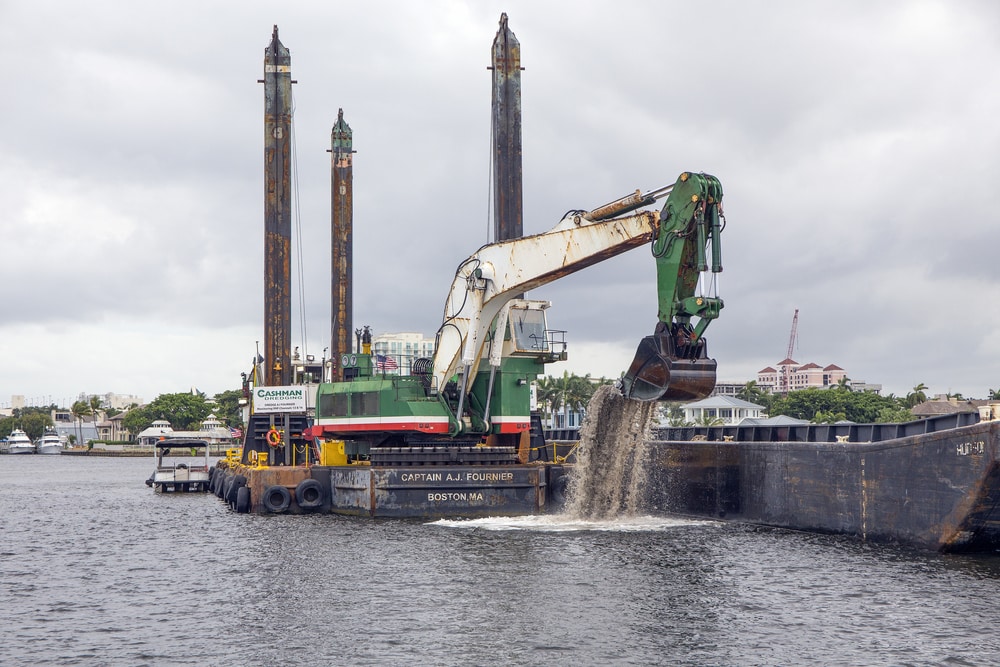
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dredging project
In the ever-evolving landscape of global trade, sourcing the right solutions for dredging projects can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With increasing demands for infrastructure development, environmental restoration, and coastal protection, understanding the complexities of dredging is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of dredging projects, exploring various types such as environmental remediation, offshore trenching, and maritime dredging. It also addresses critical applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, ensuring that you are well-equipped to make informed purchasing decisions.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including nations like Vietnam and Brazil) continue to expand, the need for effective dredging solutions becomes paramount. This guide empowers you by providing actionable insights into selecting the right equipment, understanding project requirements, and identifying reliable suppliers in the dredging industry. By navigating the complexities of dredging projects with clarity, you will enhance your operational efficiency and contribute to sustainable development in your region. Whether you are involved in large-scale construction or environmental cleanup, this resource serves as your essential roadmap to successful dredging initiatives.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Dredging Project Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dredging project
- Understanding dredging project Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of dredging project
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dredging project’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for dredging project
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dredging project
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dredging project’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dredging project Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dredging project With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dredging project
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dredging project Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dredging project
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dredging project
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding dredging project Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Remediation | Targets specific contaminants; focuses on ecological restoration | Cleanup of polluted waterways | Pros: Enhances ecosystem health; regulatory compliance. Cons: Potentially high costs; longer project timelines. |
| Coastal Protection | Involves beach re-nourishment; construction of dikes | Protecting shorelines from erosion | Pros: Long-term shoreline sustainability; enhances local tourism. Cons: Environmental impact assessments required; maintenance needed. |
| Offshore Trenching | Creates precise trenches for underwater infrastructure | Installation of pipelines and cables | Pros: Protects critical infrastructure; reduces risk of damage. Cons: Requires specialized equipment; may be costly. |
| Sand and Gravel Extraction | Focuses on sourcing construction materials | Supply for construction and landscaping | Pros: Provides essential raw materials; often more cost-effective. Cons: Environmental regulations can complicate projects; potential for over-extraction. |
| Maritime Dredging | Maintains navigability of ports and waterways | Port maintenance and river navigation | Pros: Ensures safe passage for vessels; supports trade. Cons: Regular maintenance needed; potential disruption to marine life. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Environmental Remediation Dredging?
Environmental remediation dredging is essential for restoring polluted aquatic environments. This type of dredging specifically targets harmful substances, such as heavy metals or organic pollutants, ensuring that only the contaminants are removed while preserving the surrounding ecosystem. This method is particularly suitable for industrial sites or urban areas where historical pollution is prevalent. B2B buyers should consider the regulatory landscape, as successful projects often require compliance with environmental standards, potentially influencing project timelines and costs.
How Does Coastal Protection Dredging Work?
Coastal protection dredging is aimed at preserving shorelines from erosion and degradation. This involves processes such as beach re-nourishment, where sand is dredged from offshore and deposited on eroding beaches, and the construction of protective dikes. This type of project is vital for communities reliant on coastal tourism and real estate. Buyers should evaluate the long-term environmental impacts and maintenance requirements, as ongoing assessments and interventions may be necessary to ensure effectiveness.
What Are the Benefits of Offshore Trenching Dredging?
Offshore trenching is a specialized dredging technique that creates narrow, precise trenches to install and protect underwater infrastructure, such as pipelines and power cables. This method is vital for ensuring the safety and longevity of these systems, particularly in high-traffic maritime areas. B2B buyers should consider the advanced technology and specialized equipment required for this type of dredging, as well as the potential for higher costs due to the precision and expertise involved.
Why Is Sand and Gravel Extraction Dredging Important?
Sand and gravel extraction is a crucial aspect of the construction industry, supplying essential materials for building projects. This type of dredging is often more cost-effective than land-based mining, making it an attractive option for construction companies. However, buyers must be aware of environmental regulations that govern extraction activities, as over-extraction can lead to significant ecological damage and legal repercussions. Sustainable practices are vital to maintaining the balance between resource supply and environmental stewardship.
How Does Maritime Dredging Support Navigation?
Maritime dredging is essential for maintaining the navigability of ports, harbors, and rivers. This type of dredging removes sediment build-up to ensure safe passage for ships and supports the efficiency of maritime trade. B2B buyers should assess the frequency of dredging needed, as regular maintenance can be costly and disruptive. Understanding the local marine ecosystem is also crucial, as projects may impact aquatic life, necessitating careful planning and execution to minimize harm.
