Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vulcanising rubber
Navigating the complexities of sourcing vulcanising rubber can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly demand high-performance materials, understanding the nuances of vulcanised rubber—known for its superior strength, elasticity, and durability—becomes essential. This comprehensive guide equips businesses with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions, covering the various types of vulcanising rubber, their diverse applications across sectors, and critical supplier vetting processes.
Buyers will gain valuable knowledge on factors influencing cost, the significance of sourcing from reputable manufacturers, and the importance of quality assurance in the vulcanisation process. Additionally, this guide highlights the latest trends in the global rubber market, addressing the specific needs and preferences of buyers from different regions, including emerging markets and established economies like Vietnam and Germany.
By synthesizing expert insights and actionable strategies, this guide aims to empower B2B buyers to navigate the global market confidently, ensuring that their sourcing decisions align with both their operational requirements and sustainability goals. With a thorough understanding of vulcanised rubber and its potential applications, businesses can enhance their product offerings and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Vulcanising Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vulcanising rubber
- Understanding vulcanising rubber Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vulcanising rubber
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vulcanising rubber’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vulcanising rubber
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vulcanising rubber
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vulcanising rubber’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vulcanising rubber Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vulcanising rubber With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vulcanising rubber
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vulcanising rubber Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vulcanising rubber
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vulcanising rubber
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding vulcanising rubber Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber Vulcanizate | Derived from rubber tree latex; excellent elasticity and tensile strength | Automotive tires, footwear, gaskets | Pros: High elasticity, good abrasion resistance. Cons: Susceptible to ozone and UV degradation. |
| Synthetic Rubber (SBR) | Made from petroleum by-products; offers better resistance to heat and aging | Tires, conveyor belts, seals | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Lower elasticity than natural rubber. |
| EPDM Rubber | Ethylene propylene diene monomer; excellent weather resistance and durability | Roofing membranes, automotive seals | Pros: Superior weather resistance, low-temperature flexibility. Cons: Poor oil and solvent resistance. |
| Neoprene Rubber | Synthetic rubber with good chemical stability; resistant to oils and solvents | Industrial applications, wetsuits | Pros: Versatile, good chemical resistance. Cons: Limited temperature range compared to others. |
| Silicone Rubber | High-temperature resistance, excellent flexibility; can withstand extreme conditions | Medical devices, automotive applications | Pros: Exceptional temperature stability, biocompatibility. Cons: Higher cost, lower tensile strength than other types. |
What Are the Characteristics of Natural Rubber Vulcanizate?
Natural rubber vulcanizate is derived from the latex of rubber trees, specifically Hevea brasiliensis. This type of vulcanized rubber is known for its excellent elasticity and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications where flexibility and durability are crucial, such as automotive tires and footwear. When considering procurement, buyers should note that while natural rubber offers superior performance in terms of stretch and resilience, it is more susceptible to environmental factors like ozone and UV degradation. This necessitates careful consideration of the application environment.
How Does Synthetic Rubber (SBR) Compare in Terms of Performance?
Synthetic rubber, particularly styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), is a popular choice in various industries due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. It is primarily used in tires, conveyor belts, and seals. While SBR does not match the elasticity of natural rubber, it provides excellent resistance to aging, heat, and wear, making it suitable for high-stress applications. Buyers should weigh the lower elasticity against the benefits of longevity and cost savings, especially in applications where performance over time is crucial.
What Makes EPDM Rubber a Preferred Choice for Outdoor Applications?
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is distinguished by its exceptional weather resistance and durability, making it an excellent choice for outdoor applications such as roofing membranes and automotive seals. This type of vulcanized rubber can withstand extreme temperatures and UV exposure without degrading. Buyers should consider EPDM for applications requiring long-term outdoor exposure, but they must also be aware of its limitations regarding oil and solvent resistance, which may restrict its use in certain industrial settings.
In What Situations is Neoprene Rubber Most Effective?
Neoprene rubber is recognized for its good chemical stability and resistance to oils and solvents, making it a suitable option for industrial applications and products like wetsuits. Its versatility allows it to be used in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is a concern. However, buyers should note that neoprene has a limited temperature range compared to other types of vulcanized rubber. When selecting neoprene, it is essential to evaluate the specific chemical exposure and temperature conditions to ensure optimal performance.
Why Should Buyers Consider Silicone Rubber for Specialized Applications?
Silicone rubber stands out due to its high-temperature resistance and exceptional flexibility, making it ideal for specialized applications, including medical devices and automotive components. Its ability to maintain performance in extreme conditions is a significant advantage. However, buyers must consider the higher cost associated with silicone rubber compared to other types. Additionally, while it excels in temperature stability, silicone may have lower tensile strength, which could impact its suitability for certain high-stress applications.
Key Industrial Applications of vulcanising rubber
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vulcanising rubber | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Tires and Seals | Enhanced durability and performance under extreme conditions | Quality certifications, resistance to wear, and compliance with local regulations |
| Construction | Gaskets and Seals for HVAC systems | Improved energy efficiency and reduced leakage | Material compatibility, temperature resistance, and durability under pressure |
| Consumer Goods | Footwear and Sporting Equipment | Increased comfort and longevity of products | Customization options, aesthetic appeal, and environmental impact considerations |
| Aerospace | Engine Components and Seals | High performance and reliability in critical applications | Aerospace-grade certifications, resistance to extreme temperatures, and fatigue durability |
| Industrial Machinery | Conveyor Belts and Vibration Dampers | Increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Sourcing from reputable suppliers, material specifications, and performance testing |
How is Vulcanizing Rubber Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, vulcanizing rubber is primarily utilized in the production of tires and seals. The vulcanization process enhances the rubber’s strength, elasticity, and durability, making it capable of withstanding various environmental conditions and mechanical stresses. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality vulcanized rubber is crucial to ensure performance and safety standards are met. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding tire specifications and environmental impact when sourcing these materials.
What Role Does Vulcanizing Rubber Play in Construction?
