Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber vulcanizing
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing high-quality rubber vulcanizing solutions presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The vulcanization process enhances the strength and elasticity of rubber, making it essential for a wide range of applications—from automotive components to industrial machinery. However, understanding the complexities of this process, including the various types of rubber, additives, and manufacturing techniques, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of rubber vulcanizing, providing insights into different types of vulcanized rubber, their applications across multiple industries, and effective strategies for supplier vetting. We will also explore cost considerations, helping you weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable information, this guide empowers you to navigate the often-overwhelming landscape of rubber sourcing with confidence.
Whether you’re looking to optimize your supply chain or enhance product performance, understanding the nuances of rubber vulcanizing will position you to make strategic decisions that drive business success. Let this guide be your roadmap to unlocking the full potential of vulcanized rubber in your operations.
Table Of Contents
- A Look at Rubber Vulcanizing Manufacturers & Suppliers
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber vulcanizing
- Understanding rubber vulcanizing Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of rubber vulcanizing
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber vulcanizing’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber vulcanizing
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber vulcanizing
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber vulcanizing’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber vulcanizing Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber vulcanizing With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber vulcanizing
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber vulcanizing Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber vulcanizing
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber vulcanizing
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding rubber vulcanizing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfur Vulcanization | Utilizes sulfur as the main cross-linking agent | Automotive tires, seals, gaskets | Pros: High strength and elasticity. Cons: Longer curing times may affect production speed. |
| Accelerated Vulcanization | Incorporates accelerators for faster curing at lower temps | Industrial components, footwear | Pros: Reduced processing time, improved properties. Cons: Higher costs due to additives. |
| Peroxide Vulcanization | Uses peroxides for cross-linking, suitable for specific rubbers | Medical devices, food-grade applications | Pros: Excellent heat resistance and durability. Cons: Limited to specific rubber types. |
| Steam Vulcanization | Employs steam for uniform heating and curing | Conveyor belts, automotive parts | Pros: Environmentally friendly, consistent quality. Cons: Requires specialized equipment. |
| Microwave Vulcanization | Innovative method using microwave energy for curing | Aerospace components, custom parts | Pros: Rapid curing, energy-efficient. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Sulfur Vulcanization?
Sulfur vulcanization is the most traditional and widely used method, characterized by its reliance on sulfur as the primary cross-linking agent. This process enhances the rubber’s strength, elasticity, and durability, making it ideal for applications such as automotive tires, seals, and gaskets. B2B buyers should consider the longer curing times associated with this method, which may impact production schedules. However, the resulting high-performance rubber is often worth the wait for industries that prioritize product durability.
How Does Accelerated Vulcanization Improve Efficiency?
Accelerated vulcanization incorporates chemical accelerators that facilitate faster curing at lower temperatures, significantly improving production efficiency. This method is commonly used in manufacturing industrial components and footwear. B2B buyers will benefit from reduced processing times and enhanced mechanical properties. However, the inclusion of accelerators can increase material costs, which should be factored into budget considerations when selecting this vulcanization type.
What Are the Benefits of Peroxide Vulcanization?
Peroxide vulcanization is notable for its ability to cross-link specific types of rubbers, particularly those requiring higher thermal stability. This method is frequently utilized in medical devices and food-grade applications, where safety and performance are paramount. Buyers should be aware that while peroxide vulcanization offers excellent heat resistance, it is limited to certain rubber types, which may restrict its applicability in diverse manufacturing settings.
Why Choose Steam Vulcanization for Consistent Quality?
Steam vulcanization is an environmentally friendly process that utilizes steam for curing rubber. This method ensures uniform heating and consistent quality, making it suitable for applications like conveyor belts and automotive parts. B2B buyers should consider the specialized equipment required for steam vulcanization, which may involve initial investment costs. However, the benefits of consistent quality and reduced environmental impact can justify these expenses for companies committed to sustainable practices.
How Does Microwave Vulcanization Offer Energy Efficiency?
Microwave vulcanization is an innovative method that leverages microwave energy for rapid curing of rubber. This technique is particularly advantageous for aerospace components and custom parts, where quick turnaround times are essential. While the energy efficiency and speed of this process are significant benefits, buyers must consider the higher initial setup costs associated with microwave curing systems. Nonetheless, the long-term savings on energy and time can make this an attractive option for forward-thinking manufacturers.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber vulcanizing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber vulcanizing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Tires and seals | Enhanced durability and performance | Compliance with safety standards and local regulations |
| Construction | Gaskets and seals for machinery | Improved resistance to environmental factors | Availability of specialized materials for harsh conditions |
| Consumer Electronics | Keypads and buttons | Increased tactile response and lifespan | Compatibility with various electronic components |
| Medical Devices | Tubing and seals | Safety and reliability in critical applications | Certification for biocompatibility and regulatory compliance |
| Industrial Machinery | Conveyor belts and vibration dampeners | Reduced maintenance costs and downtime | Customization options for specific machinery requirements |
How is Rubber Vulcanizing Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber vulcanizing is crucial for manufacturing tires and seals. Vulcanized rubber provides enhanced durability and performance, enabling tires to withstand high pressures and varying weather conditions. This process solves common issues like tread wear and punctures, ensuring safety and reliability. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, sourcing tires requires compliance with safety standards and local regulations, emphasizing the importance of quality certifications.