Key Industrial Applications of dredging project
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Dredging Project | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Management | Environmental Remediation Dredging | Enhances ecosystem health by removing pollutants | Seek companies with expertise in environmental regulations and local ecosystems. |
| Construction and Infrastructure | Sand and Gravel Extraction | Provides essential materials for construction projects | Evaluate the reliability of supply chains and quality of extracted materials. |
| Energy and Utilities | Offshore Trenching for Pipeline Installation | Ensures safe and efficient installation of critical infrastructure | Look for advanced technology and equipment capabilities for precision dredging. |
| Water Resource Management | Reservoir and Lake Construction | Supports clean water supply and hydroelectric power generation | Prioritize suppliers with experience in large-scale water management projects. |
| Maritime and Shipping | Maritime Dredging for Port Maintenance | Facilitates safe navigation and increases shipping efficiency | Assess the dredging company’s experience in maintaining navigational channels. |
How Does Environmental Remediation Dredging Benefit Businesses?
Environmental remediation dredging is crucial for industries focused on sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations. This application targets the removal of hazardous materials from water bodies, thereby enhancing ecosystem health and promoting biodiversity. For businesses in sectors such as waste management and manufacturing, partnering with experienced dredging companies is essential to navigate the complexities of local environmental laws and ensure that remediation efforts meet regulatory standards. Buyers should consider firms that provide specialized dredging equipment and possess a strong understanding of local ecosystems to achieve successful outcomes.
What Role Does Dredging Play in Sand and Gravel Extraction?
In construction and infrastructure development, sand and gravel are fundamental materials. Dredging is employed to extract these resources from riverbeds and coastal areas, meeting the growing demand driven by urbanization and construction projects. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is vital to source dredging services that can guarantee the quality and quantity of materials extracted. Companies should evaluate the dredging contractor’s ability to manage logistics and supply chain challenges, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with local regulations governing resource extraction.
How Does Offshore Dredging Enhance Energy Infrastructure?
Offshore trenching is a specialized dredging application that supports the installation of pipelines for energy and communication infrastructure. This process is critical for ensuring the safe placement of underwater cables and pipelines, which are vital for energy distribution and data transfer. For businesses in the energy sector, it is crucial to partner with dredging companies that utilize advanced technology for precision and efficiency. International buyers must consider the contractor’s experience in high-traffic marine environments and their capacity to comply with safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with offshore operations.
Why is Dredging Important for Reservoir and Lake Construction?
In the context of water resource management, dredging is instrumental in constructing lakes and reservoirs that provide clean drinking water and hydroelectric power. This application not only involves the excavation of sediment but also addresses environmental concerns by maintaining water quality. For international buyers in regions facing water scarcity, it is essential to work with dredging firms that have a proven track record in large-scale water management projects. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with the capability to navigate complex environmental challenges and ensure the sustainability of water resources.
How Does Maritime Dredging Support Shipping Efficiency?
Maritime dredging is essential for maintaining navigational channels in ports and harbors, ensuring safe passage for vessels. This application is critical for shipping companies and port authorities aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. For B2B buyers in the shipping industry, selecting a dredging contractor with extensive experience in port maintenance is key. Additionally, buyers should assess the contractor’s ability to provide timely dredging services to prevent silt buildup and maintain optimal water depths, thereby supporting the smooth operation of maritime logistics.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘dredging project’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance in Dredging Projects
The Problem: In many regions, including Africa and South America, regulatory compliance is a significant hurdle for B2B buyers involved in dredging projects. The complexities of local, national, and international regulations surrounding environmental protection can lead to delays, increased costs, and project cancellations. Buyers often find it challenging to navigate the maze of required permits, environmental assessments, and community consultations, leading to frustration and uncertainty about project timelines and feasibility.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, B2B buyers should engage with local regulatory bodies early in the planning phase. Conducting thorough research on the specific environmental regulations applicable to the project site is crucial. Buyers can invest in consulting services specializing in environmental compliance to ensure that all required permits are identified and obtained proactively. Additionally, incorporating an environmental management plan (EMP) can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, potentially speeding up the approval process. Establishing relationships with local stakeholders and communities can also facilitate smoother communication and foster goodwill, which may help in navigating regulatory landscapes more effectively.
Scenario 2: Managing Cost Overruns in Dredging Operations
The Problem: Cost overruns are a common pain point in dredging projects, primarily due to unforeseen site conditions, equipment failures, and changes in project scope. Buyers may find themselves unprepared for additional expenses associated with unexpected sediment types or environmental challenges, leading to budget constraints and project delays. This situation can be particularly acute in regions with fluctuating economic conditions, where maintaining budget integrity is vital for project viability.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of cost overruns, B2B buyers should adopt a comprehensive project management approach that includes thorough pre-project assessments. Utilizing geotechnical surveys to understand site conditions before mobilizing equipment can help buyers prepare for potential challenges. Establishing a contingency budget—typically 10-15% of the total project cost—can provide a financial buffer against unexpected expenses. Furthermore, employing advanced project tracking software allows for real-time monitoring of costs and timelines, enabling quick adjustments as needed. Regular communication with stakeholders and contractors can also ensure that everyone is aligned on project goals and potential challenges, reducing the likelihood of scope changes that lead to additional costs.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
Scenario 3: Ensuring Equipment Reliability and Performance
The Problem: For B2B buyers in the dredging industry, equipment reliability is crucial for the success of any project. Equipment breakdowns can lead to significant downtime, impacting project schedules and budgets. Buyers often face difficulties in selecting the right dredging equipment that meets the specific needs of their projects, especially when balancing performance capabilities against cost. This challenge is compounded in remote areas where access to maintenance services is limited.
The Solution: To address equipment reliability concerns, buyers should conduct a thorough evaluation of their project requirements before selecting dredging machinery. Engaging with reputable equipment rental companies that offer modern, well-maintained fleets can minimize the risk of breakdowns. Buyers should also consider investing in a maintenance contract that includes regular inspections and servicing, ensuring that equipment remains operational throughout the project duration. Training operators on the specific machinery used can enhance performance and reduce the likelihood of user error leading to equipment failure. Additionally, leveraging technology such as telematics can provide real-time performance data, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the chances of unexpected downtime.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dredging project
What Are the Key Materials Used in Dredging Projects?
When selecting materials for dredging projects, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in dredging applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Dredging Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in dredging equipment due to its high strength and durability. It typically has excellent tensile strength and can withstand significant stress and pressure, making it ideal for constructing dredging vessels and components. Steel’s corrosion resistance can be enhanced through galvanization or the application of protective coatings, which is crucial in marine environments.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for many dredging applications. It also offers high durability and can be easily fabricated into various shapes and sizes.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
Cons: While steel is strong, it can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, leading to increased maintenance costs over time. Additionally, the weight of steel can impact the mobility of dredging equipment.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for heavy-duty dredging tasks, including deep-sea and inland dredging, where strength and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material standards, such as ASTM or DIN. The availability of treated steel may vary, impacting procurement timelines.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Dredging Equipment?
Aluminum is increasingly used in dredging applications due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It has a lower density than steel, which can enhance the mobility of dredging equipment and reduce fuel consumption during operations. Aluminum is also non-magnetic, making it suitable for applications where magnetic interference is a concern.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its corrosion resistance, which is particularly beneficial in salty marine environments. Its lightweight nature allows for easier handling and transportation.
