment used in STS operations must adhere to specific tolerance levels regarding dimensions and operational parameters. This ensures compatibility between vessels and minimizes the risk of operational failure. For instance, couplings and flanges must align perfectly to ensure a secure connection. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide equipment adhering to stringent tolerance specifications to ensure seamless operations. -
Freeboard Measurement
Freeboard refers to the distance from the waterline to the upper deck of the ship. It is a critical factor during STS operations, as it affects the stability and safety of both vessels involved. Accurate measurement and understanding of freeboard differences are essential for preventing spills and ensuring safe cargo transfer. B2B buyers should ensure that their operational plans account for freeboard variations to mitigate risks. -
Load Capacity and Weight Distribution
Each vessel involved in STS operations has a specified load capacity that must not be exceeded. Additionally, understanding how weight distribution affects vessel stability is critical, especially during the transfer process. Buyers should invest in thorough assessments of vessel specifications and load capacities to ensure safe operations and compliance with maritime regulations. -
Communication Protocols
Effective communication protocols are essential for coordinating STS operations, especially when dealing with multiple vessels. This includes establishing clear channels for relaying critical information about cargo types, operational timelines, and emergency procedures. B2B buyers should prioritize systems that enhance real-time communication to improve operational efficiency and safety.
What Are Common Trade Terms in STS Operations?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in STS operations. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of STS operations, it’s important to source equipment from reputable OEMs to ensure quality and compliance with maritime standards. -
MOQ (минимальное количество заказа)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and procurement strategies. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs without incurring excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (запрос котировок)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from potential suppliers for specific products or services. For STS operations, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and services from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best possible value. -
Инкотермс (международные коммерческие термины)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in STS operations, as they dictate who bears the risk during transportation and delivery. -
MARPOL (Marine Pollution)
MARPOL is an international convention aimed at preventing pollution from ships. Compliance with MARPOL regulations is critical during STS operations to mitigate environmental risks. B2B buyers should ensure that all operational plans align with MARPOL guidelines to avoid legal repercussions and enhance corporate responsibility.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the safety, efficiency, and compliance of their STS operations.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sts operation Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in STS Operations
The Ship-to-Ship (STS) operation sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by global trade dynamics and the need for efficient cargo transfer solutions. As international shipping continues to expand, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, STS operations have become a vital method for transferring large volumes of oil and gas without the need for port berthing. This practice not only reduces operational costs—such as port fees and time delays—but also provides flexibility in managing large vessels that may not be able to dock due to draught restrictions.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping the STS landscape. Digitalization plays a crucial role, with advanced tracking systems, automated monitoring tools, and AI-powered analytics enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Blockchain technology is increasingly being explored for improving transparency and traceability in cargo movements, which is particularly appealing to international B2B buyers who prioritize accountability in their supply chains.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape is evolving, with stricter environmental regulations and safety standards influencing sourcing decisions. International buyers must navigate these changes effectively, ensuring compliance while optimizing their sourcing strategies. Keeping abreast of these trends allows businesses to remain competitive in the global market, as they seek partnerships that align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
How is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing in STS Operations?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of strategic sourcing in the STS operation sector, driven by increasing regulatory scrutiny and market demand for environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of STS operations is a critical concern, particularly regarding the potential for oil spills and emissions during cargo transfers. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to minimizing their ecological footprint through sustainable practices and technologies.
Ethical sourcing is essential for maintaining a positive brand reputation and meeting consumer expectations. Companies are now seeking partners who adhere to green certifications and utilize environmentally friendly materials and equipment. For example, using equipment with lower emissions and implementing spill prevention technologies can significantly reduce the environmental impact of STS operations.