In construction, vulcanized rubber is extensively used for gaskets and seals, particularly in HVAC systems. These components are essential for preventing air leaks, thus improving energy efficiency and comfort within buildings. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is vital to source materials that meet stringent building codes and standards. Additionally, considerations such as temperature resistance and compatibility with various construction materials are critical for ensuring long-lasting performance.
How is Vulcanizing Rubber Beneficial for Consumer Goods?
The consumer goods industry leverages vulcanizing rubber in products like footwear and sporting equipment. The enhanced elasticity and durability of vulcanized rubber contribute to improved comfort and longevity, appealing to consumers seeking quality. Buyers from regions like Germany and Vietnam should focus on customization options and aesthetic qualities, as well as the environmental impact of the rubber sourcing process. Ensuring compliance with international safety standards is also essential for market acceptance.
Why is Vulcanizing Rubber Important in Aerospace?
In aerospace applications, vulcanized rubber is critical for manufacturing engine components and seals. The high-performance characteristics of vulcanized rubber, including its ability to endure extreme temperatures and pressures, make it indispensable for safety and reliability in flight. International buyers must prioritize suppliers with aerospace-grade certifications and proven track records in high-stress environments to ensure compliance with stringent industry regulations.

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
How Does Vulcanizing Rubber Enhance Industrial Machinery?
Vulcanized rubber is widely used in industrial machinery for applications like conveyor belts and vibration dampers. The enhanced durability and resistance to wear significantly increase operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from reputable suppliers who can provide detailed material specifications and performance testing results to ensure that the rubber meets the specific operational demands of their machinery.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vulcanising rubber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Quality in Vulcanized Rubber Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the inconsistency of vulcanized rubber products, which can lead to significant quality control issues. Variations in the vulcanization process—such as temperature fluctuations, incorrect sulfur ratios, and inadequate mixing of additives—can result in rubber that is either too brittle or excessively soft. This inconsistency can affect the durability and performance of final products, leading to increased returns and damaged reputations in the marketplace.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality in vulcanized rubber, buyers should prioritize working with suppliers that provide comprehensive technical specifications and quality assurance protocols. Implementing a standardized vulcanization process is crucial. This includes using precise measurements of sulfur and accelerators, maintaining strict temperature controls, and employing automated mixing technologies to ensure uniformity. Additionally, buyers should request samples and conduct rigorous testing for elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance before committing to larger orders. By establishing quality benchmarks and collaborating closely with suppliers on process optimization, manufacturers can significantly reduce variability and enhance product reliability.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Vulcanization Processes
The Problem: Many companies are challenged by high production costs linked to inefficient vulcanization processes. Inefficiencies can arise from outdated machinery, inadequate training of personnel, or poor selection of raw materials. These factors can lead to prolonged production times and increased waste, ultimately affecting the bottom line and competitive positioning in the market.
The Solution: Buyers can tackle high production costs by investing in advanced vulcanization equipment that enhances efficiency and minimizes waste. Opting for modern curing ovens with better temperature control and faster heating times can lead to more effective vulcanization and reduced energy costs. Furthermore, training staff on best practices and the latest vulcanization techniques can improve overall efficiency. Establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide high-quality raw materials—such as specialized sulfur compounds and accelerators—will also ensure that the vulcanization process is optimized for cost-effectiveness. Regular audits of production processes can help identify and eliminate bottlenecks, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
Scenario 3: Limited Knowledge of Material Compatibility for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the right type of vulcanized rubber for specific applications due to a lack of understanding of material compatibility. This can result in using rubber that is unsuitable for the intended environment—whether it be exposure to extreme temperatures, chemicals, or mechanical stress—leading to premature failure of products and costly re-engineering efforts.

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
The Solution: To address the challenge of material compatibility, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of the specific requirements for each application. This includes analyzing environmental conditions, such as exposure to chemicals, UV light, or extreme temperatures. Collaborating with suppliers who have expertise in elastomer chemistry can provide invaluable insights into the best types of vulcanized rubber for particular applications. Buyers should also consider engaging in joint testing programs with their suppliers to evaluate how different formulations perform under expected operational conditions. By leveraging technical data sheets and conducting real-world performance tests, companies can make informed decisions that enhance product longevity and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vulcanising rubber
When selecting materials for vulcanizing rubber, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of various elastomers and additives. This knowledge helps international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific applications and regional compliance requirements. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the vulcanization process.
What Are the Key Properties of Natural Rubber in Vulcanization?
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of rubber trees, is known for its excellent elasticity and tensile strength. It typically has a temperature rating of -40°C to 100°C and is resistant to abrasion. However, it has limited resistance to UV light and ozone, which can lead to degradation over time.