Cons: Aluminum is generally more expensive than steel and can have lower tensile strength, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Fabrication can also be more complex due to its properties.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in smaller dredging vessels and equipment designed for shallow water or specialized tasks where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum grades suitable for marine applications and ensure compliance with international standards. Cost considerations may vary significantly by region.
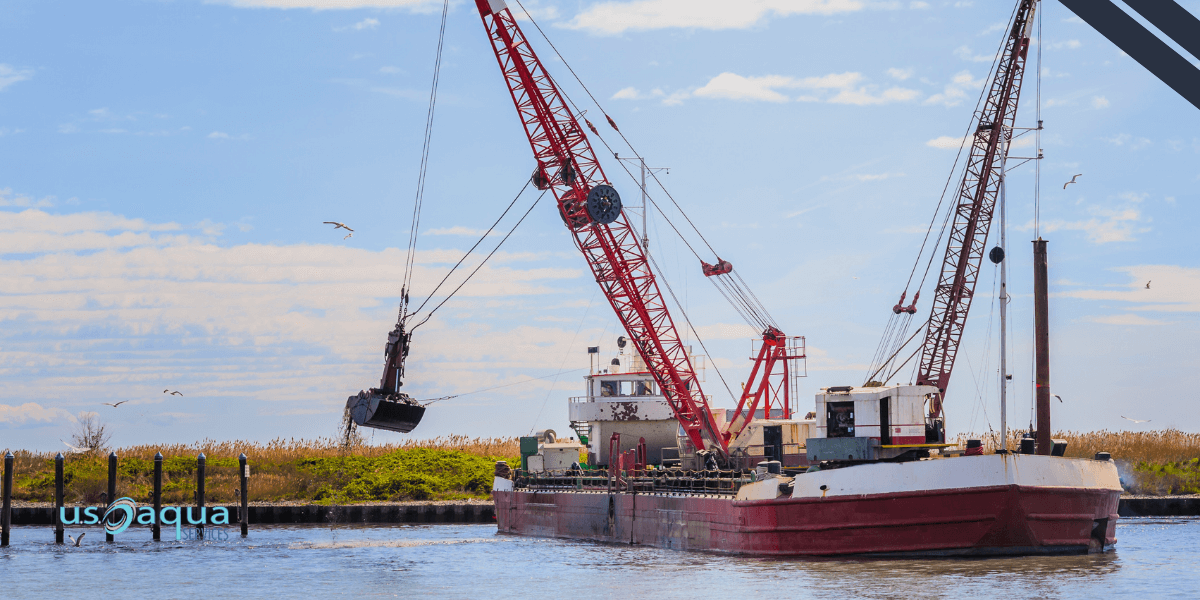
Illustrative image related to dredging project
Why Choose Composite Materials for Dredging?
Composite materials, particularly fiber-reinforced plastics, are gaining traction in dredging applications due to their unique properties. These materials offer excellent corrosion resistance and are lightweight, making them suitable for various dredging components, including pipes and hulls.
Pros: Composites are highly resistant to chemical and environmental degradation, leading to reduced maintenance costs. Their lightweight nature can enhance fuel efficiency and operational flexibility.
Cons: The initial cost of composite materials can be high, and their manufacturing processes may be more complex than traditional materials. Additionally, they may not be suitable for all types of dredging applications due to strength limitations.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for specialized dredging tasks, such as environmental remediation, where chemical resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials in their region and ensure compliance with relevant standards. Understanding the lifecycle costs of composites versus traditional materials is essential for budget planning.
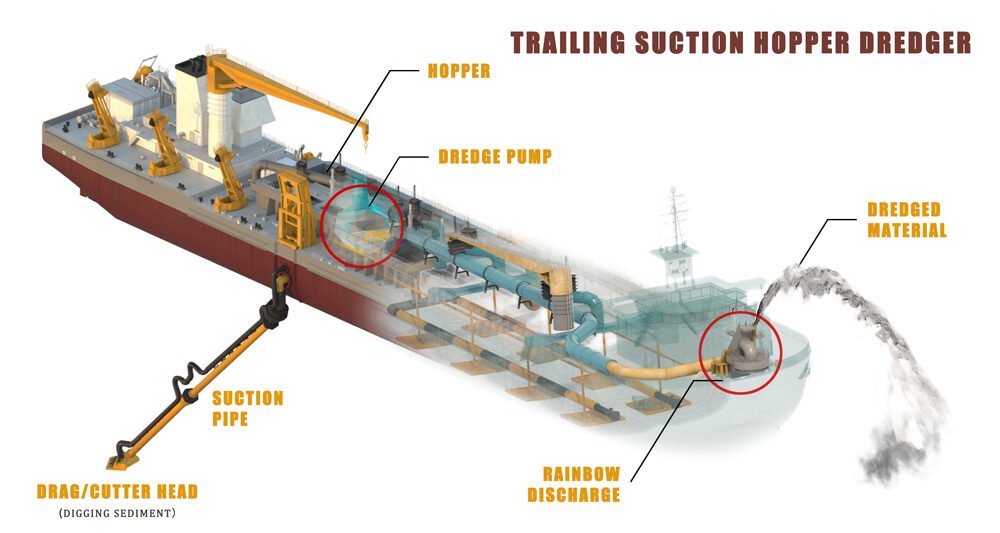
Illustrative image related to dredging project
How Does Rubber Contribute to Dredging Operations?
Rubber is commonly used in dredging applications, particularly for components like hoses and seals. Its flexibility and resilience make it an excellent choice for various operational conditions. Rubber can withstand a range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for different dredging environments.
Pros: Rubber’s flexibility allows for easy handling and installation, and it provides excellent vibration dampening, which can enhance the longevity of dredging equipment.
Cons: While rubber is durable, it can degrade over time when exposed to UV light and harsh chemicals, necessitating regular replacement. Its performance may also be affected by extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Rubber is essential for hydraulic systems and other components that require flexibility and resilience under varying operational conditions.