What Role Does Rubber Vulcanizing Play in Construction?
In construction, rubber vulcanizing is essential for producing gaskets and seals used in various machinery. These components require improved resistance to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and moisture. By utilizing vulcanized rubber, businesses can significantly reduce leaks and enhance the longevity of equipment. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers that offer specialized materials capable of withstanding harsh conditions, ensuring operational efficiency and reliability.
Why is Rubber Vulcanizing Important for Consumer Electronics?
Rubber vulcanizing plays a vital role in the production of keypads and buttons in consumer electronics. The vulcanization process enhances the tactile response and lifespan of these components, making them essential for user satisfaction. As the electronics market grows, buyers, especially in regions like Germany and Vietnam, must consider compatibility with various electronic components and the availability of diverse designs to meet consumer preferences.
How is Rubber Vulcanizing Applied in Medical Devices?
In the medical field, rubber vulcanizing is used for manufacturing tubing and seals that require high safety and reliability standards. The vulcanization process ensures that these components are durable and resistant to wear, which is critical in medical applications. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the materials are certified for biocompatibility and adhere to stringent regulatory compliance, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers.
What are the Benefits of Rubber Vulcanizing in Industrial Machinery?
Rubber vulcanizing is extensively used in industrial machinery for components like conveyor belts and vibration dampeners. The enhanced strength and elasticity of vulcanized rubber reduce maintenance costs and downtime, leading to greater operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, especially in developing regions, it’s essential to seek customization options that cater to specific machinery requirements, ensuring optimal performance in diverse operational environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber vulcanizing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Inconsistent Quality in Vulcanized Products
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges B2B buyers face when sourcing vulcanized rubber products is the inconsistency in quality. Variations in the vulcanization process can lead to products that differ in strength, elasticity, and durability, resulting in increased failure rates and costly returns. Buyers may find that their suppliers do not adhere to standardized processes, leading to unpredictable performance characteristics. This inconsistency can be particularly detrimental in industries like automotive or aerospace, where safety and reliability are paramount.

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
The Solution: To combat quality inconsistencies, buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to international quality certifications, such as ISO 9001. When engaging with suppliers, request detailed information about their vulcanization processes, including the types of sulfur and additives used, as well as temperature and time parameters. Establishing a collaborative relationship with the supplier can also help, allowing for transparency in production methods. Additionally, conducting regular quality audits and requiring samples from production runs can ensure that the products meet the expected standards before bulk orders are made. By emphasizing quality control throughout the supply chain, buyers can significantly reduce risks associated with inconsistent product performance.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Customizing Rubber Vulcanization Specifications
The Problem: Another common pain point for buyers is the challenge of customizing vulcanized rubber to meet specific application needs. Many suppliers offer standardized products that may not align with unique project requirements, such as specific temperature resistances, flexibility, or hardness levels. This lack of customization can lead to inefficiencies, where businesses either settle for inadequate solutions or face delays in finding suitable alternatives.
The Solution: To effectively address customization challenges, buyers should engage with suppliers that specialize in custom rubber formulations. When discussing requirements, be explicit about the intended application, environmental conditions, and performance metrics. Utilize a detailed technical specification sheet to communicate these needs clearly. Furthermore, consider collaborating with suppliers who have R&D capabilities, as they can develop tailored formulations that meet specific demands. Establishing a prototype phase can also allow buyers to test the customized products before full-scale production, ensuring that the final product meets all necessary criteria.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs and Material Waste in Vulcanization Processes
The Problem: Cost management is a critical issue for B2B buyers dealing with rubber vulcanization, especially in regions with fluctuating raw material prices. Inefficient vulcanization processes can lead to significant material waste, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of production. Buyers may also struggle with hidden costs associated with improper vulcanization, such as the need for rework or scrapping defective products.
The Solution: To mitigate costs and waste, buyers should invest in suppliers that utilize advanced vulcanization technology, which can optimize material usage and reduce cycle times. Inquire about the supplier’s waste management practices and their approach to minimizing scrap during production. Establishing a partnership with suppliers who employ lean manufacturing principles can further enhance efficiency. Additionally, consider investing in training for both staff and suppliers on best practices in vulcanization to minimize errors. By focusing on efficiency and effective communication with suppliers, buyers can reduce waste and keep production costs in check, ultimately improving their bottom line.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber vulcanizing
What Are the Key Materials for Rubber Vulcanizing?
When selecting materials for rubber vulcanizing, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis will focus on four common materials used in the vulcanization process: natural rubber, synthetic rubber (SBR), EPDM rubber, and silicone rubber. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its application in various industries, particularly for international B2B buyers.
How Does Natural Rubber Perform in Vulcanization?
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of rubber trees, is known for its excellent elasticity and tensile strength. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -50°C to 100°C, making it suitable for a variety of applications. However, it has a lower resistance to heat and aging compared to synthetic alternatives.