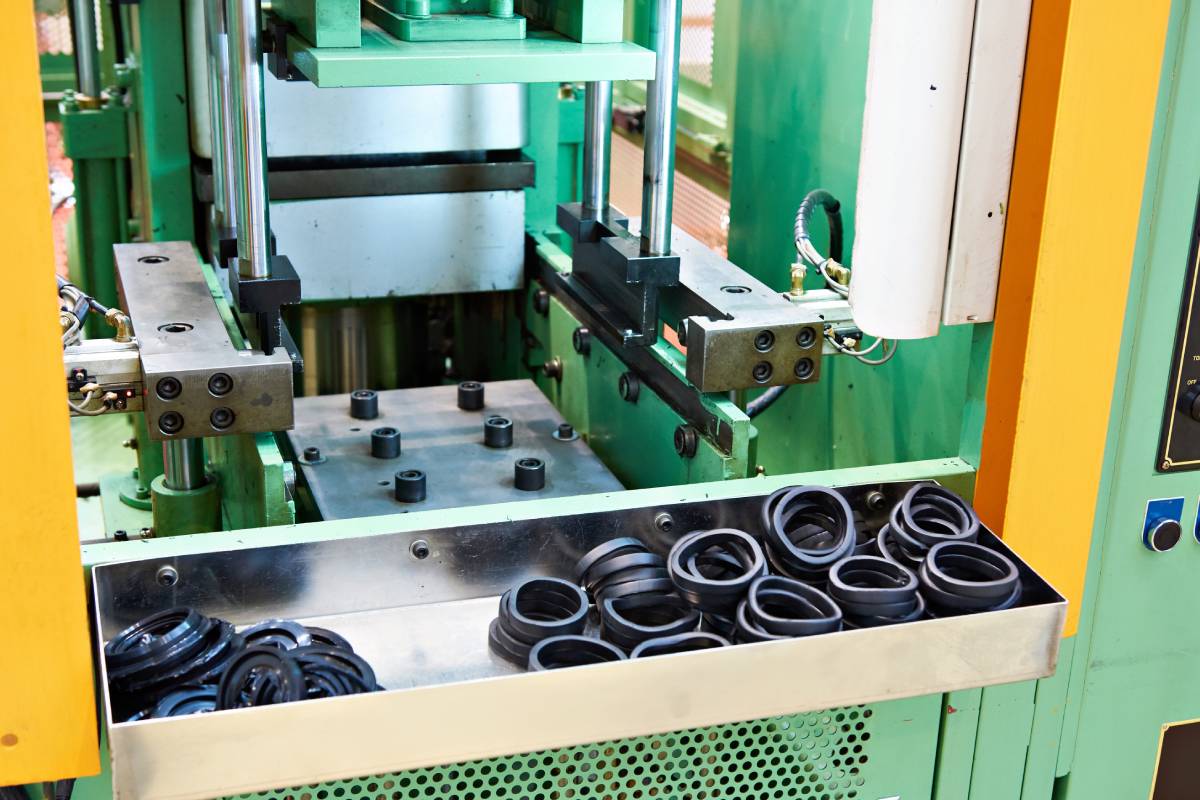

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
Pros: Natural rubber is cost-effective and offers superior elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for applications like tires and seals.
Cons: Its susceptibility to environmental factors and lower thermal stability compared to synthetic alternatives can limit its use in harsh conditions.
Impact on Application: Natural rubber is best suited for applications requiring flexibility and elasticity but may not be ideal for environments with significant UV exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with regional standards such as ASTM D2000 and ISO 9001, which govern the quality and performance of natural rubber products.
How Does Synthetic Rubber Compare in Terms of Performance?
Synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), offers enhanced resistance to heat, aging, and chemicals. SBR can withstand temperatures from -40°C to 120°C, while EPDM performs well in extreme temperatures, ranging from -50°C to 150°C.
Pros: These materials are highly durable, resistant to ozone and UV light, and versatile for various applications, including automotive parts and industrial seals.
Cons: The manufacturing process for synthetic rubber can be more complex and costly than that for natural rubber.
Impact on Application: Synthetic rubber is suitable for applications requiring high durability and resistance to harsh chemicals, making it a preferred choice in industrial settings.

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations and standards, such as DIN and JIS, which may dictate specific performance criteria for synthetic rubber products.
What Role Do Additives Play in Enhancing Vulcanized Rubber?
Additives like sulfur, accelerators, and fillers are crucial in the vulcanization process. Sulfur is the primary agent that creates cross-links between polymer chains, enhancing strength and elasticity. Common accelerators include zinc oxide and thiazoles, which speed up the vulcanization process.
Pros: Additives can significantly improve the mechanical properties of vulcanized rubber, such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
Cons: The choice and quantity of additives can complicate the manufacturing process and may increase costs.
Impact on Application: The right combination of additives can tailor the rubber’s properties for specific applications, such as automotive tires or industrial gaskets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the compatibility of additives with local regulations, including REACH in Europe, which governs chemical safety.
How Do Fillers Affect the Cost and Performance of Vulcanized Rubber?
Fillers, such as carbon black and silica, are often added to vulcanized rubber to enhance its strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Carbon black can improve tensile strength and abrasion resistance, while silica can enhance thermal stability.
Pros: Fillers can reduce production costs and improve the overall performance of vulcanized rubber.
Cons: Overuse of fillers can lead to a decrease in elasticity and flexibility, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Fillers are essential for applications requiring high wear resistance, such as conveyor belts and tires.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the fillers used comply with international standards such as ASTM D624 and ISO 4649.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Vulcanizing Rubber
| Material | Typical Use Case for vulcanising rubber | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Tires, seals, gaskets | Excellent elasticity and resilience | Susceptible to UV and ozone damage | Low |
| Synthetic Rubber (SBR/EPDM) | Automotive parts, industrial seals | High durability and chemical resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Additives (Sulfur, Accelerators) | Custom formulations for various applications | Enhanced mechanical properties | Increased manufacturing costs | Medium |
| Fillers (Carbon Black, Silica) | Conveyor belts, tires | Improved strength and wear resistance | Can reduce elasticity | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials used in vulcanizing rubber, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vulcanising rubber
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Vulcanized Rubber?
The manufacturing of vulcanized rubber is a complex process that involves several critical stages, each designed to enhance the material’s properties and ensure its suitability for various applications. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Vulcanization?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves the preparation of raw materials. This typically includes both natural and synthetic rubber, which are sourced from reliable suppliers. The rubber is then mixed with specific additives, including sulfur, accelerators, and fillers, to enhance its properties. The proportions of these components are crucial; for instance, sulfur is generally used in concentrations ranging from 5% to 30%, depending on the desired characteristics of the final product.
During this stage, additives such as zinc oxide and stearic acid are also included to facilitate the vulcanization process. The mixing must be done under controlled conditions to ensure uniform distribution of the ingredients. This stage often employs advanced machinery, such as internal mixers or banbury mixers, to achieve a homogeneous mixture.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process?
Once the rubber mixture is prepared, the next step is the forming process. This involves shaping the rubber into its intended form, which can vary widely depending on the final application. Common techniques include extrusion, molding, and calendering.
-
Extrusion: This technique involves forcing the rubber through a die to create continuous shapes, such as hoses or seals. The extruded rubber is then cut to the required lengths.