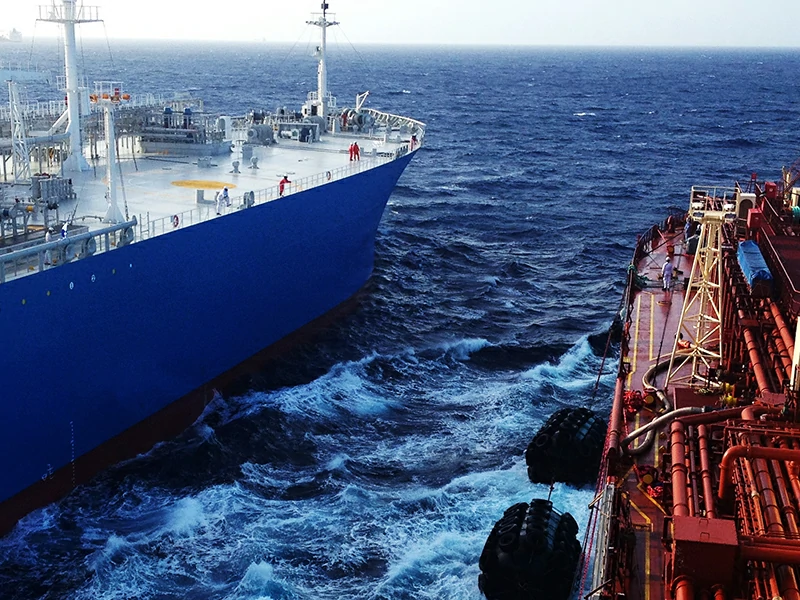

Illustrative image related to sts operation
Furthermore, buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who are proactive in their sustainability initiatives, such as adopting renewable energy sources for operational power or utilizing eco-friendly materials in their operations. This not only mitigates environmental risks but also aligns with the growing global emphasis on corporate social responsibility.
What is the Historical Context of STS Operations and Its Importance for B2B Buyers?
The practice of Ship-to-Ship (STS) transfer dates back several decades, initially gaining traction in the oil and gas industries as a solution to logistical challenges presented by large vessel operations. Historically, STS operations were seen primarily as a response to the limitations of port facilities, particularly in regions where deep-water access was restricted.
As global trade expanded, STS operations evolved to become a strategic component of supply chain management, allowing for more efficient cargo handling and distribution. This evolution has been critical for B2B buyers, as it offers a flexible solution that can adapt to changing market demands and shipping regulations.
In recent years, the historical context of STS operations has influenced current practices, with an increasing focus on safety, environmental compliance, and operational efficiency. Understanding this evolution helps B2B buyers appreciate the complexities and benefits of STS operations, enabling them to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their business objectives and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sts operation
-
How do I ensure compliance with international regulations for STS operations?
To ensure compliance with international regulations for Ship-to-Ship (STS) operations, familiarize yourself with the guidelines set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), particularly MARPOL Annex I. Obtain the necessary approvals for your STS operation plan from relevant maritime authorities and ensure that it aligns with local and international environmental standards. Additionally, maintain proper documentation, including the Oil Record Book, and keep communication channels open with port authorities to report any operational changes or delays. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier for STS operations?
When selecting a supplier for STS operations, consider their experience and expertise in handling similar cargo types, as well as their compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Evaluate their equipment quality and maintenance protocols, as well as the training provided to their personnel. Additionally, assess their past performance, including customer reviews and operational safety records, to ensure they can meet your logistical and operational needs. -
What is the best approach to mitigate risks associated with STS operations?
To mitigate risks associated with STS operations, conduct thorough pre-operation planning, including risk assessments that identify potential hazards such as spills or equipment failures. Ensure that both vessels are equipped with adequate safety and firefighting equipment, and that crew members are trained to respond to emergencies. Establish clear communication protocols between vessels and maintain a contingency plan for unexpected scenarios, thereby enhancing operational safety and compliance with regulatory requirements. -
How can I customize STS services to fit my specific logistical needs?
Customizing STS services involves discussing your specific cargo requirements, timelines, and operational preferences with your supplier. Ensure that they can accommodate your needs, whether it’s the type of cargo, the volume, or the specific location for the operation. Engage in detailed discussions about equipment specifications and operational procedures to tailor the STS operation to your business requirements while ensuring compliance with safety standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for STS operations?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for STS operations can vary depending on the supplier and the type of cargo being transferred. Generally, suppliers may set MOQs based on the operational costs, logistics, and equipment usage. It is crucial to engage directly with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that suit your operational needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
What payment terms are typically accepted for STS operations?
Payment terms for STS operations can vary widely among suppliers, often depending on the scale of the operation and the relationship established with the buyer. Common practices include upfront payments, deposits, or payment upon completion of the operation. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms in advance and explore options for credit or flexible payment plans, especially for larger operations, to facilitate smooth transactions. -
How do I conduct quality assurance (QA) checks for STS operations?