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
Pros: Natural rubber is highly elastic and offers superior abrasion resistance. It is also cost-effective, which can be advantageous for large-scale manufacturing.
Cons: Its susceptibility to ozone and UV degradation limits its outdoor applications. Additionally, natural rubber may not be suitable for environments with extreme temperatures or chemical exposure.
Impact on Application: Natural rubber is ideal for products requiring flexibility and resilience, such as tires and seals. However, it may not perform well in harsh environments, which is crucial for buyers in regions with varying climates.
What Are the Benefits of Synthetic Rubber (SBR)?
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a popular synthetic alternative that combines strength and flexibility. It has a broader temperature range of -40°C to 120°C and exhibits better resistance to aging and abrasion than natural rubber.
Pros: SBR is versatile and can be tailored with additives to enhance specific properties, such as chemical resistance. It is also more affordable than many other synthetic rubbers.
Cons: While SBR offers good mechanical properties, it may not match the elasticity of natural rubber. Its performance can also be compromised in extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: SBR is commonly used in automotive tires and industrial applications. Buyers should consider its compatibility with various chemicals, especially in sectors like automotive and manufacturing.
Why Choose EPDM Rubber for Vulcanization?
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is known for its outstanding weather resistance and durability. It can operate efficiently in temperatures ranging from -50°C to 150°C, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros: EPDM is highly resistant to ozone, UV radiation, and heat, making it ideal for roofing and automotive applications. Its excellent elasticity ensures longevity and performance.
Cons: EPDM is less effective in oil and fuel applications, limiting its use in certain industrial sectors. Additionally, it can be more expensive than other rubber types.
Impact on Application: Given its durability and weather resistance, EPDM is often used in seals, gaskets, and roofing materials. Buyers in regions with harsh weather conditions should prioritize EPDM for outdoor applications.
What Advantages Does Silicone Rubber Offer in Vulcanization?
Silicone rubber is renowned for its high-temperature resistance, withstanding temperatures from -60°C to 230°C. It is also chemically inert, making it suitable for various applications, including food and medical sectors.
Pros: Silicone rubber maintains its properties over a wide temperature range and is resistant to UV light and ozone. Its biocompatibility makes it a preferred choice for medical applications.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is generally higher than other rubber types. Additionally, silicone rubber can be less durable under mechanical stress.
Impact on Application: Silicone rubber is ideal for applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical resistance, such as in the food industry and medical devices. Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, especially in regulated industries.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rubber Vulcanizing
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber vulcanizing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Tires, seals, gaskets | Excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance | Susceptible to UV and ozone degradation | Low |
| Synthetic Rubber (SBR) | Automotive tires, industrial products | Versatile and cost-effective | Lower elasticity compared to natural rubber | Medium |
| EPDM Rubber | Roofing, seals, gaskets | Outstanding weather and UV resistance | Limited effectiveness in oil applications | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber | Medical devices, food industry | High-temperature resistance and biocompatibility | Higher cost and lower mechanical durability | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance characteristics, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber vulcanizing
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Rubber Vulcanizing?
The manufacturing process for rubber vulcanization is intricate and consists of several key stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent demands of various applications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed decisions when sourcing rubber products.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved?
The initial phase involves preparing the raw materials, which typically include natural or synthetic rubber, sulfur, and various additives. The rubber is first processed to remove impurities and then mixed with sulfur and accelerators. This mixture, known as a compound, often includes fillers, oils, and colorants to enhance the properties of the final product. The precise formulation is critical, as it determines the mechanical characteristics of the vulcanized rubber.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
Once the material is prepared, it undergoes the forming process, where the rubber compound is shaped into the desired product. This can be achieved through various methods, including:
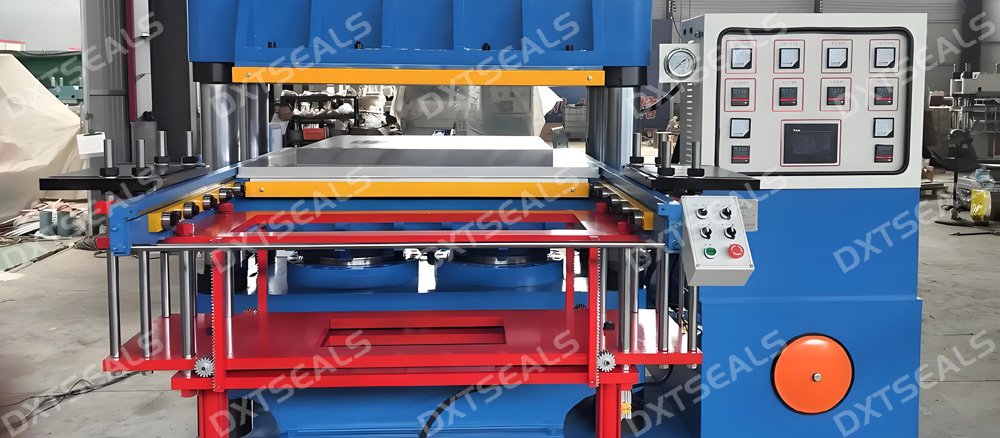

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
-
Molding: The compound is placed in a mold and subjected to heat and pressure, which not only shapes the rubber but also initiates the vulcanization process. This step is crucial for producing complex shapes with high precision.