-
Molding: In this method, rubber is placed into a mold and subjected to heat and pressure. This is particularly common for products like tires and gaskets. The molds are typically made from steel or aluminum and designed to withstand high temperatures during vulcanization.
-
Calendering: This technique is used to produce flat sheets of rubber, which can later be cut and shaped into specific products.
Each method has its own advantages and is chosen based on the product requirements, production volume, and cost considerations.
How Is Assembly and Finishing Achieved?
After forming, the rubber components may undergo assembly, especially for products that require multiple parts. For instance, tires have several components that must be assembled before final vulcanization.
The finishing stage includes surface treatment and inspection to ensure that the rubber products meet quality standards. This may involve trimming excess material, applying coatings, or performing additional treatments to enhance durability and appearance.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Vulcanized Rubber?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for vulcanized rubber. International and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining product quality.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most widely recognized quality management standards applicable to various industries, including rubber manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have a robust quality management system in place, focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
In addition to ISO standards, specific certifications may be required based on the application of the rubber products. For example, products intended for automotive applications may need to meet the requirements set forth by the American Petroleum Institute (API) or the European Union’s CE marking for products sold within Europe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process. Ensuring the quality of inputs is crucial for maintaining overall product quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This is conducted during various stages of production. IPQC helps identify any deviations from quality standards early in the manufacturing process, allowing for corrective actions before the final product is completed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This is the last step before the product is shipped to customers. FQC involves comprehensive testing and inspection of the finished products against predefined specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in QC for Vulcanized Rubber?
Testing methods are essential for verifying the quality and performance of vulcanized rubber. Common testing techniques include:

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
-
Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the rubber’s ability to withstand tension without breaking.
-
Elongation Testing: Assesses how much the rubber can stretch before it deforms permanently.
-
Hardness Testing: Determines the hardness of the rubber, which is critical for applications requiring specific physical properties.
-
Abrasion Resistance Testing: Evaluates the rubber’s resistance to wear and tear, crucial for products like tires that experience significant friction.
These tests are often conducted according to international standards, ensuring that the results are reliable and comparable across different manufacturers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to high-quality standards is vital. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can include reviewing their quality management systems and production capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s performance over time, including any issues encountered and how they were resolved.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s products and processes. This is particularly valuable for buyers sourcing products internationally, as it helps mitigate risks associated with quality discrepancies.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When sourcing vulcanized rubber products from international suppliers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of the following nuances:
Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding rubber products, especially those used in automotive and industrial applications. Understanding these regulations can help buyers avoid compliance issues.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across cultures. Being sensitive to these differences can foster better relationships with suppliers.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International shipping can introduce additional complexities, including customs regulations and shipping times. Establishing clear logistics plans and understanding the supplier’s capabilities in this area is essential for smooth operations.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for vulcanizing rubber are multifaceted and require careful consideration by B2B buyers. By understanding these processes and implementing effective verification strategies, buyers can ensure they source high-quality vulcanized rubber products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vulcanising rubber’
The purpose of this guide is to provide B2B buyers with a practical checklist for sourcing vulcanizing rubber. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right materials and suppliers to meet their production needs, ultimately enhancing product quality and operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly define the technical requirements of the vulcanized rubber you need. This includes understanding the type of rubber (natural vs. synthetic), the specific properties required (e.g., tensile strength, elasticity, heat resistance), and the intended application (such as automotive, industrial, or consumer products).
– Key Considerations: Identify the environmental factors the rubber will face, such as temperature extremes or chemical exposure.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in vulcanized rubber. Focus on companies that have a proven track record in your specific industry or application.
– Important Factors: Look for suppliers with certifications (like ISO) and positive reviews or testimonials from previous clients. This can indicate reliability and product quality.
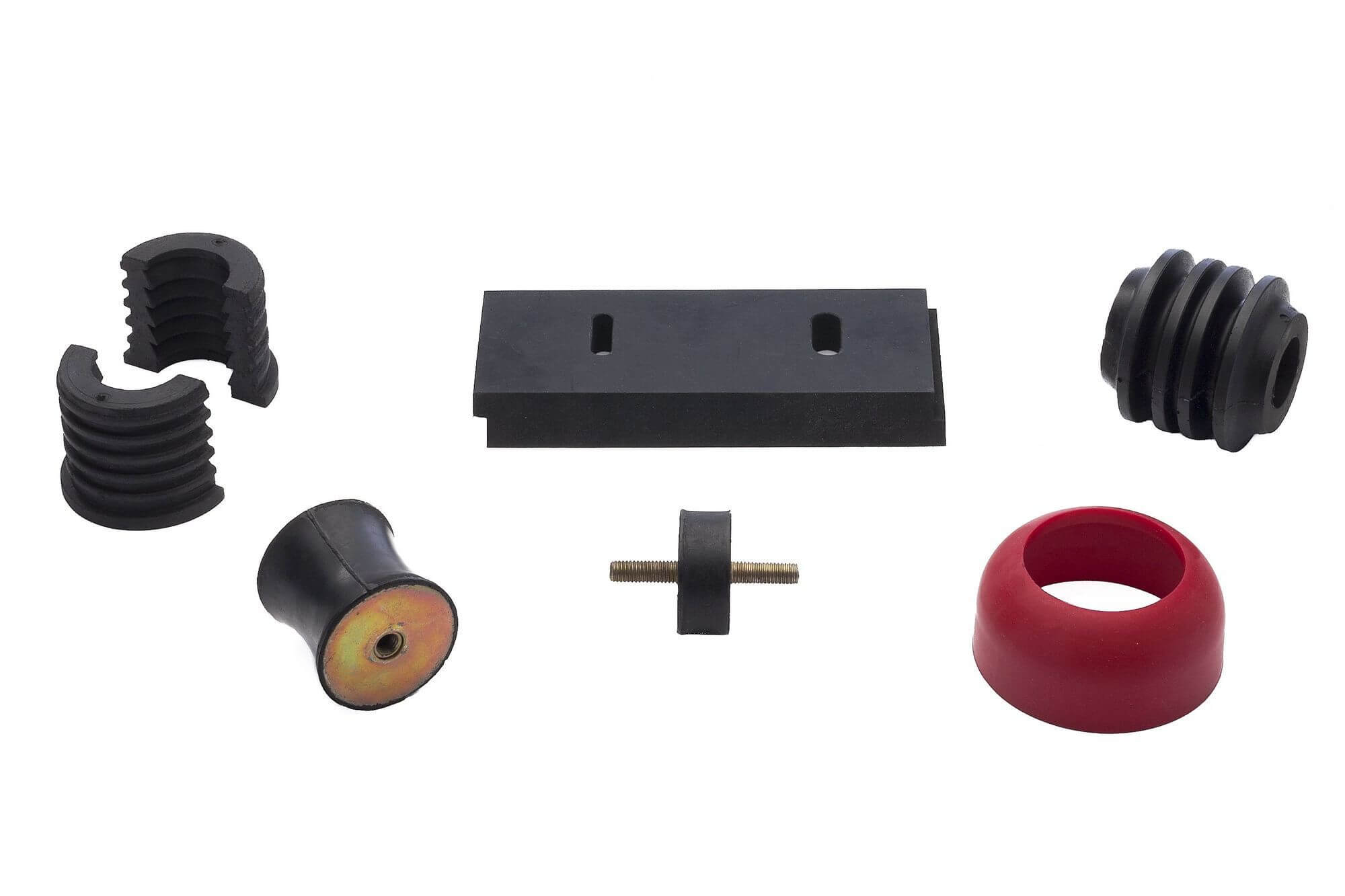

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the technical capabilities of potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. This includes evaluating their manufacturing processes, technology used, and capacity to handle your order volume.