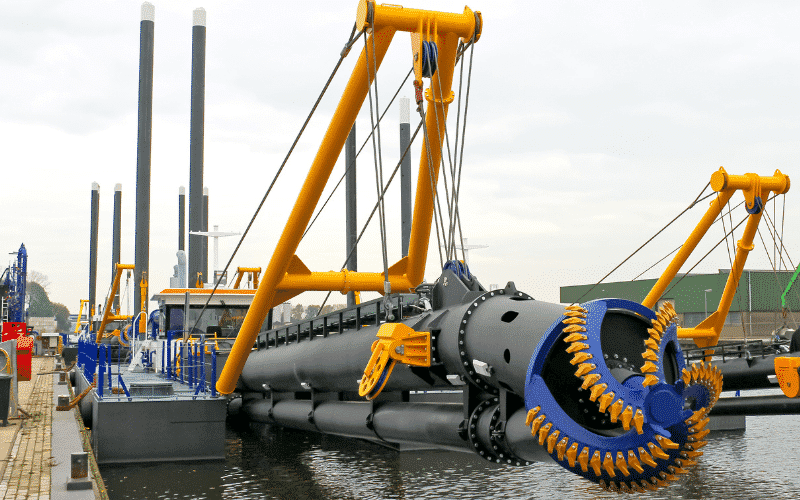
Illustrative image related to dredging project
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific types of rubber suitable for marine applications and ensure compliance with regional standards. Availability may vary, impacting project timelines.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Dredging Projects
| Material | Typical Use Case for dredging project | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty dredging equipment | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight dredging vessels | Corrosion resistance | Higher cost and lower strength | High |
| Composite | Specialized dredging components | Chemical resistance | High initial cost | High |
| Rubber | Hoses and seals in dredging systems | Flexibility and resilience | Degrades under UV exposure | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers involved in dredging projects, helping them make informed decisions that align with project requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dredging project
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Dredging Equipment?
The manufacturing process for dredging equipment is multifaceted, involving several critical stages to ensure the production of high-quality and reliable machinery. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing dredging solutions.
1. Material Preparation
The initial stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials, which typically include high-strength steel and other alloys. The choice of materials is crucial as they must withstand harsh marine environments and resist corrosion. Suppliers often use advanced techniques such as laser cutting and plasma cutting to achieve precise dimensions, ensuring components fit together seamlessly during assembly.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
2. Forming
In the forming stage, the raw materials undergo various processes to create the desired shapes. Techniques such as bending, rolling, and stamping are commonly employed. For dredging equipment, which often features complex geometries, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is frequently utilized. This technology allows for high precision and repeatability, which is essential in maintaining the performance and durability of the equipment.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This process can be labor-intensive and requires skilled technicians to ensure that parts are correctly aligned and securely fastened. Advanced assembly techniques, including robotic welding and automated fastening systems, are increasingly being adopted to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Each piece of equipment is typically assembled in accordance with specific engineering standards to guarantee functionality and safety.
4. Finishing
The final manufacturing stage involves finishing processes that enhance the equipment’s durability and aesthetic appeal. This includes surface treatments such as galvanizing, painting, and coating with anti-corrosion materials. These treatments are critical for dredging machinery, which operates in challenging aquatic environments. Quality assurance checkpoints during this phase ensure that the finishing processes meet industry standards and customer specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Dredging Equipment Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of dredging equipment, as it directly affects performance, safety, and longevity. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA processes and standards is essential for ensuring that they procure reliable products.
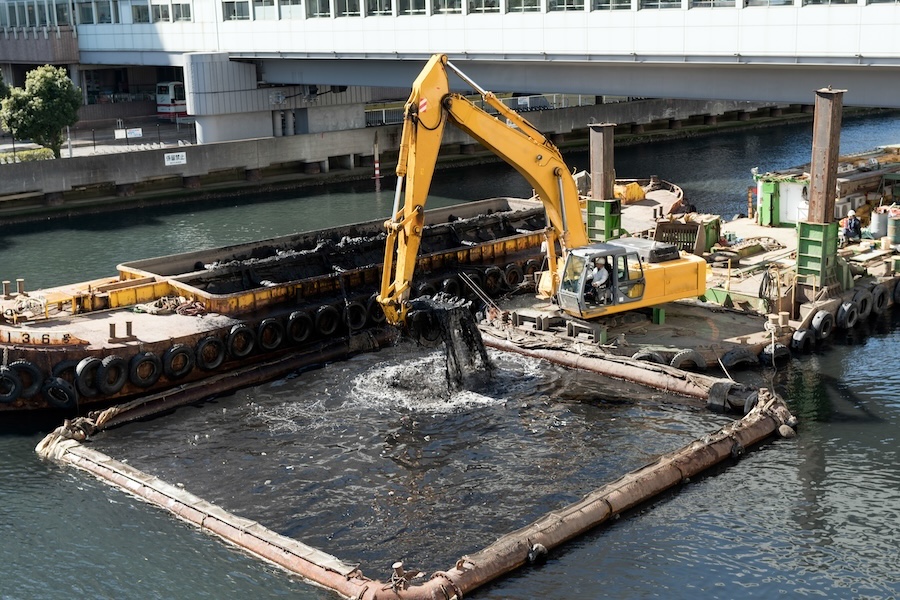

Illustrative image related to dredging project
International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications
Most reputable manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management system requirements. This certification is crucial for ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for specific components offer further assurance regarding compliance with safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure that products meet specified standards.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to verify that they meet the required specifications. Suppliers should provide certificates of conformity or material test reports.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections and tests are performed at critical stages. This may include dimensional checks, weld inspections, and non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle testing to detect any defects that may affect the equipment’s integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This includes functional tests to ensure the equipment operates as intended and visual inspections to check for surface defects or finish quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Dredging Equipment QC?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the quality of dredging equipment. Key methods include:
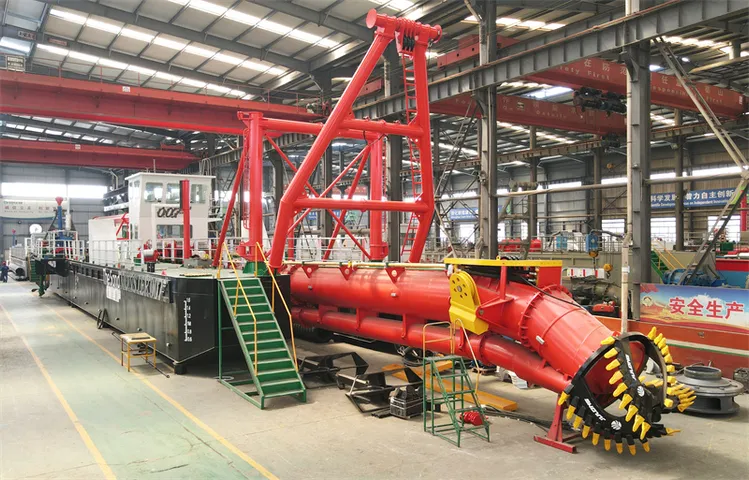

Illustrative image related to dredging project
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This is often performed on components such as pumps and hoses to ensure they can withstand the pressures encountered during operation.
-
Performance Testing: Equipment is often tested under simulated operational conditions to assess performance metrics such as efficiency, power consumption, and operational reliability.
-
Environmental Testing: Given the exposure to corrosive marine environments, manufacturers may conduct tests simulating long-term exposure to saltwater to evaluate corrosion resistance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control processes is paramount to ensure that they receive equipment that meets their requirements.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the QC processes, equipment used, and adherence to standards. This can also help build a relationship with the supplier.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality control reports, including data from inspections and tests. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with agreed-upon standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s products and processes. This can be particularly valuable when dealing with new suppliers or when large investments are at stake.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from different regions may face unique challenges regarding quality control.