-
Extrusion: For products requiring uniform cross-sections, such as hoses or seals, the rubber is forced through a die. Extrusion allows for continuous production and is often more efficient than molding for specific applications.
-
Calendering: This technique is used to produce sheets of rubber. The compound is passed through rollers to achieve the desired thickness and surface finish.
What Happens During the Assembly Stage?
In the assembly stage, various components may be combined if the final product consists of multiple parts. This could involve joining molded rubber parts or attaching rubber components to metal or plastic substrates. Adhesives or mechanical fasteners may be employed to ensure a secure bond. The assembly process must adhere to strict quality standards to guarantee that the final product performs reliably under operational conditions.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the aesthetic and functional qualities of the rubber products. Common finishing techniques include:
- Trimming: Excess rubber is removed to achieve precise dimensions and improve appearance.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as buffing, coating, or applying anti-abrasive treatments may be used to enhance durability and performance.
- Quality Inspection: Before packaging, products undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures in Rubber Vulcanizing?
Quality assurance is critical throughout the manufacturing process, particularly in industries where performance and safety are paramount. For B2B buyers, understanding these measures can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
What International Standards Should Be Considered?
To ensure consistent quality, many manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE for products sold in Europe or API for oil and gas applications, may also apply. These standards help ensure that products are manufactured to high-quality specifications and can be trusted for use in critical applications.
What QC Checkpoints Are Essential?
Quality control is typically segmented into several checkpoints during the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify that they meet specified standards. This step is vital to prevent defects from entering the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks are performed during the manufacturing process to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and curing times. Any deviations are promptly addressed to mitigate the risk of defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once products are finished, they undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet all specifications. This may include mechanical testing, dimensional checks, and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s processes and adherence to quality standards. This is particularly important when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality control documentation and test reports can help buyers understand the reliability of the products being sourced.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These organizations can conduct audits and testing to verify compliance with international standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control and certification can be challenging, especially for B2B buyers operating across different continents. Here are a few nuances to consider:
Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions have unique regulatory requirements. For instance, products intended for the European market must comply with CE marking, while those for the U.S. market may need to meet ASTM standards.
-
Documentation Requirements: Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide all necessary documentation, including certificates of compliance, test reports, and material safety data sheets (MSDS). This documentation is crucial for customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
-
Cultural and Legal Considerations: Understanding cultural nuances and legal frameworks can aid in building strong supplier relationships. This includes being aware of local business practices and negotiation styles, which can vary significantly from one region to another.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for rubber vulcanization are critical for ensuring the reliability and performance of rubber products. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that meet their quality standards. Engaging in thorough due diligence, including audits and quality checks, can safeguard against risks associated with sourcing rubber products internationally.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber vulcanizing’
In the global marketplace, sourcing quality rubber vulcanizing services is critical for businesses that rely on durable and high-performance rubber products. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure rubber vulcanizing services effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs for rubber vulcanization is the first step in the procurement process. Define the type of rubber (natural or synthetic) and the required properties, such as elasticity, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength. This clarity helps suppliers provide tailored solutions that meet your performance expectations.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in rubber vulcanization. Look for companies with a strong track record in your industry and positive reviews from previous clients. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry associations to compile a list of candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO 9001). Certifications indicate a commitment to quality management and may reflect their ability to deliver consistent products. Additionally, check for any industry-specific certifications that may be relevant to your requirements.
Step 4: Request Samples and Technical Data
Engage with shortlisted suppliers by requesting samples of their vulcanized rubber products. Analyze these samples for quality and performance metrics. Additionally, ask for technical data sheets that provide insights into the materials used and the vulcanization process, ensuring they align with your specifications.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s production capacity is vital, especially if you require large volumes. Inquire about their machinery, technology, and workforce expertise. A supplier with advanced equipment and skilled personnel can better accommodate your requirements and timelines.
Step 6: Discuss Customization Options
Customization may be necessary to meet specific application needs. Discuss with suppliers their ability to modify formulations or processes to create tailored rubber solutions. This flexibility can be crucial for achieving desired performance characteristics in your final products.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Establish a Clear Contract
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate terms related to pricing, lead times, and delivery schedules. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, quality assurances, and payment terms are clearly documented in a contract. A well-defined agreement minimizes misunderstandings and protects your interests throughout the procurement process.
Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing rubber vulcanizing services, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their technical and commercial needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber vulcanizing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Vulcanizing Sourcing?