– Specific Details: Inquire about their vulcanization methods and any proprietary technologies that enhance product performance.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the vulcanized rubber to evaluate its properties and performance. Testing the samples in your production environment can help you gauge compatibility and effectiveness.
– Testing Parameters: Consider performing tests for durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear, which are critical for ensuring product longevity.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the vulcanized rubber meets relevant industry standards and regulations in your region. This is particularly crucial for industries like automotive and healthcare, where compliance can impact safety and performance.
– Documentation Needed: Request documentation proving compliance with regulations such as REACH or RoHS, depending on your market requirements.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms. Clear agreements on these points can prevent misunderstandings later in the process.
– Considerations: Discuss bulk order discounts, lead times, and potential penalties for late deliveries to safeguard your supply chain.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the quality of the vulcanized rubber you receive. This can involve regular inspections, testing of batches upon arrival, and feedback mechanisms with your supplier.
– Continuous Improvement: Establish a collaborative relationship with your supplier to address any quality issues promptly, ensuring continuous improvement in material performance.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement process for vulcanizing rubber, ensuring that they source materials that meet their technical specifications and business needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vulcanising rubber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Vulcanizing Rubber Sourcing?
When sourcing vulcanized rubber, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The core material for vulcanized rubber is either natural or synthetic rubber, often mixed with sulfur and various additives such as accelerators and fillers. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on global supply and demand, particularly influenced by oil prices for synthetic rubber.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as some in Africa and South America, manufacturers may benefit from reduced overheads. Conversely, in regions like Europe, labor costs are higher, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory operations. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, which can vary by supplier.
-
Tooling: Custom molds and tooling can be expensive. The initial investment in tooling is often spread over large production volumes, making it more economical for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of vulcanized rubber is crucial, particularly for applications in automotive and industrial sectors. QC processes, including testing and certification, add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can be substantial, especially for international shipping. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and tariffs must be considered in the cost analysis.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Vulcanized Rubber Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of vulcanized rubber, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often lead to reduced unit prices. Suppliers are more inclined to offer discounts for larger quantities, which can significantly lower the overall cost per unit.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products tailored to specific applications typically incur higher costs due to the additional resources required for development and production. Standardized products, on the other hand, are more cost-effective.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the quality certifications required (e.g., ISO or ASTM) can impact prices. Higher-quality materials or certifications often come at a premium but can yield better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their track record, while new entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The shipping terms agreed upon between the buyer and seller (Incoterms) can significantly influence pricing. Understanding responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs is essential to avoid unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Practices for B2B Buyers Negotiating Vulcanized Rubber Pricing?
B2B buyers must adopt strategic approaches to ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing vulcanized rubber.
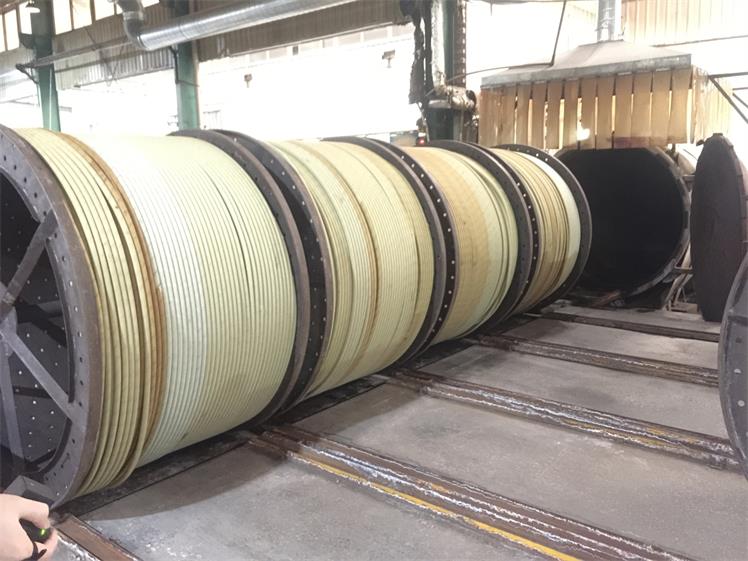

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
-
Negotiation Tactics: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures and be willing to negotiate terms. Understanding the supplier’s cost drivers can empower buyers in negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, potential downtime, and disposal costs. A lower upfront price may result in higher long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, it is crucial to factor in currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions. In regions like Europe, additional regulations may also influence pricing.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market rates and help in making informed decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on numerous factors including market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and regional economic conditions. Always consult multiple sources and conduct thorough research to ensure accurate budgeting for vulcanized rubber sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vulcanising rubber With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Vulcanising Rubber
In the realm of manufacturing and product design, selecting the right material is crucial. Vulcanising rubber is widely known for its superior strength and elasticity, but other solutions exist that may better suit specific applications or budget constraints. This analysis compares vulcanising rubber with two viable alternatives: polyurethane and thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Vulcanising Rubber | Polyurethane | Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, excellent elasticity, abrasion-resistant | Very good durability, excellent abrasion resistance, versatile | Good elasticity, lower strength compared to vulcanised rubber |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate | Generally lower than vulcanised rubber |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires complex processes and specialized equipment | Easier to process, can be molded and cast | Simple processing, can be injection molded |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but long-term performance can depend on environmental factors | Low maintenance; resistant to wear and tear | Low maintenance, but can be sensitive to heat and UV exposure |
| Best Use Case | High-stress applications like tires, seals, and gaskets | Applications needing flexibility and durability like wheels and coatings | Consumer products, automotive parts, and medical devices |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyurethane?