-
Regional Standards: Buyers should be aware of specific regulations and standards that apply in their region, which may differ from those in the manufacturing country. Understanding these can help ensure compliance and avoid costly delays.
-
Communication Barriers: Language differences can pose challenges in understanding quality documentation. It’s advisable to establish clear communication channels and possibly engage local representatives who can bridge any gaps.
-
Cultural Expectations: Different countries may have varying expectations regarding quality and service. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the cultural norms of their suppliers to foster better relationships and negotiate effectively.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in dredging projects, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they procure high-quality, reliable equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘dredging project’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring dredging project services effectively. Dredging is a vital operation in various industries, including construction, environmental remediation, and coastal protection. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right partners and equipment to meet their project needs.
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Clearly outlining your project requirements is essential for a successful dredging operation. Determine the scope, objectives, and specific challenges you expect to face. This step will help you articulate your needs to potential suppliers, ensuring they can provide the appropriate solutions.
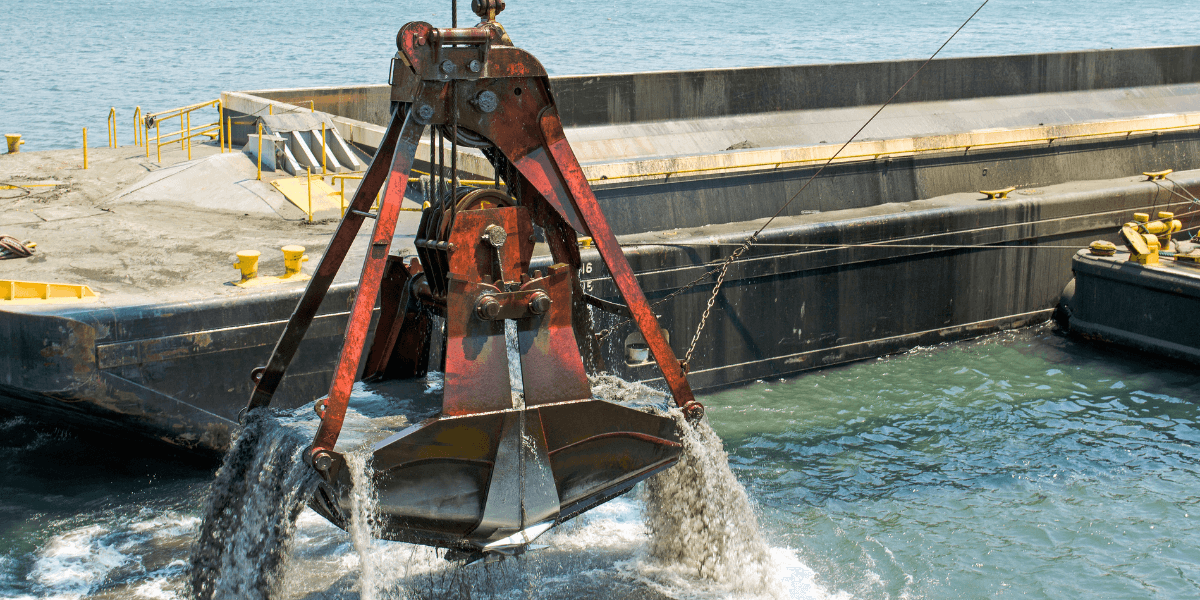

Illustrative image related to dredging project
- Key Considerations:
- Type of dredging (e.g., environmental remediation, pipeline dredging)
- Volume and type of materials to be removed
- Environmental regulations and compliance requirements
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable dredging companies with experience in your project type. A robust supplier should have a proven track record and the necessary certifications to perform the work safely and effectively.
- What to Look For:
- Customer reviews and testimonials
- Industry certifications (e.g., ISO, local regulatory compliance)
- Case studies of previous projects similar to yours
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing to a supplier, assess their technical capabilities and resources. This evaluation ensures they can meet your project demands in terms of equipment, manpower, and technology.
- Essential Factors:
- Availability of specialized dredging equipment
- Skilled workforce and training programs
- Capacity to handle large-scale projects or specific environmental challenges
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals outlining their approach to your project. This step is critical for comparing different suppliers and understanding their methodologies.
- Proposal Elements to Analyze:
- Project timelines and milestones
- Cost breakdown, including equipment rental and labor
- Safety measures and environmental impact assessments
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensuring that your chosen supplier possesses the necessary certifications is crucial for compliance and quality assurance. This verification helps mitigate risks associated with environmental and safety standards.
- Key Certifications to Check:
- Environmental protection certifications
- Safety management system certifications
- Local and international dredging regulations compliance
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits
If possible, arrange site visits to the supplier’s operational facilities or previous project sites. Observing their equipment and methods in action provides insights into their operational capabilities and standards.
- What to Observe:
- Condition of equipment and maintenance practices
- Safety protocols in place during dredging operations
- Team’s professionalism and adherence to regulations
Step 7: Negotiate Contract Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the contract terms to ensure clarity and mutual understanding. This final step is vital for outlining responsibilities, payment schedules, and dispute resolution processes.
- Key Contract Elements:
- Clear scope of work and deliverables
- Payment terms and conditions
- Terms for handling unforeseen circumstances or changes in project scope
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for dredging projects with confidence, ensuring they select the best suppliers to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dredging project Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Dredging Projects?
Understanding the cost structure of a dredging project is essential for B2B buyers to budget effectively and make informed decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the costs of fuel, dredging equipment, and any consumables required for the project. The type of dredging (e.g., environmental remediation, coastal protection) will influence material costs significantly.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for operating dredging equipment and managing project logistics. Labor costs can vary based on local wage rates and the complexity of the project.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with the dredging operation, such as facility maintenance, administrative expenses, and utilities. These costs are often factored into the hourly rate charged for dredging services.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment, including dredging vessels and excavation tools, contribute to the overall cost. The need for advanced technology can further increase this expense.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and project specifications requires ongoing quality control measures. QC costs can be a significant portion of the total expenditure.
-
Logistics: Transporting equipment and materials to and from the dredging site can involve substantial logistics costs, particularly for remote locations.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will factor in their profit margins, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Dredging Project Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of dredging projects, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger projects often benefit from economies of scale, resulting in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider bundling multiple projects to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements for dredging equipment or specific project needs can lead to increased costs. Providing clear specifications upfront can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials that meet strict environmental or safety certifications can increase costs. Buyers should assess the long-term benefits of investing in higher-grade materials.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact overall costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Dredging Projects?