When sourcing rubber vulcanizing, it is essential to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, particularly the type of rubber (natural vs. synthetic) and the additives used in the vulcanization process (like sulfur and accelerators), significantly impacts pricing. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and availability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the vulcanization process, including mixing, molding, and curing. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and expertise level of the workforce. For instance, labor costs in Europe may be higher than in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which may influence the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom molds and tooling required for specific product shapes can incur significant upfront costs. The complexity of designs and the production volume will affect the amortization of these costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the vulcanized rubber meets quality standards is crucial, particularly for industries like automotive and aerospace. The costs associated with QC processes and certifications (such as ISO) can add to the total expense.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are essential, especially for international shipping. These costs can vary based on the distance, shipping methods, and any customs duties applicable.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on competition, market conditions, and the supplier’s operational efficiencies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rubber Vulcanizing Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of rubber vulcanizing, which buyers should consider to optimize their sourcing strategy.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger order volumes generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for favorable terms based on their purchasing power.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and materials. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help mitigate unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certified products (e.g., meeting specific industry standards) often come at a premium. Buyers should assess the balance between quality and cost to ensure the right fit for their application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality but at a higher price, while emerging suppliers might provide competitive rates to gain market entry.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping costs, risk, and insurance. This can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
What Are Effective Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Strategies for Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost-efficiency strategies are crucial.
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing and terms. Leverage your purchasing volume as a bargaining chip. Consider multiple suppliers to create competition.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, longevity, and performance of the vulcanized products. This holistic view can reveal better value options.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local taxes that can impact the final cost. Additionally, consider the supplier’s payment terms and the potential for discounts on early payments.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and price fluctuations in rubber and its derivatives. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations and help in anticipating cost changes.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for rubber vulcanizing sourcing can vary widely based on numerous factors discussed above. This analysis serves as a guideline and should not be construed as definitive pricing. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and consult with suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber vulcanizing With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Rubber Vulcanizing
In the realm of rubber processing, vulcanization is a widely recognized method for enhancing the strength and elasticity of rubber products. However, various alternative solutions can achieve similar objectives, catering to different manufacturing needs and economic considerations. This analysis compares rubber vulcanizing against two viable alternatives: thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) processing and heat-resistant rubber formulations. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Vulcanizing | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Processing | Heat-Resistant Rubber Formulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength and elasticity, excellent abrasion resistance | Moderate strength, flexible and can be molded | Good heat resistance, less elastic than vulcanized rubber |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to complex process | Lower, as TPEs are cheaper to produce | Moderate, depending on formulation specifics |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Easier to process, compatible with standard molding techniques | Requires specific formulations, but easier than vulcanization |
| Maintenance | Low, but requires careful handling during production | Low, generally maintenance-free after production | Moderate, may degrade under extreme conditions |
| Best Use Case | Applications requiring high durability and flexibility, e.g., tires, seals | Consumer goods, automotive parts, and applications needing flexibility | High-temperature environments, e.g., engine components |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Processing
TPEs combine the properties of rubber and plastic, allowing for easy processing and recycling. They can be melted and reshaped multiple times, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability, such as consumer goods and automotive components. The primary advantage of TPEs is their lower cost and ease of manufacturing compared to vulcanized rubber. However, TPEs may not match the strength and abrasion resistance of vulcanized rubber, which can be a limitation in high-stress applications.
2. Heat-Resistant Rubber Formulations
Heat-resistant rubber formulations are designed to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for applications in automotive and industrial settings. These formulations can be engineered to offer good mechanical properties while resisting heat degradation. While they provide specific advantages in high-temperature environments, they typically lack the overall elasticity and strength of vulcanized rubber. Additionally, the cost can vary depending on the specific formulation, which may affect budget considerations for large-scale production.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a rubber processing method, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and application-specific needs. Rubber vulcanizing remains a top choice for applications demanding superior strength and elasticity, while thermoplastic elastomers offer a cost-effective alternative for less demanding scenarios. Heat-resistant rubber formulations are ideal for environments exposed to extreme temperatures. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals and product specifications of the buyer’s industry, ensuring the chosen solution meets both performance and economic objectives.