Polyurethane is a versatile material known for its durability and flexibility. It performs well in applications requiring both strength and elasticity, making it suitable for items like wheels, seals, and coatings. The processing of polyurethane is less complex than that of vulcanised rubber, allowing manufacturers to use simpler molding techniques. However, while it provides excellent abrasion resistance, its performance can degrade under extreme temperatures or prolonged exposure to moisture. Additionally, the cost of polyurethane can be moderate, making it a cost-effective alternative for many applications.
What Makes Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs) a Worthy Alternative?
Thermoplastic elastomers combine the properties of rubber with the processing advantages of thermoplastics. TPEs offer good elasticity and can be easily molded, making them ideal for consumer products, automotive parts, and medical devices. Their lower cost compared to vulcanised rubber can be appealing for budget-conscious manufacturers. However, TPEs generally do not match the strength and abrasion resistance of vulcanised rubber, which may limit their use in high-stress environments. Additionally, TPEs can be sensitive to heat and UV exposure, necessitating careful consideration of their application.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When deciding between vulcanising rubber and its alternatives, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and processing capabilities. Vulcanising rubber excels in high-stress environments where strength and elasticity are paramount, while polyurethane and TPEs offer flexibility and cost savings for less demanding applications. By understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each material, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and product specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vulcanising rubber
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Vulcanizing Rubber?
When evaluating vulcanized rubber for industrial applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial. Here are some essential specifications that buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of rubber based on its composition and intended use. Common grades include natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). Each grade has unique properties suited for specific applications. For instance, SBR is often used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent wear resistance. Choosing the appropriate material grade ensures that the rubber meets performance requirements, reduces product failure rates, and enhances overall durability.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of stress a material can withstand while being stretched before breaking. For vulcanized rubber, tensile strength typically ranges from 10 to 25 MPa, depending on the formulation. High tensile strength is vital for applications subjected to heavy loads, such as automotive parts and industrial machinery. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers ensure that the rubber can endure operational stresses without compromising integrity.
3. Elongation at Break
Elongation at break indicates how much a rubber material can be stretched before it ruptures, usually expressed as a percentage. Vulcanized rubber typically exhibits elongation values between 300% to 700%. This property is critical for applications requiring flexibility and resilience, such as seals and gaskets. Buyers should prioritize materials with high elongation to ensure components can withstand dynamic movements and thermal expansion.
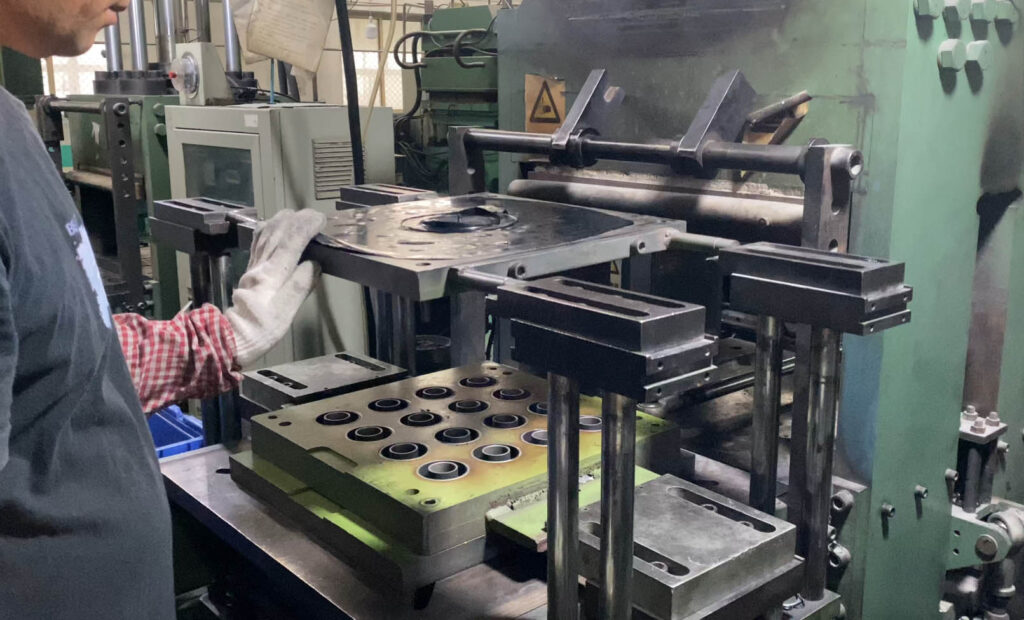

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
4. Hardness
Hardness, measured on the Shore A scale, reflects the rubber’s resistance to indentation. Vulcanized rubber typically ranges from 30 to 90 Shore A, with softer rubber being more flexible and harder rubber offering greater durability. The hardness level is significant in applications where specific surface characteristics are needed, such as in automotive tires or anti-vibration mounts. Buyers must match hardness to the intended application to optimize performance.
5. Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is a measure of how well a material can withstand wear due to friction. Vulcanized rubber generally exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to unvulcanized rubber. This property is crucial in applications exposed to continuous movement and contact, such as conveyor belts and flooring. Understanding abrasion resistance can help buyers select materials that will last longer and reduce maintenance costs.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in the Vulcanizing Rubber Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
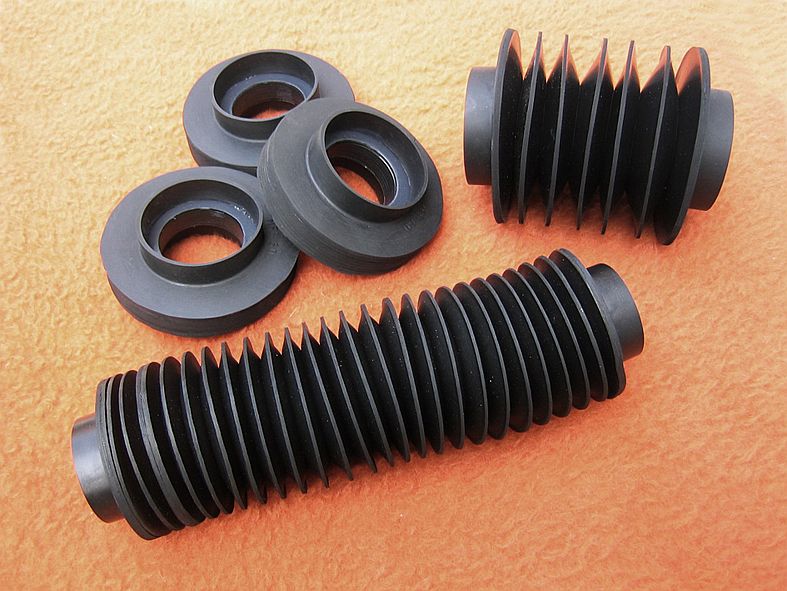

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of vulcanized rubber, OEMs often require custom rubber components for their products. Understanding OEM specifications ensures that buyers receive materials compatible with existing manufacturing processes.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the rubber industry, MOQs can vary significantly based on the product type and customization level. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory effectively and negotiate better pricing based on order volume.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price proposals for specific products or services. Including detailed specifications for vulcanized rubber in an RFQ allows suppliers to provide accurate quotes. This process is essential for budgeting and comparing offers from multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of international sales terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For vulcanized rubber, understanding Incoterms is vital for determining shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can streamline logistics and reduce disputes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring vulcanized rubber, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vulcanising rubber Sector
What are the Key Drivers Shaping the Vulcanizing Rubber Market?
The vulcanizing rubber market is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for durable and high-performance materials across industries such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods. With the rise in vehicle production, particularly in emerging markets in Africa and South America, the demand for vulcanized rubber in tires and seals is surging. Additionally, the growth of e-commerce and logistics sectors is amplifying the need for robust packaging solutions, further enhancing the market potential.
Technological advancements are also reshaping sourcing trends. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is facilitating improved quality control and supply chain efficiency. B2B buyers are increasingly leaning towards suppliers who can offer real-time data analytics and transparent sourcing processes. Furthermore, as companies strive to enhance operational efficiency, there is a growing trend towards strategic partnerships and long-term contracts with reliable suppliers to mitigate risks associated with fluctuating raw material prices.
How are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Vulcanizing Rubber Industry?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the vulcanizing rubber sector, with buyers increasingly prioritizing environmentally responsible practices. The vulcanization process itself has environmental implications, particularly due to the use of sulfur and other chemicals. Consequently, there is a rising demand for “green” certifications and materials, such as eco-friendly synthetic rubbers that minimize environmental impact.
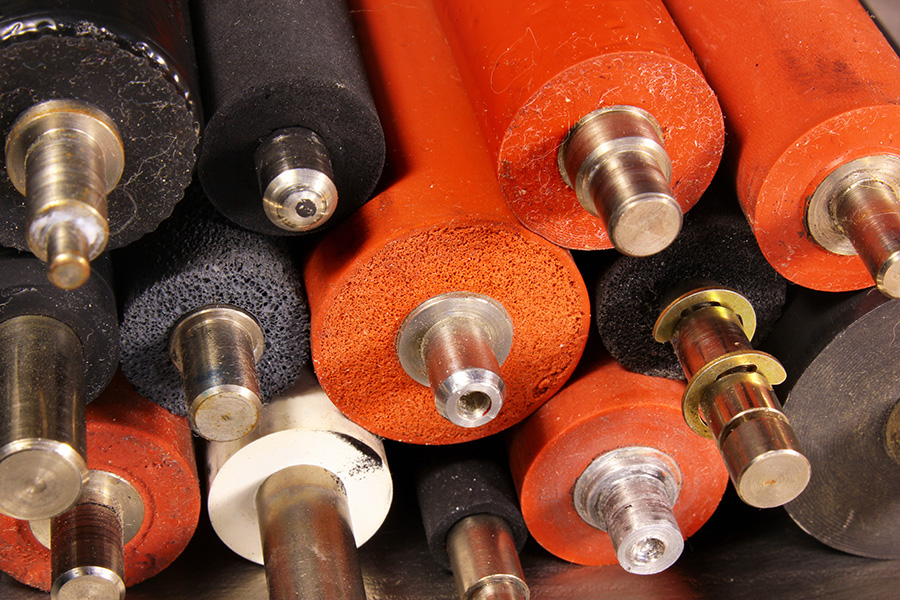

Illustrative image related to vulcanising rubber
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek transparency in their supply chains to ensure fair labor practices and sustainable sourcing of raw materials. Companies are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who comply with international standards and certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications. This shift not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with consumer expectations for corporate social responsibility.