To maximize cost efficiency, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Engage in open discussions about project scope and potential cost-saving measures.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on initial pricing, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. This holistic view can prevent long-term financial pitfalls.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Procurement: Different regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, have unique market dynamics and regulatory environments. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local practices and costs to avoid surprises.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: When soliciting bids, ask for itemized quotes that break down costs by component. This transparency will facilitate better comparisons and negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for dredging projects can vary significantly based on geographic location, project specifics, and market conditions. This analysis provides a framework for understanding cost structures and pricing influencers but should not be construed as definitive pricing. Always consult with multiple suppliers and conduct thorough market research to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing for your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing dredging project With Other Solutions
When considering waterway maintenance and environmental restoration, dredging projects are often the go-to solution. However, various alternative methods can also achieve similar outcomes. This analysis will compare dredging with two viable alternatives: sedimentation control systems and environmental restoration through bioremediation. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Dredging Project | Sedimentation Control Systems | Bioremediation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly effective for deep sediment removal and maintaining navigability. | Reduces sediment accumulation but may not fully remove existing buildup. | Targets specific pollutants, improving water quality over time. |
| Cost | High initial investment; operational costs vary based on project scale. | Generally lower setup costs; ongoing maintenance may add to expenses. | Cost-effective for long-term environmental benefits; varies by application. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor; can be logistically complex. | Easier to install with standard equipment; less technical expertise needed. | Requires environmental assessments and specific conditions for effectiveness. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure effectiveness; equipment upkeep can be costly. | Ongoing maintenance is minimal but depends on environmental factors. | Minimal maintenance once established; requires monitoring and potential adjustments. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large-scale projects needing significant sediment removal (e.g., ports, rivers). | Best for managing sediment in smaller areas or preventing further buildup. | Most effective for sites with specific contaminants needing remediation. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Sedimentation Control Systems?
Sedimentation control systems use physical barriers or structures like silt fences, sediment traps, or sediment basins to manage sediment flow. One of the primary advantages of these systems is their lower cost compared to dredging projects. They are relatively easy to implement and maintain, making them suitable for smaller-scale operations or projects with limited budgets. However, these systems may not be as effective in completely removing existing sediment, and their effectiveness can be influenced by environmental conditions such as heavy rainfall or flooding.
How Does Bioremediation Compare to Dredging Projects?
Bioremediation employs natural processes, often involving microorganisms, to degrade or neutralize contaminants in water bodies. This method is particularly effective for addressing specific pollutants and improving overall water quality over time. A significant advantage of bioremediation is its cost-effectiveness in the long run, as it can provide sustained environmental benefits with minimal ongoing maintenance. However, the effectiveness of bioremediation is highly dependent on site conditions and may require extensive environmental assessments before implementation, making it less straightforward than dredging.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between dredging and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific goals of their project, budget constraints, and site conditions. For large-scale sediment removal or restoration projects requiring immediate results, dredging may be the most effective choice. Conversely, for projects focused on long-term sediment management or targeted pollutant remediation, sedimentation control systems or bioremediation could provide viable, cost-effective alternatives. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and limitations of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives and environmental responsibilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dredging project
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Dredging Projects?
Understanding the technical specifications of dredging projects is crucial for B2B buyers involved in procurement or project management. These specifications not only influence project feasibility but also impact cost, timeline, and overall success.
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in dredging equipment and processes. This includes the structural integrity of dredgers, pipelines, and other components, which must withstand varying environmental conditions. High-grade materials ensure durability, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements, thereby lowering long-term operational costs. For buyers, selecting equipment with the right material grade can significantly affect project outcomes, especially in harsh environments.
2. Dredging Depth
Dredging depth is the maximum vertical distance from the water surface to the deepest point that can be dredged. This property is vital for ensuring that waterways are navigable and that sediment removal meets project requirements. It affects the design and selection of dredging equipment, as different dredgers are suited for specific depth ranges. Buyers need to evaluate project specifications carefully to ensure that the chosen dredging equipment can meet the required depth without incurring excessive costs or operational challenges.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the acceptable variation in dredging depth and material removal. High precision is often required in projects such as environmental remediation or underwater infrastructure installation. Tighter tolerances can lead to higher operational costs due to specialized equipment and skilled labor. Buyers must balance the need for precision with budget constraints, understanding that lower tolerance levels may enhance project quality but increase expenses.
4. Flow Rate
Flow rate indicates the volume of material that can be excavated and transported within a specific time frame, usually measured in cubic meters per hour. It is crucial for project scheduling and efficiency. A higher flow rate can expedite project completion but may also require more robust equipment. Buyers should assess flow rate capabilities in relation to project timelines and budget to optimize operational efficiency.
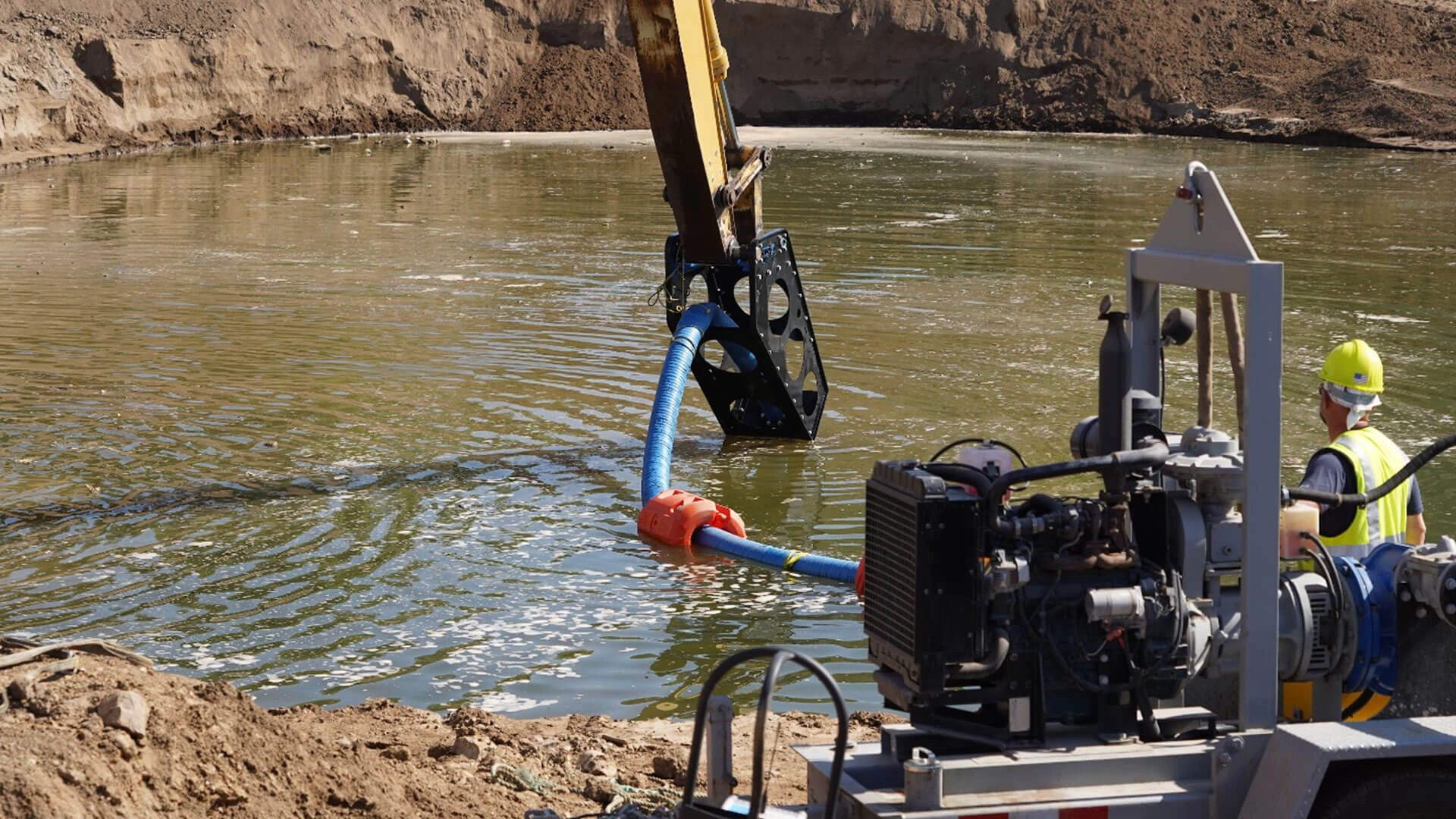

Illustrative image related to dredging project
5. Pump Power
The power of the dredging pump is essential for determining the efficiency of material transport. It influences the distance and height to which dredged material can be moved, directly impacting operational efficiency. Buyers should consider pump power in conjunction with the overall dredging system to ensure that the equipment can handle the specific demands of their projects.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies in Dredging Projects?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in dredging projects. Understanding these terms can enhance decision-making and streamline procurement processes.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In dredging, purchasing from OEMs can assure buyers of quality and compatibility. It is crucial for ensuring that the equipment meets the required specifications and performance standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In dredging, understanding MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers must negotiate MOQ terms to ensure they can meet project needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products or services. In the dredging industry, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare options and negotiate terms effectively. It is a critical step in the procurement process, ensuring transparency and competitiveness.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. In dredging projects, understanding Incoterms is vital for clarifying who is responsible for costs, risks, and logistics at various stages of transportation. This knowledge helps buyers avoid misunderstandings and ensures smooth operations.
5. Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
EIA is a process used to evaluate the potential environmental effects of a proposed project before it commences. In dredging, conducting an EIA is often a regulatory requirement and helps buyers ensure compliance with environmental laws. Understanding EIA can guide project planning and risk management.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of dredging projects more effectively, ensuring better decision-making and successful project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the dredging project Sector
What Are the Key Drivers of the Global Dredging Market?
The global dredging market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by urbanization, infrastructure development, and environmental restoration projects. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are investing heavily in dredging activities to maintain navigable waterways, support coastal development, and restore ecosystems. The increasing demand for clean water sources and sustainable energy solutions further propels the need for dredging, particularly in the construction of lakes and reservoirs.
Emerging technologies are reshaping how dredging projects are executed. Automation and advanced positioning systems enhance precision and efficiency, allowing for more environmentally friendly operations. Digital platforms for project management and equipment rental are becoming increasingly prevalent, providing B2B buyers with real-time data and analytics to make informed decisions. Furthermore, innovations in dredging equipment, such as hybrid systems and eco-friendly dredgers, are gaining traction, reflecting a broader shift towards sustainability.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Trends in Dredging Projects?
Sustainability is a critical consideration in the dredging sector. The environmental impact of dredging activities, including sediment displacement and habitat disruption, necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to environmental regulations and possess certifications for sustainable practices. This includes using ‘green’ materials and technologies that minimize ecological footprints.
Ethical supply chains are becoming non-negotiable for many organizations. Dredging companies are now expected to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through transparent reporting and responsible sourcing of materials. Additionally, partnerships with local communities and adherence to international environmental standards are essential for maintaining a positive corporate reputation. As the industry evolves, buyers should seek out suppliers that not only deliver quality services but also contribute positively to environmental and social outcomes.
What Is the Historical Context of Dredging in the B2B Sector?
The history of dredging dates back centuries, originally employed for agricultural purposes and the construction of canals. Over time, the practice evolved with advancements in technology, leading to the development of specialized dredging equipment. The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, as the demand for navigable waterways and ports surged.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards environmental remediation and sustainability, reflecting a growing awareness of the ecological implications of dredging. Today, the dredging industry is characterized by a commitment to balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship, a trend that is expected to intensify as international regulations become more stringent and public awareness of environmental issues increases.
Conclusion
As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of the dredging market, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The interplay of technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and historical context will shape the future of dredging projects. By leveraging these insights, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals while supporting responsible and sustainable practices in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dredging project
1. How do I determine the right type of dredging project for my needs?
To identify the appropriate dredging project, assess the specific requirements of your site and objectives. Consider factors such as the type of water body (coastal, inland, or lake), the purpose of the dredging (environmental remediation, construction support, or material extraction), and any regulatory compliance issues. Engaging with experienced dredging contractors can provide insights into the best practices and technologies suitable for your project. Additionally, a thorough analysis of the sediment composition and existing environmental conditions is vital for effective planning.
2. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a dredging contractor?
When choosing a dredging contractor, evaluate their experience, technical expertise, and track record in similar projects. Consider their equipment capabilities and whether they can handle the specific demands of your project, such as environmental considerations or material types. Additionally, verify their certifications, safety records, and compliance with international and local regulations. Request references and case studies to assess their performance. A contractor with strong logistical support and local knowledge can also enhance project efficiency.
3. What are the typical payment terms for international dredging projects?
Payment terms for international dredging projects can vary widely based on the contractor, project size, and location. Typically, terms may involve an upfront deposit (often 10-30%), followed by progress payments tied to project milestones, and a final payment upon completion. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timeline. Always clarify the currency of transactions, potential taxes, and any additional fees related to international trade to avoid misunderstandings.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
4. How can I ensure the quality assurance of dredging materials?
To ensure quality assurance in dredging projects, establish clear specifications and standards for the materials being removed or deposited. Collaborate with your contractor to implement a quality control plan that includes regular testing and inspection of sediments. Consider employing third-party environmental consultants to conduct independent assessments. Additionally, request documentation of the dredging process, such as logs and reports, to maintain transparency and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
5. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international dredging projects?
Logistics play a crucial role in the success of international dredging projects. Key considerations include the transportation of dredging equipment to the project site, local infrastructure capabilities, and the availability of support services. Assess the proximity to ports for shipping and the accessibility of the worksite for heavy machinery. Additionally, ensure compliance with local customs regulations and import/export requirements to avoid delays. A well-planned logistics strategy can mitigate risks and enhance project timelines.
6. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for dredging equipment rentals?
Minimum order quantities for dredging equipment rentals vary by supplier and project scope. Some companies may have no MOQ, while others may require a minimum rental period based on equipment type and usage. It’s essential to discuss your project needs with potential suppliers to understand their policies. Customizing rental agreements for specific project durations and equipment types can often lead to more favorable terms, ensuring you get the right equipment without unnecessary costs.