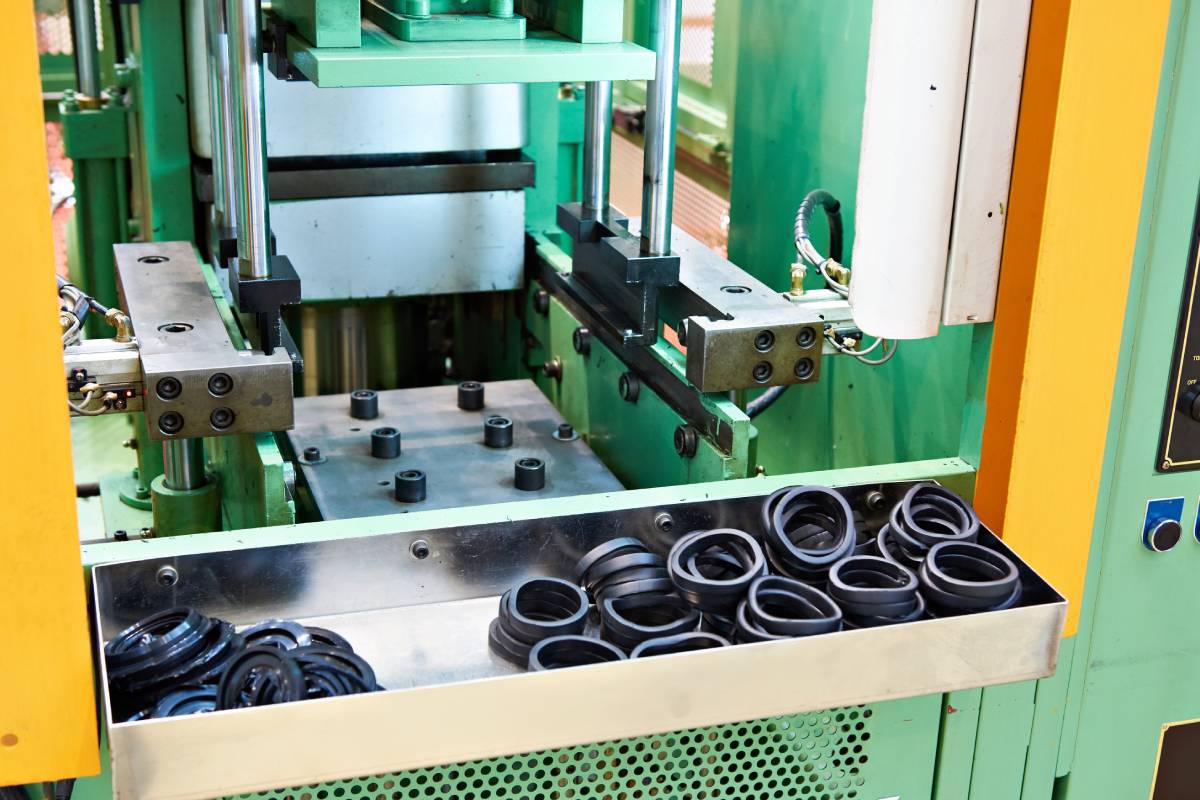

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber vulcanizing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Vulcanizing?
Understanding the essential technical properties of rubber vulcanization is crucial for B2B buyers in various industries. These properties not only dictate the performance of rubber products but also influence purchasing decisions, manufacturing processes, and overall product quality.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of rubber based on its composition and intended use. Common grades include natural rubber (NR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it affects durability, elasticity, and resistance to environmental factors. B2B buyers should align material grades with specific applications—such as automotive, industrial, or consumer goods—to ensure optimal performance.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limits of variation in dimensions during the manufacturing process. In rubber vulcanization, tight tolerances are critical for components that require precise fitting, such as seals and gaskets. Tolerance specifications help maintain product consistency and reduce manufacturing waste, making them a key consideration for buyers focused on quality and cost-efficiency.
3. Hardness (Shore A)
Hardness, measured in Shore A, indicates the firmness of the rubber material. The scale ranges from 0 (very soft) to 100 (very hard), with different hardness levels suitable for various applications. For example, softer rubber may be ideal for cushioning products, while harder rubber is preferred for structural applications. Understanding hardness allows B2B buyers to select products that meet specific performance criteria.

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
4. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures a material’s resistance to being pulled apart and is expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or megapascals (MPa). High tensile strength is crucial for products exposed to stress and strain, such as tires and industrial belts. Buyers should prioritize tensile strength in their specifications to ensure reliability and longevity in demanding applications.
5. Elongation at Break
Elongation at break is the percentage increase in length that a rubber sample can withstand before breaking. This property reflects the rubber’s elasticity and ability to return to its original shape after deformation. A high elongation percentage is advantageous for applications that require flexibility, such as automotive components and footwear. Buyers must evaluate elongation properties to meet the performance requirements of their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Rubber Vulcanizing?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the rubber vulcanization market. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the rubber industry, OEMs often provide components for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product compatibility.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses determine their purchasing strategy and ensures they meet supplier requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. An effective RFQ outlines the technical specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines required. B2B buyers should craft detailed RFQs to receive accurate and competitive quotations, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and duties, which is crucial for minimizing risks and misunderstandings in cross-border trade. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers negotiate better shipping terms and manage logistics effectively.
5. Curing Agents
Curing agents, often including sulfur and accelerators, are additives used in the vulcanization process to enhance rubber’s properties. Understanding the role of curing agents enables buyers to select the right formulations for their applications, affecting product performance and longevity.

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of rubber vulcanization more effectively, leading to better purchasing decisions and improved product outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber vulcanizing Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Rubber Vulcanizing Market?
The global rubber vulcanizing market is currently witnessing robust growth, driven by several factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for durable and high-performance rubber products across various industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods. As manufacturers strive for quality, vulcanized rubber’s superior strength and elasticity make it the preferred choice for applications requiring resilience and longevity.
Emerging technologies such as advanced mixing and molding techniques are transforming the vulcanization process, enhancing efficiency and reducing production time. Automation and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also becoming prevalent, enabling manufacturers to optimize supply chain management and improve operational efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these advancements present opportunities to source high-quality products at competitive prices while ensuring timely delivery.
Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on sustainability is shaping market dynamics. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who incorporate eco-friendly practices and materials in their production processes. This trend is particularly significant in Europe and parts of South America, where regulatory pressures and consumer preferences are shifting towards sustainable sourcing.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in Rubber Vulcanizing?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor for B2B buyers in the rubber vulcanizing sector. The environmental impact of rubber production, particularly in terms of deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions, has raised concerns among consumers and regulatory bodies. Consequently, businesses are prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainable practices in their supply chains.
Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who offer ‘green’ certifications and materials, such as recycled rubber or bio-based additives that reduce the ecological footprint of vulcanized rubber products. Certifications like ISO 14001 and Cradle to Cradle are gaining traction, as they assure buyers of a supplier’s commitment to environmental management and sustainable practices.
Moreover, the shift towards circular economy principles is influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are exploring options for recycling used vulcanized rubber products, thereby minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency. This approach not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also offers cost-saving opportunities for businesses looking to reduce raw material expenses.
What Is the Historical Context of Rubber Vulcanizing in B2B?
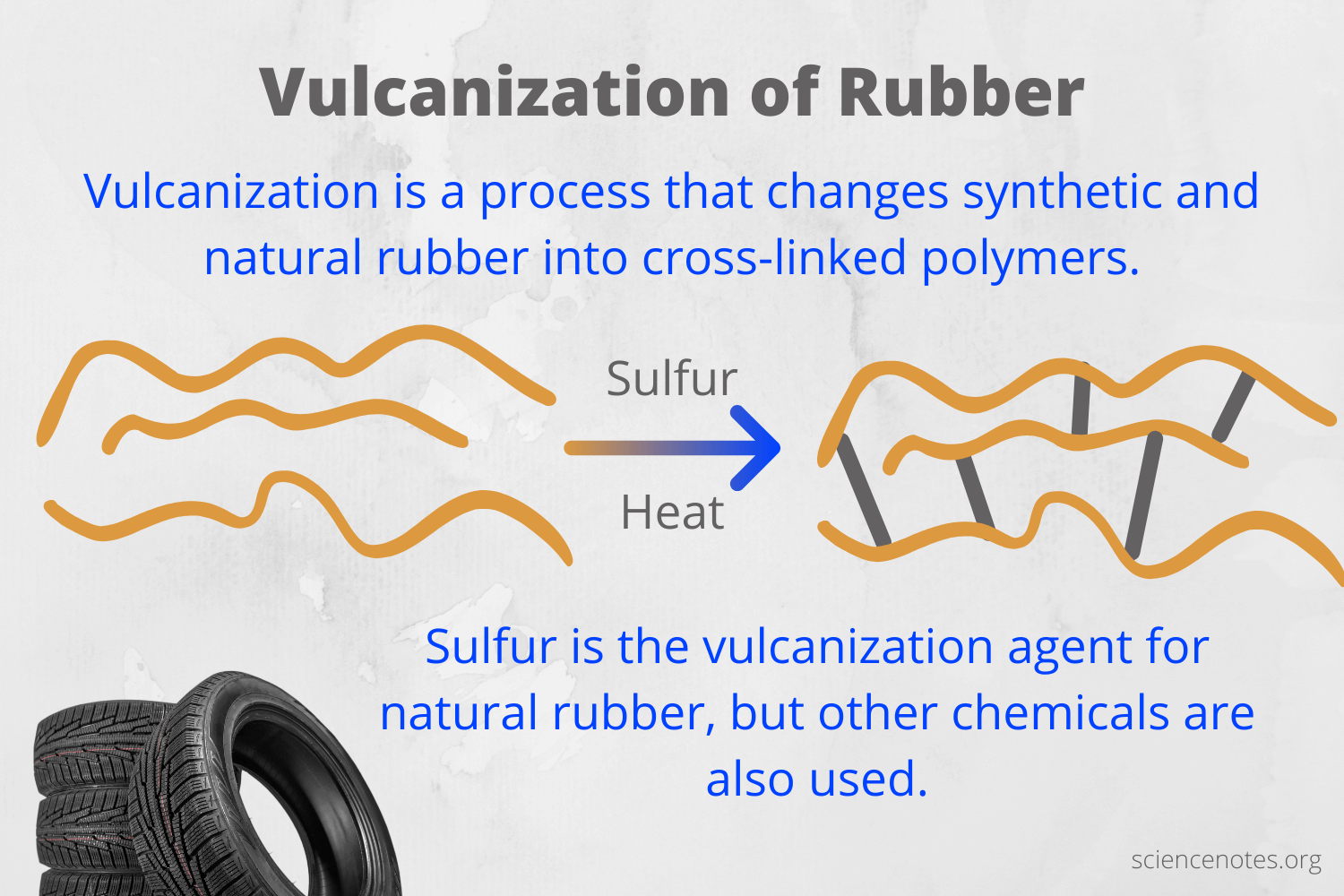
The history of rubber vulcanizing dates back to the mid-19th century when Charles Goodyear discovered the vulcanization process, which involves heating rubber with sulfur to enhance its properties. This breakthrough revolutionized the rubber industry, enabling the production of stronger, more durable materials suitable for a wide range of applications.
Initially, vulcanized rubber was primarily used in tires and footwear, but its versatility has led to its adoption in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Over the years, the introduction of synthetic rubber and advanced additives has further expanded the potential applications of vulcanized rubber, making it a staple in modern manufacturing.