How Has the Vulcanizing Rubber Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the vulcanizing rubber market dates back to the mid-19th century when Charles Goodyear discovered the vulcanization process, which revolutionized rubber production. Initially, natural rubber was limited in application due to its instability and susceptibility to temperature changes. However, the introduction of sulfur and heat during the vulcanization process enhanced its strength, elasticity, and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
As industrialization progressed, the demand for vulcanized rubber surged, particularly in the automotive and manufacturing sectors. The development of synthetic rubber during World War II further diversified the market, offering alternatives that could withstand harsher conditions and reducing dependency on natural rubber sources. Today, the vulcanizing rubber industry continues to innovate, focusing on sustainable practices and high-performance materials to meet the evolving needs of global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vulcanising rubber
-
How do I choose the right supplier for vulcanising rubber?
Selecting the right supplier involves assessing their experience, reputation, and production capabilities. Look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001 that indicate quality management practices. Request samples to evaluate material quality and performance. Additionally, check references and reviews from other B2B buyers in your region to ensure reliability. Establishing clear communication regarding your specifications and expectations is vital to fostering a successful partnership. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for vulcanising rubber?
MOQs for vulcanising rubber can vary significantly between suppliers based on production capabilities and your specific requirements. Typically, MOQs can range from 500 to 1,000 kg, but some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders for new clients or specific projects. Always clarify MOQ before proceeding with negotiations, as this will impact your inventory management and cash flow. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vulcanising rubber?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation skills. Common terms include a 30% deposit with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer flexible terms, such as letter of credit, especially for larger orders. It’s advisable to discuss payment options upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow and financial strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing vulcanising rubber?
To ensure quality, request detailed product specifications, including material properties and performance standards. Many suppliers will provide quality control documentation and testing results. Consider conducting on-site inspections or audits if feasible. Additionally, establish clear quality benchmarks and discuss remedies for any defects or non-conformities to protect your business interests. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing vulcanising rubber?
Logistics for importing vulcanising rubber involve selecting reliable shipping partners and understanding customs regulations in your country. Be aware of potential duties and taxes, and ensure proper documentation accompanies your shipment to avoid delays. Establish a clear timeline for delivery, and consider using freight forwarders who specialize in rubber products to navigate international shipping complexities. -
How does vulcanising rubber differ from traditional rubber in terms of applications?
Vulcanised rubber exhibits enhanced strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance compared to traditional rubber. These properties make it suitable for demanding applications such as automotive tires, industrial seals, and gaskets. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will help you choose the right type of vulcanised rubber, ensuring durability and performance in your products. -
What customization options are available for vulcanising rubber products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including varying hardness levels, colors, and additives for specific applications. You can also request tailored formulations that enhance particular properties such as heat resistance or chemical stability. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs clearly to your supplier to develop a product that meets your operational requirements. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing vulcanising rubber internationally?
International sourcing of vulcanising rubber can present challenges such as language barriers, cultural differences, and varying quality standards. Additionally, navigating logistics and customs regulations can complicate the process. To mitigate these challenges, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, establish clear communication channels, and consider working with local agents or consultants who understand the market landscape.
Top 4 Vulcanising Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Walker Rubber – Custom Rubber Extrusions
Domain: walker-rubber.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Rubber Extrusions, Custom Rubber Extrusions, Angle Extrusion, Rubber Boat Window Seals, Brick Grabs, Cab Tyres, Rubber Cable Protection, Coloured Extrusions, Container Door Seal Extrusion, Conveyor Side Skirting, Rubber Door Seals, EPDM Extrusions, Rubber Expansion Seals, Rubber Façade Seal Extrusions, Flame Retardant Extrusions, Food Grade Extrusions, Rubber Gate Seals, Rubber Glazing Seals, H Pr…
2. RubberCal – Corrugated Wide Rib Rubber Runner Mats
Domain: rubbercal.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Rubber vulcanization process involves heating natural sheet rubber with sulfur to strengthen its molecular structure. This process reduces elasticity but enhances strength, abrasion resistance, and eliminates thermoplastic properties. Key product: “Corrugated Wide Rib” Rubber Runner Mats, available in custom lengths up to 50ft, suitable for commercial or industrial use, featuring textured undersid…
3. ElastoStar – Silicone & Rubber Solutions
Domain: elastostar.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Closed Cell Silicone Sponge Rubber, Metal & X-Ray Detectable Rubber, Silicone Rubber O-Rings, Die Cutting Gaskets, Platinum Cured Rubber Tubing, Rubber U-Channel, Rubber P-Channel, Extruded Rubber Bulb Seal
4. WARE – Boiler Rentals & Services
Domain: wareinc.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: WARE is an industrial & commercial boiler rental and service company specializing in sales, service, valve repair, rentals, parts, turnkey solutions, and boiler training. They offer a wide range of boiler rentals for various applications and industries, new, used, and remanufactured boiler equipment, industrial boiler room auxiliary equipment like deaerators and heat exchangers, combustion equipme…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vulcanising rubber
What Are the Key Advantages of Strategic Sourcing for Vulcanizing Rubber?
In the competitive landscape of vulcanized rubber manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal component for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chains. By focusing on the procurement of high-quality raw materials and leveraging supplier relationships, companies can significantly enhance product performance, reduce costs, and improve time-to-market. The superior strength and elasticity of vulcanized rubber make it essential for applications across various sectors, from automotive to consumer goods. As international markets continue to evolve, understanding regional dynamics—particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—will be crucial for buyers seeking reliable and innovative sourcing solutions.
How Can You Position Your Business for Future Success in Vulcanized Rubber?
Looking ahead, the demand for vulcanized rubber is poised for growth, driven by advances in technology and increasing applications. As a B2B buyer, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies. Engage with suppliers who offer not only competitive pricing but also a commitment to sustainability and innovation. By fostering strong partnerships and remaining adaptable to market changes, your business can thrive in this dynamic environment. Consider taking proactive steps today—whether through supplier diversification or investing in emerging technologies—to secure your place in the future of the vulcanized rubber industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.