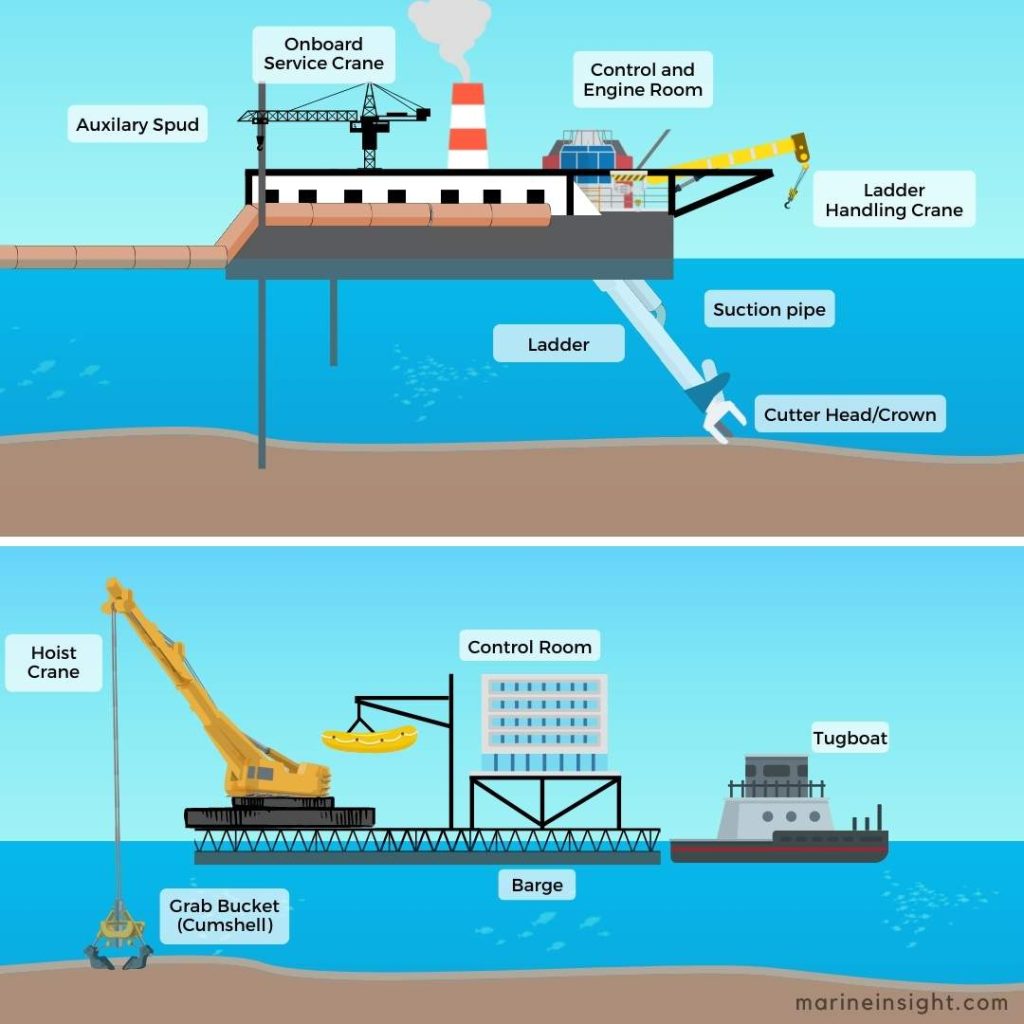
Illustrative image related to dredging project
7. How can I vet potential suppliers for dredging projects?
To effectively vet potential suppliers for dredging projects, conduct thorough research on their background, including years in business, project history, and customer reviews. Request references from past clients to gauge their reliability and performance. Evaluate their certifications, safety protocols, and compliance with local and international standards. Additionally, assess their financial stability, which can be indicative of their ability to fulfill contract obligations. A personal meeting or site visit can also provide valuable insights into their operational capabilities.
8. What are the environmental considerations in dredging projects?
Environmental considerations are paramount in dredging projects to minimize ecological impact. Conduct environmental assessments to identify sensitive areas and potential impacts on local habitats. Implement best management practices, such as sediment control measures, to reduce turbidity and protect aquatic life. Engage with local environmental authorities to ensure compliance with regulations and obtain necessary permits. Transparency with stakeholders, including local communities, can foster trust and cooperation throughout the project.
Top 4 Dredging Project Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. USDredge – Environmental Dredging Solutions
Domain: usdredge.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. Environmental Remediation Dredging: Targets and extracts harmful materials from waterways to clean up the environment. 2. Coastal Protection Dredging: Involves beach re-nourishment and construction of dikes to protect coastal areas from degradation. 3. Offshore Trenching Dredging: Excavates precise trenches for underwater infrastructure like pipelines and power cables, ensuring their protection…
2. USACE – Dredging Services
Domain: sam.usace.army.mil
Introduction: Dredging is essential for maintaining navigation channels for ships, involving underwater excavation to keep ports accessible. It includes initial excavation and periodic maintenance dredging to remove sediments. Over 400 ports and 25,000 miles of navigation channels are dredged in the U.S. annually. Dredged materials vary by location: main approaches (sand), bar channels (coarse-grained sand), en…
3. Quoddy Tides – Cruise Ship Dredging Project
Domain: quoddytides.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Proposed dredging project off Eastport breakwater to accommodate larger cruise ships; current docking limit is 800 feet, dredging would allow ships up to 1,100 feet; environmental assessment to be conducted before proceeding; estimated cost for survey and testing is $100,000; potential completion of study in 2026 and dredging in 2027; increased fees for cruise ship passengers to $10; dockage fee o…
4. Royal IHC – Dredging Solutions
Domain: royalihc.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Dredging is the removal of underwater soil, such as sand or gravel, and its transport. It is essential for various applications including channel and port maintenance, construction or deepening, coastal protection, land reclamation, mining, offshore works, and environmental improvement. Key factors in dredging projects include the volume of soil to be dredged, soil characteristics (type and grain …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dredging project
In the ever-evolving landscape of dredging projects, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for success. By understanding the diverse types of dredging—ranging from environmental remediation to coastal protection—international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project needs. Emphasizing the importance of selecting the right dredging equipment and services not only enhances project efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with environmental impact and operational delays.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
Moreover, engaging with reliable dredging partners ensures access to the latest technologies and expertise, ultimately leading to cost-effective solutions. As the global demand for dredging continues to rise, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a significant opportunity for businesses to capitalize on this trend.
Looking ahead, the future of dredging projects will be shaped by advancements in technology and an increasing focus on sustainability. Companies that prioritize strategic sourcing will be better positioned to navigate these changes and drive value in their operations. Now is the time for international buyers to forge partnerships that not only meet immediate project requirements but also support long-term goals in a dynamic industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to dredging project
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.