For B2B buyers, understanding the evolution of rubber vulcanizing helps contextualize current market trends and sourcing practices, providing insights into the long-term reliability and performance of vulcanized rubber products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber vulcanizing
1. How do I choose a reliable supplier for rubber vulcanizing?
To select a trustworthy supplier for rubber vulcanizing, start by evaluating their industry experience and reputation. Look for certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request references from other clients, and consider visiting their facilities if possible. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, including technology and equipment used in the vulcanization process. Engaging in thorough communication regarding your specific needs can also reveal their responsiveness and customer service quality.
2. What are the benefits of sourcing vulcanized rubber internationally?
Sourcing vulcanized rubber internationally can offer several advantages, including access to a wider range of materials and technologies that may not be available locally. It often provides cost savings due to lower production costs in certain countries. Additionally, international suppliers may offer specialized products tailored to specific applications, enhancing your product offerings. However, consider factors like shipping times, customs regulations, and potential language barriers when planning your procurement strategy.
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for vulcanized rubber products?
Minimum order quantities for vulcanized rubber products can vary widely among suppliers, ranging from small batches of a few hundred units to larger quantities in the thousands. Factors influencing MOQ include the complexity of the product, production costs, and the supplier’s capacity. Discuss your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business requirements while considering potential cost benefits of larger orders.
4. How can I customize vulcanized rubber products to meet my specifications?
Customization of vulcanized rubber products typically involves discussing your specific requirements with the supplier, including dimensions, material properties, and intended applications. Many suppliers offer customization options such as color, additives, and specific elastomer blends. It’s essential to provide detailed specifications and collaborate with the supplier’s technical team to ensure that the final product meets your expectations. Be prepared for potential lead times associated with custom orders.
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing rubber vulcanizing?
Payment terms for sourcing rubber vulcanizing can vary by supplier and may include options like upfront payment, partial payment, or payment upon delivery. Common practices include 30% upfront with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. International buyers should consider the implications of currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect your interests, including payment security measures such as letters of credit or escrow services.
6. How do I ensure quality assurance for vulcanized rubber products?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed quality control processes from your supplier. Inquire about their testing methods, including tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance of the vulcanized rubber. Establish a clear quality agreement outlining specifications and tolerances. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or audits to verify compliance with your quality standards before shipment. Regular communication with the supplier during production can help address any issues proactively.
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vulcanized rubber?
When importing vulcanized rubber, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, transit times, and customs clearance processes. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with rubber products to navigate potential regulatory requirements. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices and packing lists, is prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in storage and handling needs upon arrival to prevent damage or degradation of the products.
8. How can I assess the environmental sustainability of my rubber vulcanizing supplier?
To evaluate the environmental sustainability of your rubber vulcanizing supplier, review their practices regarding waste management, emissions, and use of sustainable materials. Inquire about their compliance with international environmental standards, such as ISO 14001. Assess whether they implement eco-friendly manufacturing processes, such as reducing energy consumption and recycling materials. Engaging suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance your brand’s reputation and align with your corporate social responsibility goals.
A Look at Rubber Vulcanizing Manufacturers & Suppliers
We are currently compiling a detailed list of top rubber vulcanizing suppliers. Please check back later.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber vulcanizing
In the ever-evolving landscape of rubber vulcanization, strategic sourcing remains a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing suppliers who leverage advanced vulcanization techniques, businesses can ensure access to high-quality, durable rubber products that meet the rigorous demands of various applications, from automotive to industrial uses. Understanding the nuances of vulcanized versus traditional rubber is essential; the enhanced strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance of vulcanized rubber not only improve product performance but also reduce long-term costs associated with maintenance and replacement.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to expand, the importance of forging strong supplier relationships cannot be overstated. Buyers should actively seek out innovative manufacturers who are committed to sustainable practices and technological advancements in rubber processing.
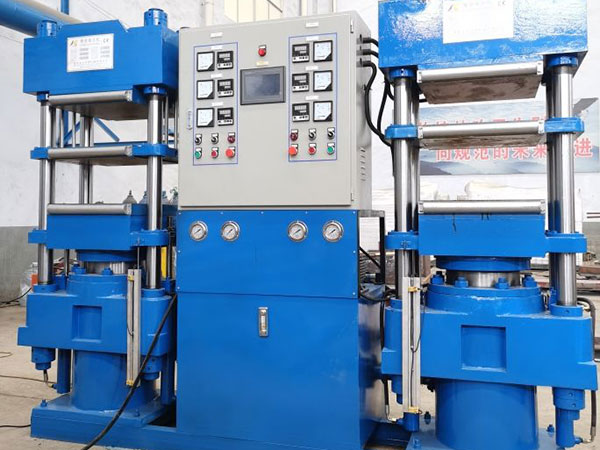

Illustrative image related to rubber vulcanizing
Looking ahead, the global demand for vulcanized rubber is set to rise, driven by increasing applications across diverse industries. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and align them with suppliers who can provide competitive advantages. Engage with your suppliers today to explore collaborative opportunities that can enhance your product offerings and market reach.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.