Conducting quality assurance (QA) checks for STS operations involves establishing clear operational standards and protocols that align with regulatory guidelines. Implement pre-operation inspections of equipment, safety gear, and communication systems. Post-operation evaluations should include documenting the operational process, assessing compliance with the STS operation plan, and reviewing any incidents or irregularities to improve future operations and ensure accountability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for STS operations?
Logistics for STS operations require careful planning of vessel positioning, timing, and coordination with port authorities. Consider factors such as weather conditions, tidal influences, and navigational hazards that may affect the operation. Ensure that both vessels have the necessary permits, and establish a timeline that accommodates potential delays. Engaging a logistics expert familiar with maritime operations can help streamline the process and enhance overall efficiency.
Top 4 Sts Operation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Marine Insight – Key Aspects of Ship-to-Ship Transfer (STS)
Домен: marineinsight.com
Зарегистрирован: 2010 (15 лет)
Введение: Ship-to-Ship Transfer (STS) refers to the transfer of cargo, such as oil or gas, between two merchant tanker vessels positioned alongside each other. Key requirements for conducting STS operations include: adequate training for oil tanker staff, proper STS equipment on both vessels, pre-planning of the operation, attention to vessel differences (freeboard and listing), obtaining permission from re…
2. Breakaway Couplings – Ship to Ship Transfer Solutions
Домен: breakawaycouplings.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Введение: Ship to Ship (STS) transfer, also known as lightering, involves two storage tankers mooring side-by-side to transfer cargo, typically crude oil and liquefied gas, in open sea or at the outer port limit. Key procedures include lowering fenders, berthing ships, connecting hoses, and transferring cargo. Safety is governed by international guidelines, with an operation plan required for each transfer….
3. Britannia Pandi – STS Transfer Operations Guide
Домен: britanniapandi.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Введение: Ship to Ship (STS) transfer operations guidance includes protocols for safe cargo transfer between two ships, either stationary or underway. Key considerations include:
– Ship dimensions and interaction effects
– Mooring supervisors and communication methods
– Designation of Constant heading ship and Manoeuvring ship
– Daylight availability for operations
– Wind velocity thresholds (typically…
4. SQE Marine – STS Transfer Operations
Домен: sqemarine.com
Зарегистрирован: 2011 (14 лет)
Введение: Ship to Ship (STS) Transfer Operations of Dry Bulk cargo involves the transfer of dry bulk cargo between sea-going Bulk Carriers, which can occur at sea or in port. The operations are considered high risk and require detailed preparation and trained personnel. The latest RightShip RiSQ 3.1 includes a new chapter for STS Transfer, mandating each ship to have an effective STS Transfer Plan covering …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sts operation
In the evolving landscape of ship-to-ship (STS) operations, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international buyers aiming to optimize their logistics and supply chain efficiencies. Understanding the operational intricacies and regulatory frameworks governing STS can significantly enhance procurement strategies, allowing businesses to leverage cost savings while ensuring compliance with environmental standards. The ability to conduct STS operations not only reduces port charges and berthing time but also offers flexibility in cargo management across various geographies.
Moreover, as global trade dynamics shift, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for efficient STS solutions will only grow. Buyers must prioritize partnerships with experienced service providers who can guarantee the safety and reliability of operations, mitigate risks associated with environmental impact, and ensure adherence to international regulations.

Illustrative image related to sts operation
Looking ahead, the future of STS operations will hinge on the integration of advanced technologies and best practices to streamline processes and enhance safety measures. International B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed and proactive in their sourcing strategies to navigate these challenges and seize opportunities in the global market. Embrace the potential of strategic sourcing in STS operations to drive your business success forward.
Важный отказ от ответственности и условия использования
⚠️ Важное заявление об отказе от ответственности
Информация, представленная в данном руководстве, включая сведения о производителях, технические характеристики и анализ рынка, предназначена исключительно для информационных и образовательных целей. Она не является профессиональной консультацией по закупкам, финансовой или юридической консультацией.
Несмотря на то, что мы приложили все усилия для обеспечения точности и своевременности информации, мы не несем ответственности за любые ошибки, упущения или устаревшую информацию. Условия рынка, сведения о компании и технические стандарты могут быть изменены.
Покупатели B2B должны проводить независимую и тщательную юридическую экспертизу. перед принятием решения о покупке. Это включает в себя прямые контакты с поставщиками, проверку сертификатов, запрос образцов и обращение за профессиональной консультацией. Риск, связанный с использованием любой информации, содержащейся в данном руководстве, несет исключительно читатель.